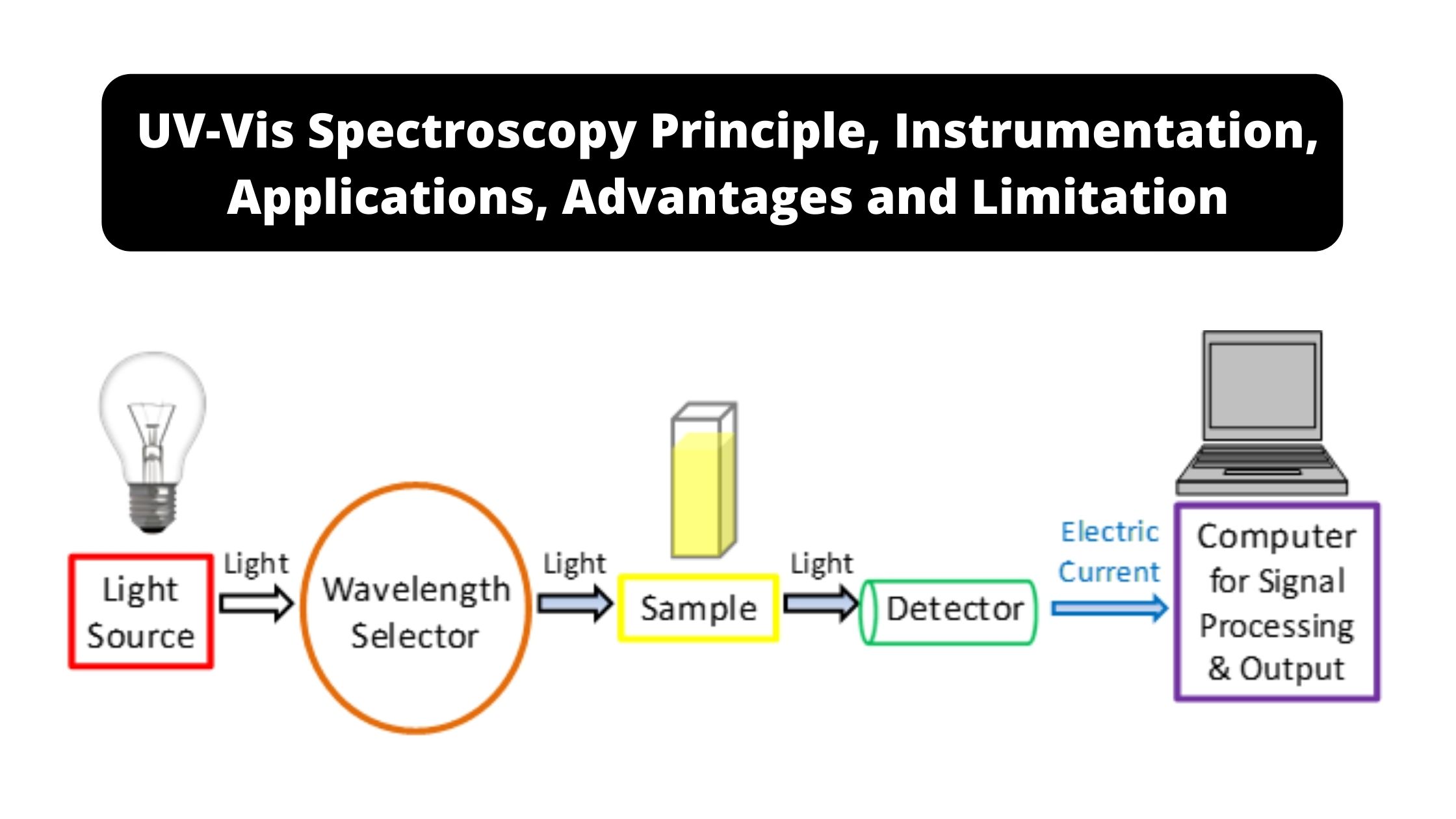
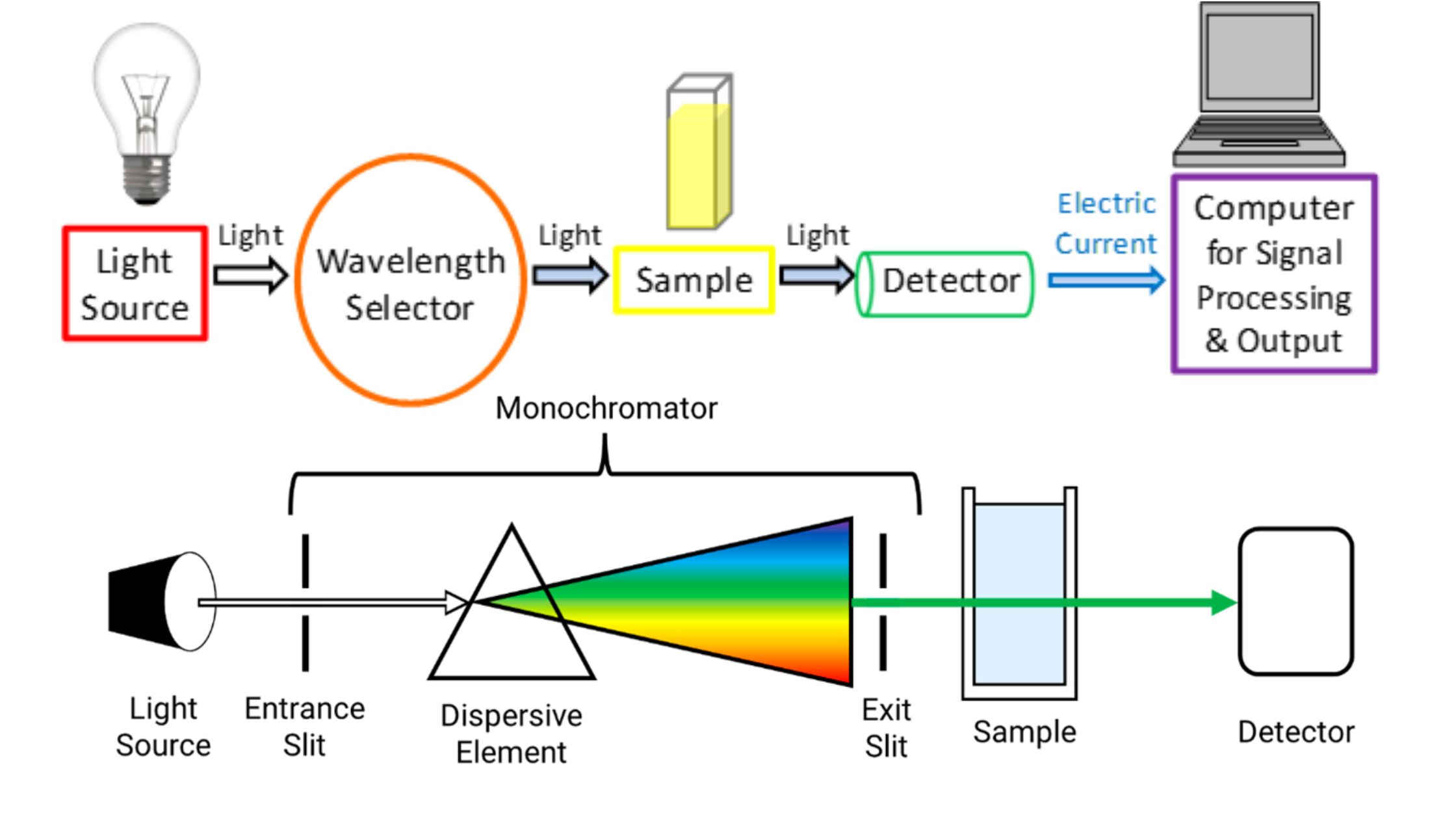
UV-Vis Spectroscopy – Principle, Instrumentation, Applications, Advantages, and Limitation
UV-Vis Spectroscopy, short for Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy, is an analytical technique widely used in the fields of chemistry, physics, biochemistry, and molecular biology. It’s based on the absorption or transmission of UV and visible light by substances. At its core, UV-Vis Spectroscopy involves shining ultraviolet or visible light through a sample and measuring how much of … Read more