Contents
Sheep blood agar
- Sheep Blood Agar is a very nutritious medium that is used in growing and isolating various kinds of microorganisms.
- The Sheep Blood Agar made up of the Oxoid formulation. The formulated medium is believed to have an improved nutritional value, resulting in a higher growth rate and a larger colony size, as well as providing more stable hemolytic reactions, particularly for streptococci.
- The base was specifically designed to be used using sheep blood, as horse blood has been shown to cause diverse and conflicting hemolytic reactions when mixed with other blood Agars.
- The nutritional ingredients include pancreatic digest of casesin, neutralized peptone and yeast extract. Additionally, the presence of sodium chloride gives an osmotically balanced environment for the bacterial cells.
- The addition of 5% defibrinated sheep’s blood permits the identification the hemolytic reaction, a crucial distinct characteristic.
The principle of sheep blood agar
Haemolysins are exotoxins created by bacteria that kill Red blood cell clots. The haemolytic process can be observed on blood Agar Plates. In blood agar plates, colonies of haemolytic bacterium may be covered by a the clear, uncoloured zone, in which the Red blood cells are destroyed and the haemoglobin has been destroyed into a colorless substance. This is called beta haemolysis.
Other kinds of bacteria may reduce haemoglobin to methaemoglobin . This creates a greenish-colored zone surrounding the colonies, this is known as alpha haemolysis. Gamma haemolysis is a form of haemolysis in which no changes in the medium are noticed.
Blood Agar Base No. 2, which is supplemented with sheep’s blood is utilized to study haemolytic reaction (patterns) of various organisms. However, this produced heterogeneous haemolytic (a and two) reactions because of the physical distinctions between horse blood and sheep blood. Sheep Blood Agar Base with the addition of sheep blood was created to maximize the healing of living organisms without disrupting the haemolytic reaction.
Sheep Blood Agar Base was created for compatibility with sheep’s blood and offer better haemolytic reaction of living organisms. Casein Enzymic Hydrolysate and yeast extract supply nitrogen carbon, amino acids, and vitamins. A digestive process that is peptically digested by animal tissues is the main source of nitrogen. The osmotic balance is maintained by sodium chloride. balance. Sheep Blood Agar Base showed an impressive improvement as well as the anticipated beta haemolytic effects with S. Pyogenes, in contrast to other bases for blood agar which are supplemented by blood.
Composition of sheep blood Agar
| Ingredients | Gms / Litre |
| Casein enzymic hydrolysate | 14 |
| Peptic digest of animal tissue | 4.500 |
| Yeast extract | 4.500 |
| Sodium chloride | 5.000 |
| Agar | 12.500 |
| Sheep Blood | 5.000 |
| Final pH ( at 25°C) | 7.3±0.2 |
The procedure of sheep blood Agar
- Let the medium be at the temperature of room.
- Utilizing an inoculum taken that is taken from the specimen conduct an eight-quadrant pattern to get well-isolated colonies.
- Incubate in an atmosphere that is aerobic or CO2-supplemented at 35°C.
- Examine within 18-24 hours.
Results and Interpretation of Sheep blood agar
Sheep Blood Agar is a good choice as a plating medium for primary use. Primary isolation is used to isolate and separate species present in a sample. This separation permits the identification of colony types , and can reveal the presence of important bacteria in clinical practice. While examining plates, a hand magnifier or stereoscope must be used to examine tiny colonies. The different colonial morphologies appearing on the agar plate must be noted along with the number of morphotypes found. Hemolysis is another beneficial differential characteristic, which is best observed when bright light is reflected through the plate. The four different kinds of hemolysis can be describedas:
- Alpha-hemolysis (a) Partial hemolysis that produces an emerald-colored discoloration of the colony
- Beta-hemolysis (b) is the complete elimination in red blood cells, resulting in a clear area surrounding the colon
- Gamma-hemolysis (g) is the absence of hemolysis that causes no change in the medium
- Alpha-prime-hemolysis (a’) – A small zone of complete hydrolysis that is surrounded by an area of partial hemolysis.
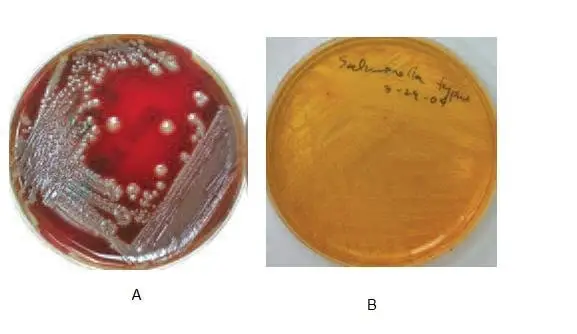
Further tests must be conducted on isolated colonies of pure culture to enable an accurate identification.
| Organism | Expected Result |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Growth, α-hemolysis |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | Growth, β-hemolysis |
| Escherichia coli | Growth, γ-hemolysis |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Growth, γ-hemolysis |
Use of Sheep blood agar/purpose of sheep blood agar
- For the cultivation of highly selective organisms such as Neisseria as well as Streptococcus.
- The study of haemolytic reactions. It improves and enhances haemolysis.
- It is used to differentiate the hemolysis based on bacteria (a- hemolytic, b- or the g-hemolytic) they produce on Agar.
- Agar from sheep’s blood is the preferred choice to make a throat culture.
Storage and Shelf Life of Sheep blood agar
- Sheep Blood Agar is best kept out of direct light between 4 and 8 degrees Celsius.
- The medium side must be the highest to avoid excessive accumulation of water on the agar surface.
- In these conditions, this product is shelf-lifed at 12 weeks from the time of its manufacture.
Related Posts
- Robertson’s Cooked Meat Medium (RCM Medium) – Composition, Preparation, Uses
- Nutrient Agar – Principle, Composition, Preparation, Results, Uses
- Viral Transport Media (VTM) – Definition, Principle, Preparation, Application
- Decarboxylase Broth Protocol
- Culture Media Examples, Components and Primary Purpose








keep it