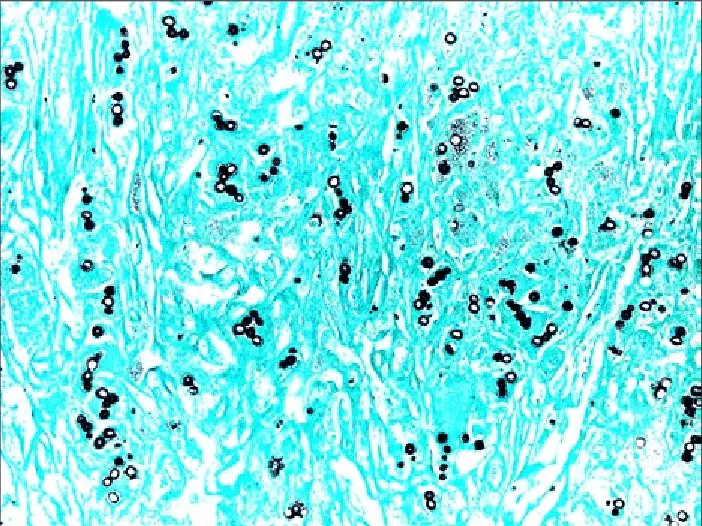
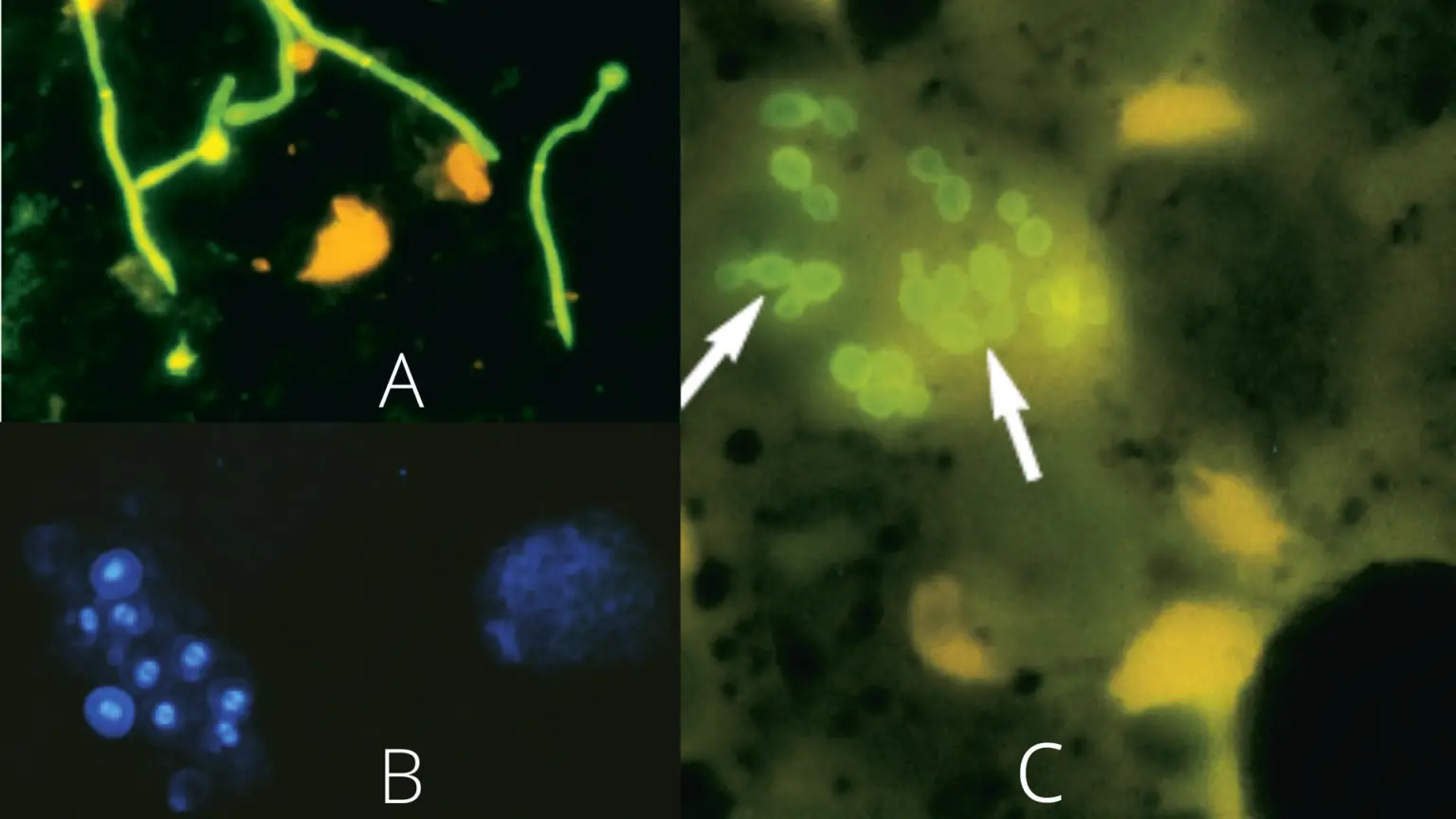
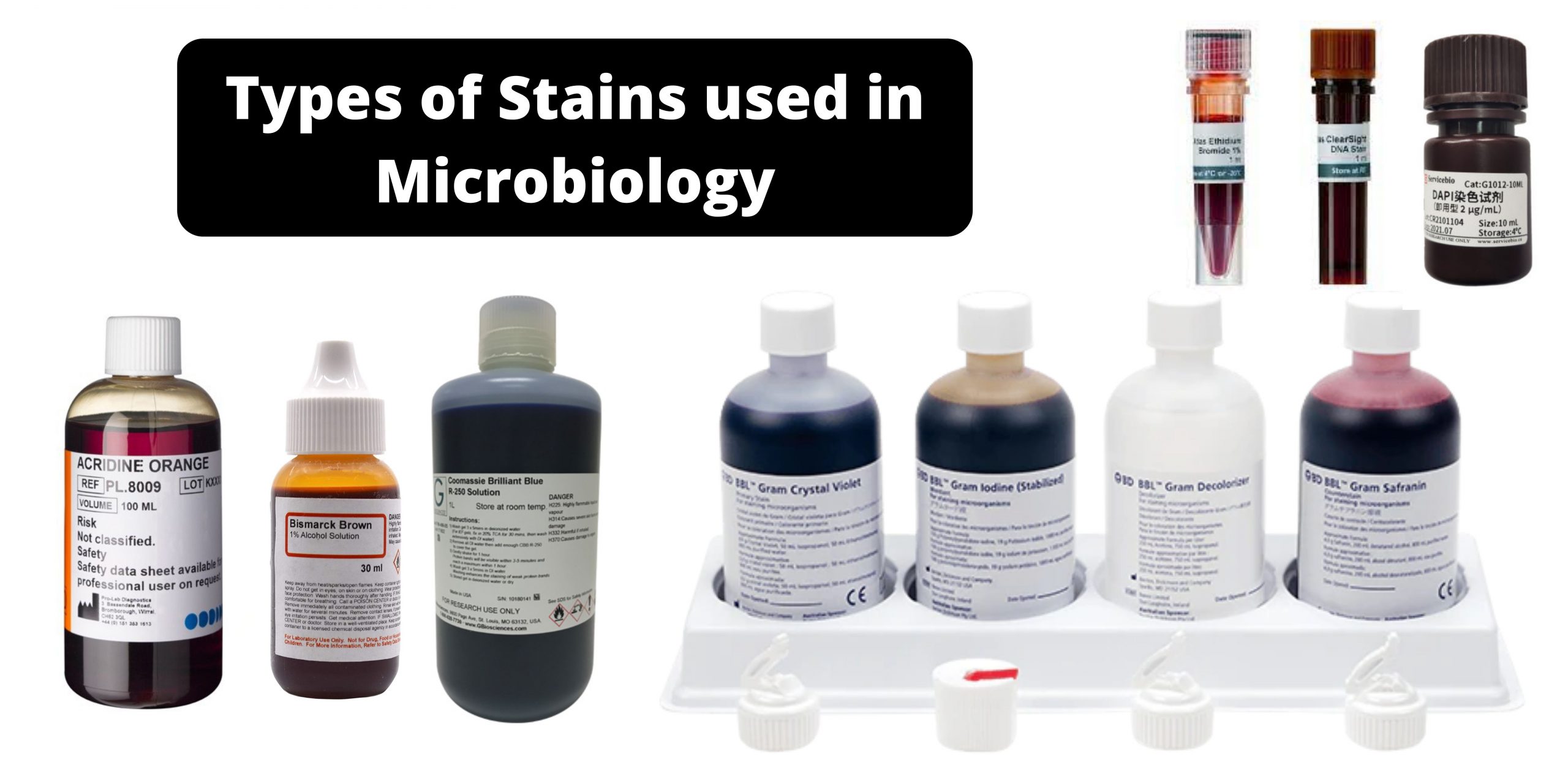
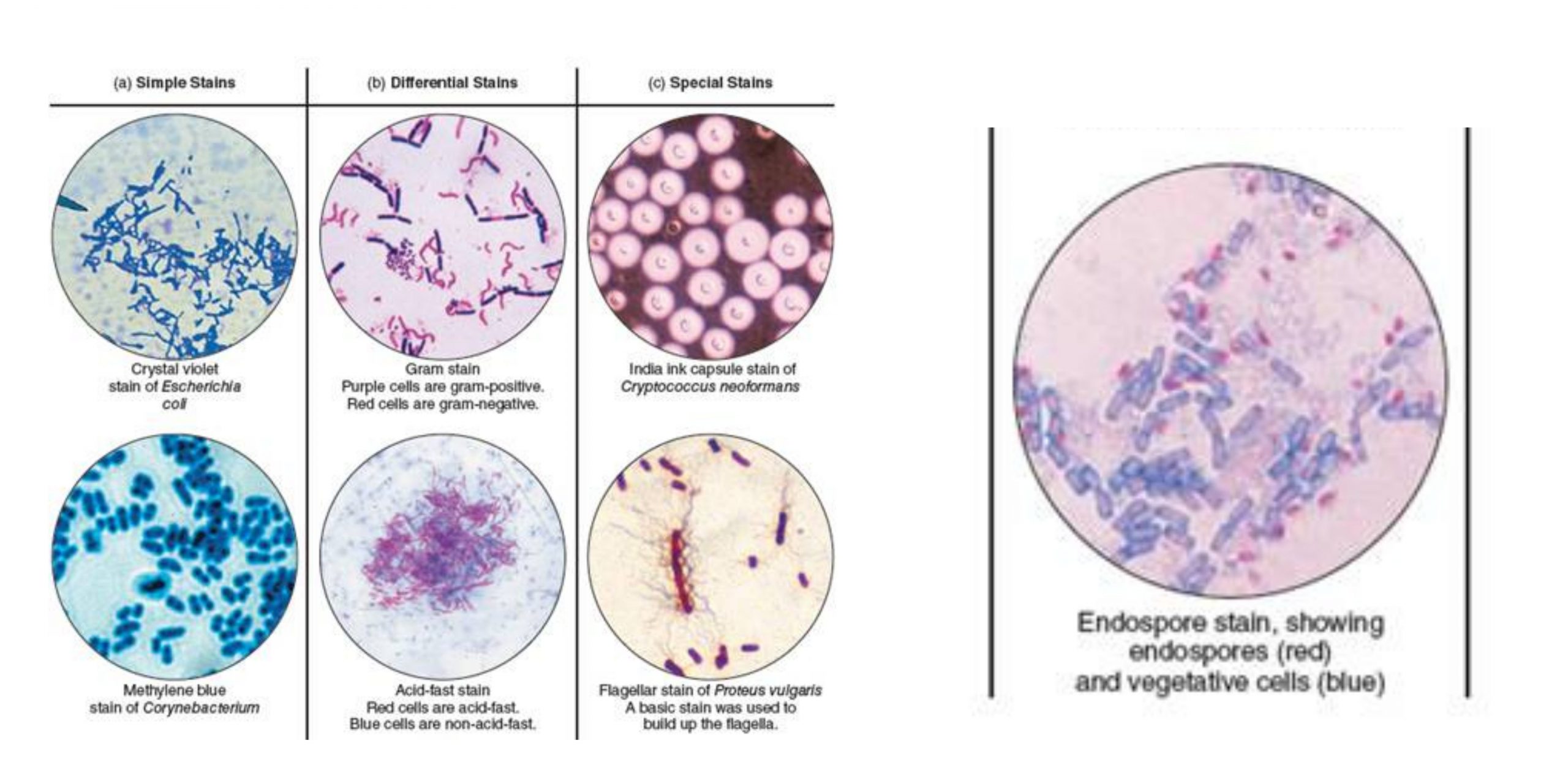
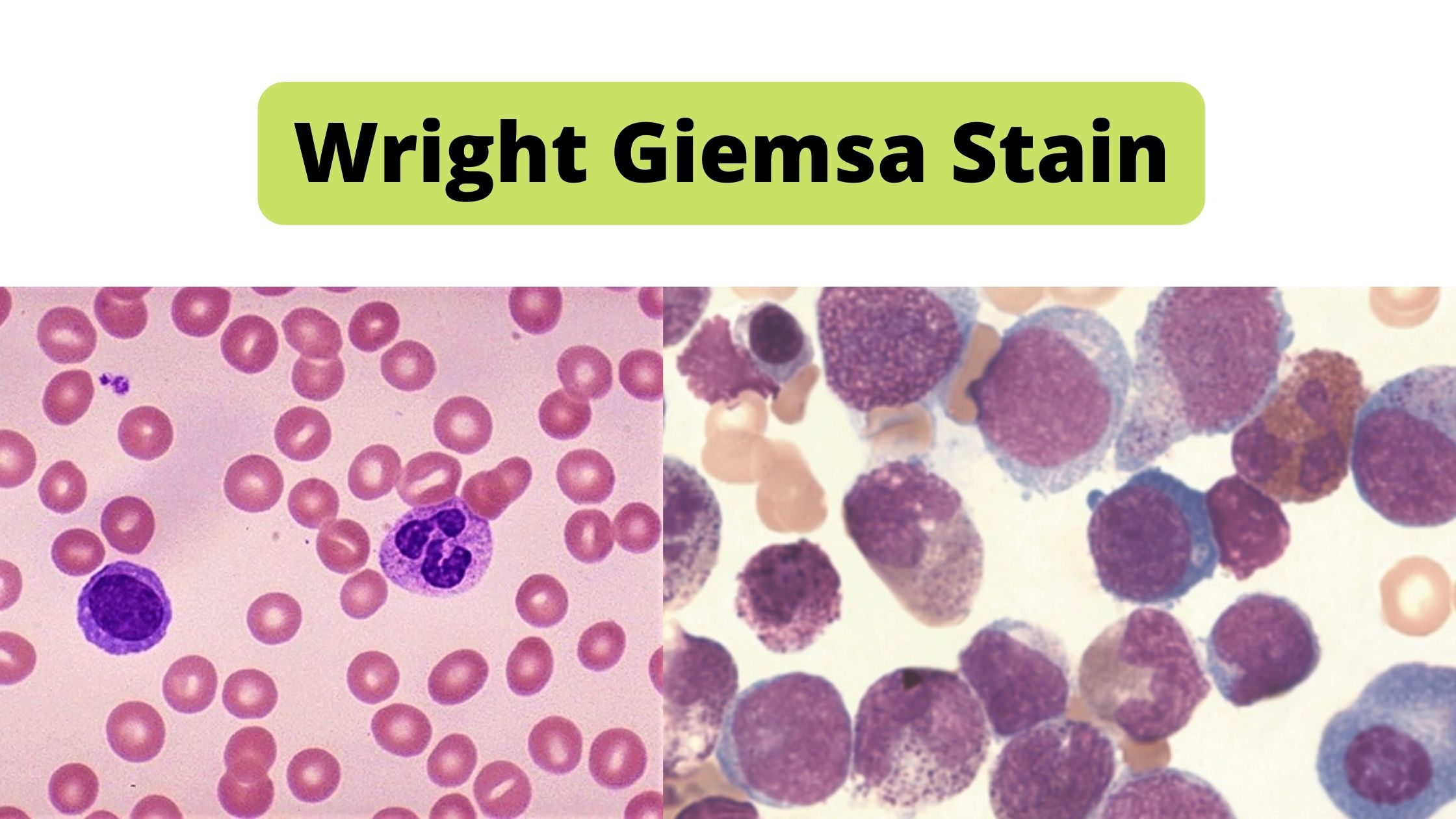
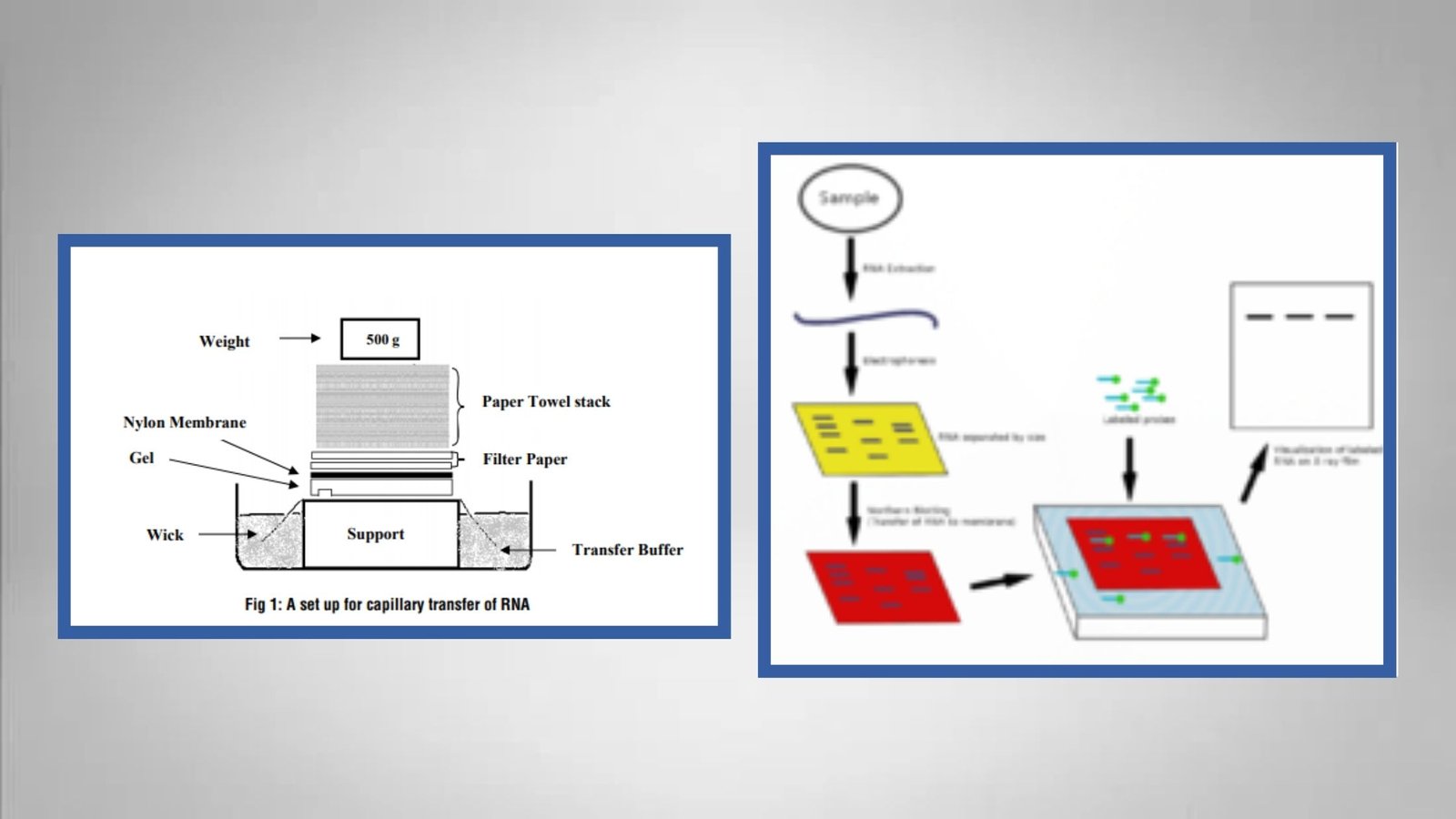
Grocott-Gomori’s Methenamine Silver Staining – Principle, Procedure, Applications
Grocott-Gomori’s Methenamine Silver (GMS) stain is the histological staining method that is used mainly for the detection of fungal microorganisms in tissue sections and smears. It is the process that was first developed by Gomori and later modified by Grocott, and it is used because of its high sensitivity to demonstrate carbohydrates present in the … Read more