Pollen Under The Microscope
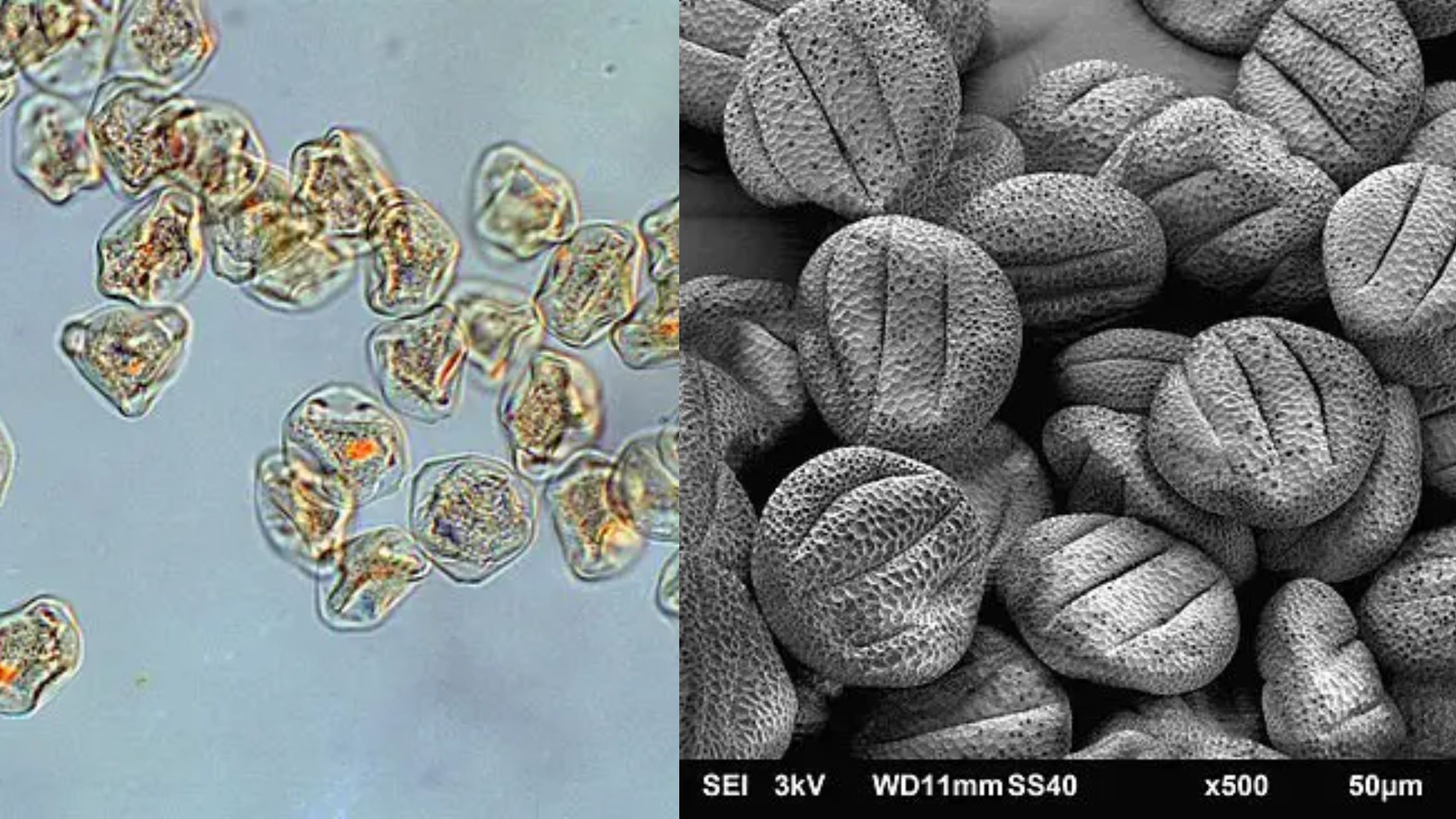
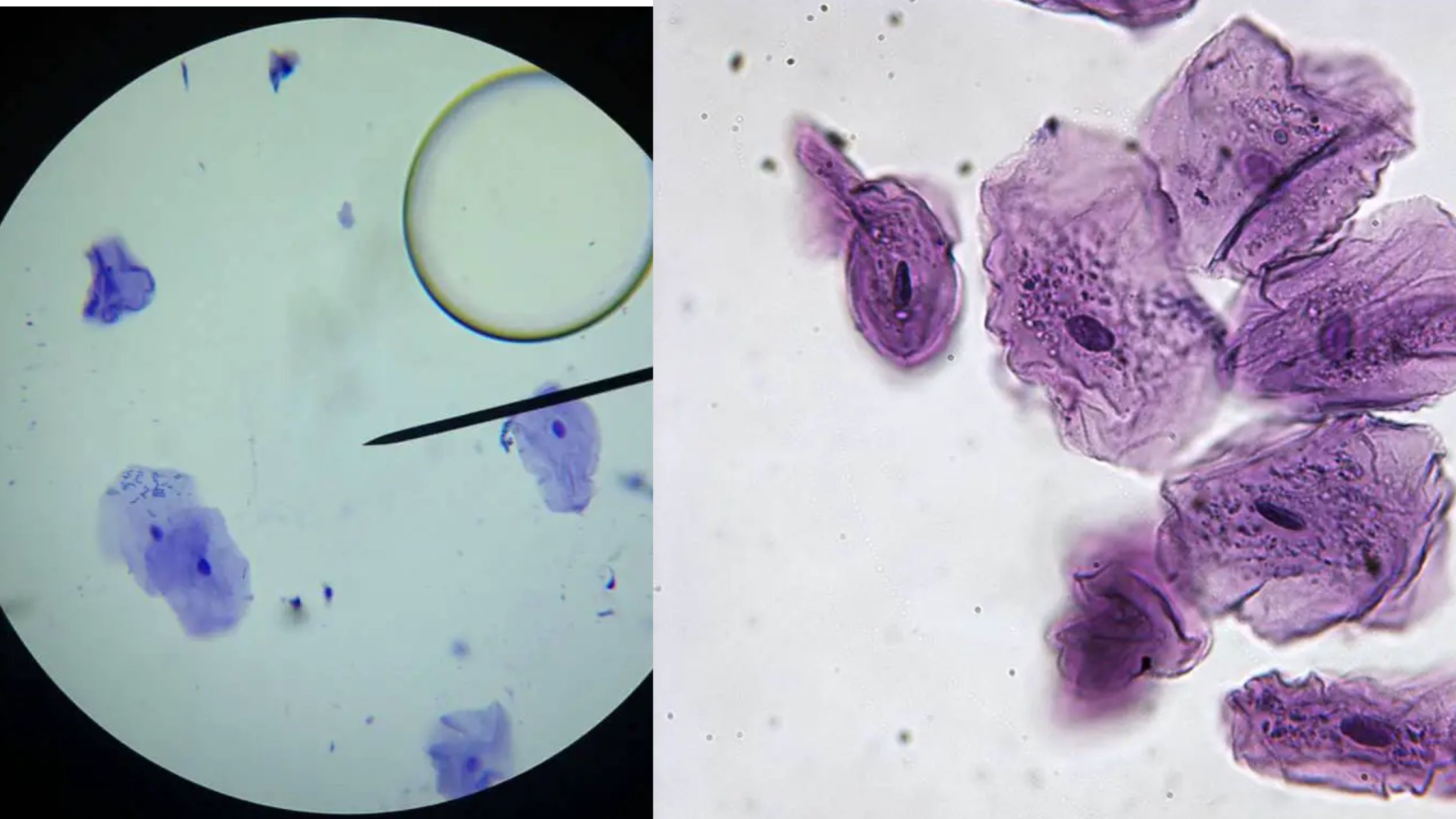
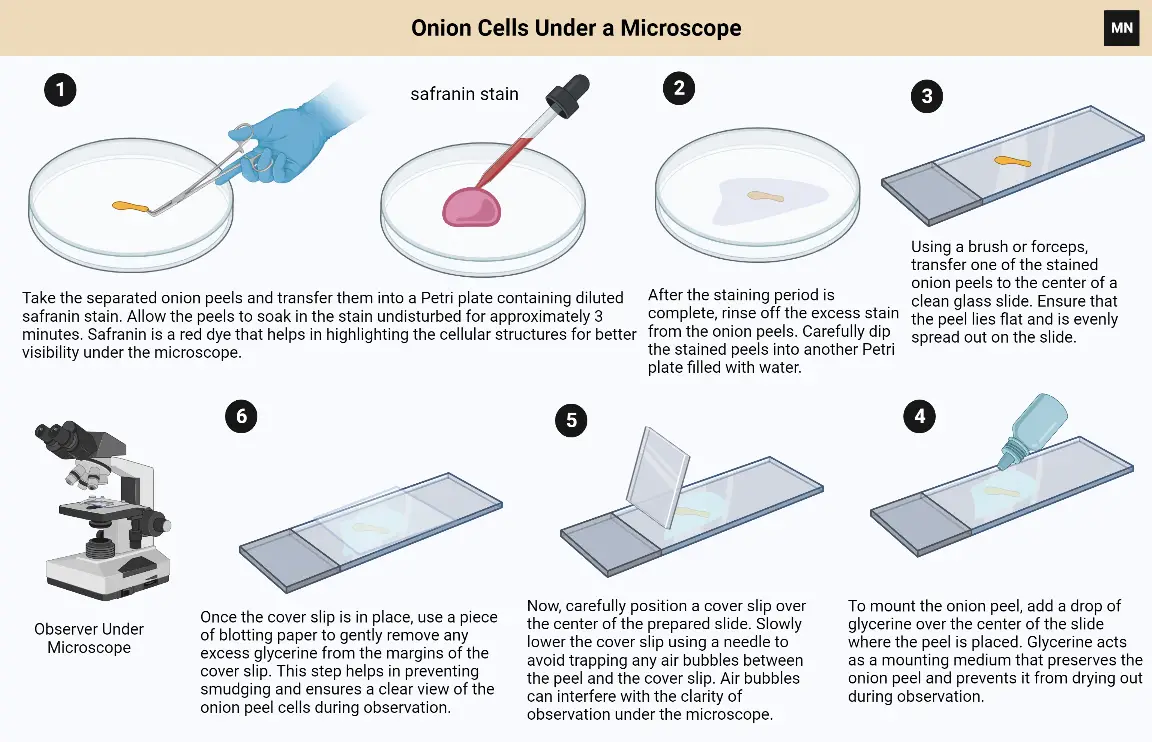
What is Pollen? Requirements for Pollen Microscopy Sample Collection for Pollen Microscopy Observation of Pollen Under Stereo Microscope Requirements Procedure for Observation of Pollen Under Stereo Microscope Observing pollen grains under a stereo microscope is a captivating journey into the hidden world of botanical wonders. With its ability to provide a three-dimensional view, the stereo … Read more