What is Mounting?
A temporary wet mount is a laboratory technique that is used to observe the plant tissue or living microorganisms under a microscope.
In Mounting technique, the specimen to be observed is held on a microscopic slide by using a coverslip. After that, the slide is observed by using a microscope to examine the motility, cell structure, and shape of the specimen.
Types of Mounting Technique
There are different types of mounting techniques such as;
- The Dry mount technique is used to study pollen, hair, feathers or plant materials, etc.
- In this method, the specimen is directly placed over a slide and then covered with a coverslip to protect it from dust.
- Wet mount or temporary mount:
- Wet mount or temporary mount technique is used to study the movement and behavior of living microorganisms.
- In this method, a drop of water is placed over a slide and then the specimen is placed within it.
- After that covers it with a coverslip and observe under a microscope. The lactofuchsin mount is an example of Wet mount.
- Prepared mount or permanent mount:
- The Prepared mount or permanent mount technique is mainly used for pathological and biological research, where the specimen is needed to fix over the slide to prevent decay.
- In this technique, the water content is removed from the slide by replacing it with paraffin, splitting it into very small slices by using a microtome, laying the slices on a microscope slide, staining the tissue by using different stains to expose specific tissue parts, clearing the tissue to execute it transparent and wrapping it with a coverslip and mounting medium.
Function of Cover Slip
- The coverslip keeps the solid specimens pressed flat, and liquid specimens formed into a flat sheet of even thickness.
- It keeps the specimen in right place.
- It defends the specimen from dust and random contact.
- It prevents the objective lens from reaching the specimen and vice versa.
Preparation of Temporary Wet Mount (TWM)
Aim
To make a temporary mount of a living organism in order to reveal the motility, structure, shape, and other components of the specimen.
Principle
In this method, the culture of a living organism is placed over a slide and then a coverslip is placed over this specimen. After that, the slide is observed under a microscope to confirm the specimen is motile or nonmotile. It also helps to determine the structure and shape of the specimen.
Requirement
- Old Culture Broth of Organisms (Rhizopus sp. Penicillium, Aspergillus, Spirogyra and Chlamydomonas, Volvox, etc.) or Material to be mounted.
- Needles
- Blotting paper
- Compound microscope
- Glass Slide.
- Cover Slide.
- Dropping Pipettes.
- glycerine
Procedure
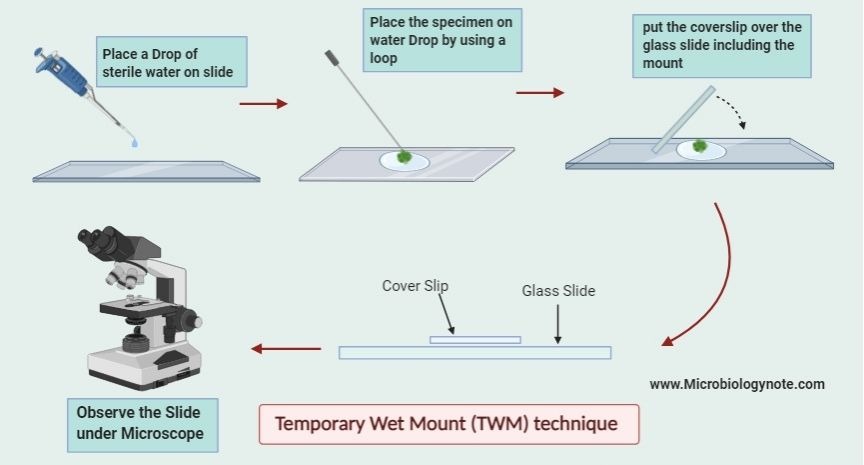
- Pace a drop of sterile water on a glass slide by using a Dropping Pipette.
- Then, pick the mounting material or culture of the living organism by using a sterile needle and transfer it to the drop of water.
- Now add glycerine to the mount and gently put the coverslip over the glass slide including the mount. Don’t smash the mount much.
- Use the Blotting paper to remove the excess amount of water and glycerine from the slide.
- Don’t put pressure over the cover slide because easily breakable.
- Now observe the slide by using a microscope.
Observation
Note the size, shape, and characteristics of the motility of bacteria.
Precautions
- Avoid using an excess amount of water.
- Maintain the coverslip gently. Coverslips crack quickly so manage them nicely.
- Practice proper staining procedure.
- Don’t smash the mount too much.
- Use a sterile needle to transfer the mount to the slide.
References
- https://discover.hubpages.com/education/How-To-Make-A-Temporary-Wet-Mount-A-Biology-Lab-Slide
- https://biocyclopedia.com/index/microbiology_methods/basic_techniques_biotechnologies/preparing_a_wet_mount.php
- https://www.microscope.com/education-center/how-to-guides/mount-slides/
- https://byjus.com/biology/preparing-a-temporary-mount-of-a-leaf-peel-to-show-stomata/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microscope_slide