- All the major groups of microbes remain suspended within the atmosphere, which are ranges from various algae to viruses.
- The microbial flora of the atmosphere is transient and variable.
- The microbial content of the outer atmosphere is changing with the season, it contains various pollen, algae, mosses, grains, spores of fungi, ferns, bacteria, and viruses.
- These air-spora or air-born particles can cause disease in living beings such as animals, plants, and humans. They are responsible for influenza, colds and mycoses, etc. The term air spora was first introduced by Gregory.
- Among these air-borne particles, the fungal spore is considered as the most important air-spora.
- The air is a good carrier for microorganisms but not a good medium for their growth.
- The numbers and the types of suspended microorganisms on-air varies based on source and location.
- Solid impingement devices and liquid impingement devices are used to determine the microbial content of the air sample.
- In Solid impingement devices, a solidified agar plate or sticky faced microscope slide or filter disk is used on which the microorganisms are impinged or collected directly.
- In liquid impingement devices, a broth medium or sterile water is used, through which a fine spray of air sample is passed; as a result, the organisms are trapped on them. After that, the aliquots are collected from the broth or water and cultured to identify the microorganism.
- Various types of impactors and impingers are used for the sampling of air-born microbes. There are different types of impactors such as the Casella slit samplers, the Cascada impactor, Hirstspore trap, the Andersen sampler. Also several types of impingers such as the porton impinger, pre-impinger, the multistage liquid impinger.
- For the studying of microbial content of air, two widely accepted methods are used such as gravity slide and settle-plate techniques.
- In gravity slide methods, glycerin jelly is smeared over microscopic glass slides, then expose the petroleum jelly or silicone grease or vaseline horizontally, adhesive surface facing upwards in a shelter, so that although protected from the rain they are freely exposed to the air for a particular period of time.
- After that observe the trapped pollen and bacteria on slide by using a microscope.
- In the settle-plate method, horizontally expose a petri dish containing agar medium for 5-10 minutes. After that the plates are incubated and count the appeared colonies over the plate. In this practical we will isolate the microbes from air by using the settle-plate method.
Contents
Principle
The Isolation of Microorganism From Air is performed by using the settle-plate technique. In this method a suitable medium is poured over a sterile petri dish and then allow it to slidify. After that the plate is exposed to the open air for a few minutes. Then the plates are incubated for the formation of microbial colonies on the plate. Observe the colonies by using a microscope.
Requirements
- Czapek-Dox agar medium with rose bengal (For fungal cell isolation).
- Nutrient Agar (NA) medium.
- Streptopenicillin.
- Sterile petri dishes.
- Sterile syringe and needles.
- Colony counter.
- Burner or spirit lamp.
Procedure
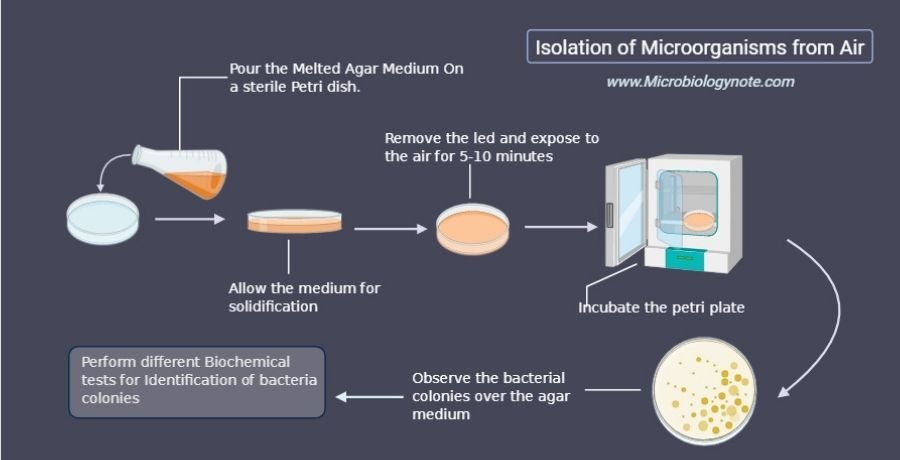
- Prepared the Czapek-dox agar medium and NA medium.
- Pour the melted Czapek-dox agar medium with streptopenicillin and NA medium in a petri dish.
- Keep them at room temperature in a steady condition to allow them to solidify.
- After solidification remove the covers of petri plates and expose them to the air for 5-10 minutes.
- After 5-10 minutes cover these plates.
- Incubate the Czapek-dox agar plates at 25 degrees centigrade for 2-7 days whereas NA plates at 37 degree centigrade for 24-48 hours.
- After incubation, observe the colony formation on both plates (Czapek-Dox medium and NA medium) and count them.
- Perform further biochemical tests for the identification of those microbial colonies.
Note
- Czapek medium, also known as Czapek’s agar (CZA) or Czapek-Dox medium. This media is used for propagating fungi and other organisms.
- Czapek medium is composed of iron sulfate(0.01g), potassium chloride (0.5g), magnesium sulfate(0.5g), monopotassium phosphate(1g), cane sugar(30g), sodium nitrate (2g) and distilled water (1000 lit).
- The Czapek-Dox agar is an optimum growth medium for Aspergillus brasiliensis, Candida albicans, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Aspergillus niger.
- The Nutrient agar medium is used to grow both spore-forming and non-spore-forming gram-negative cocci, gram-positive bacilli, and gram-negative bacilli.









would you please give me the reference for this method , please?