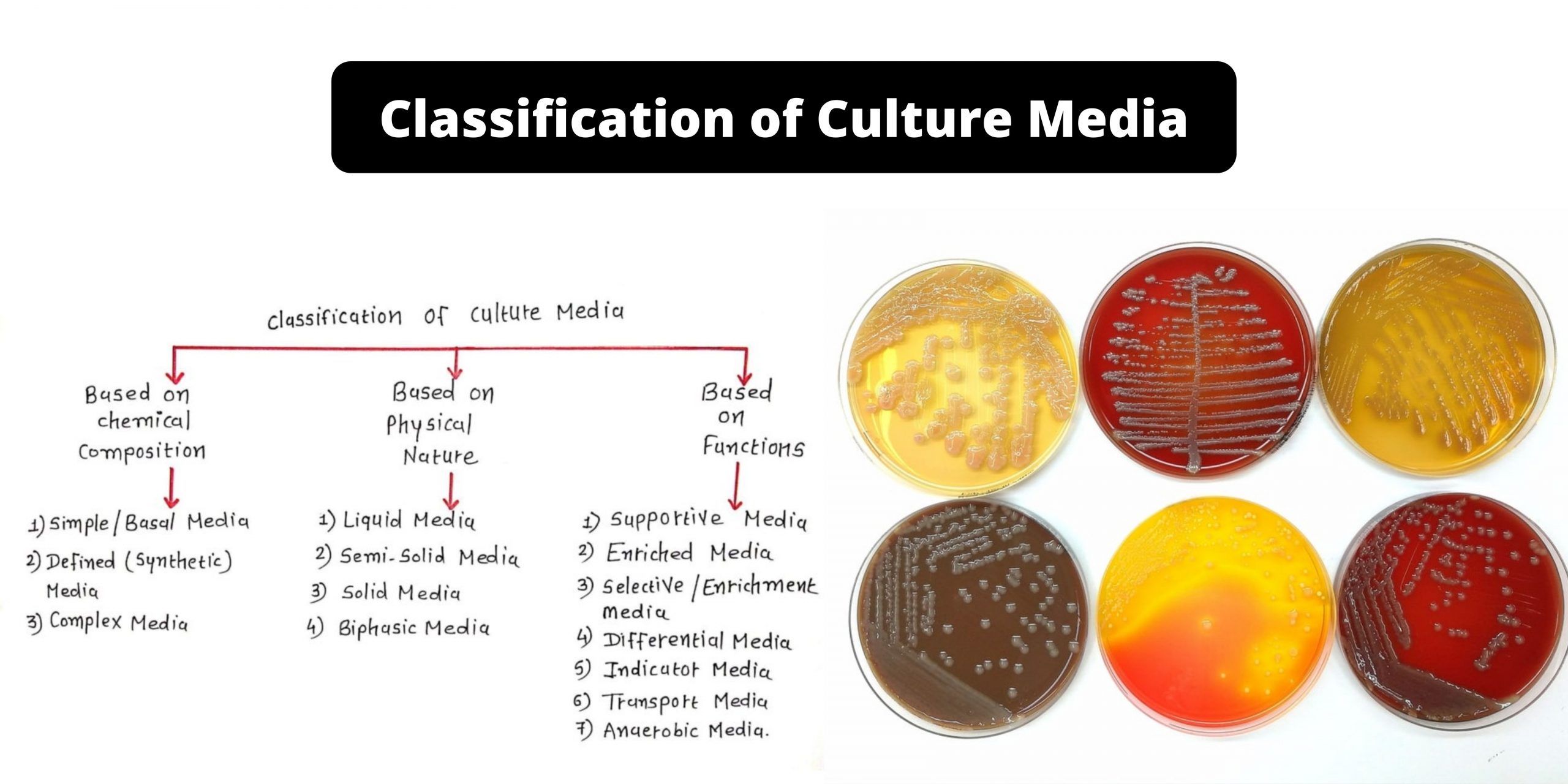
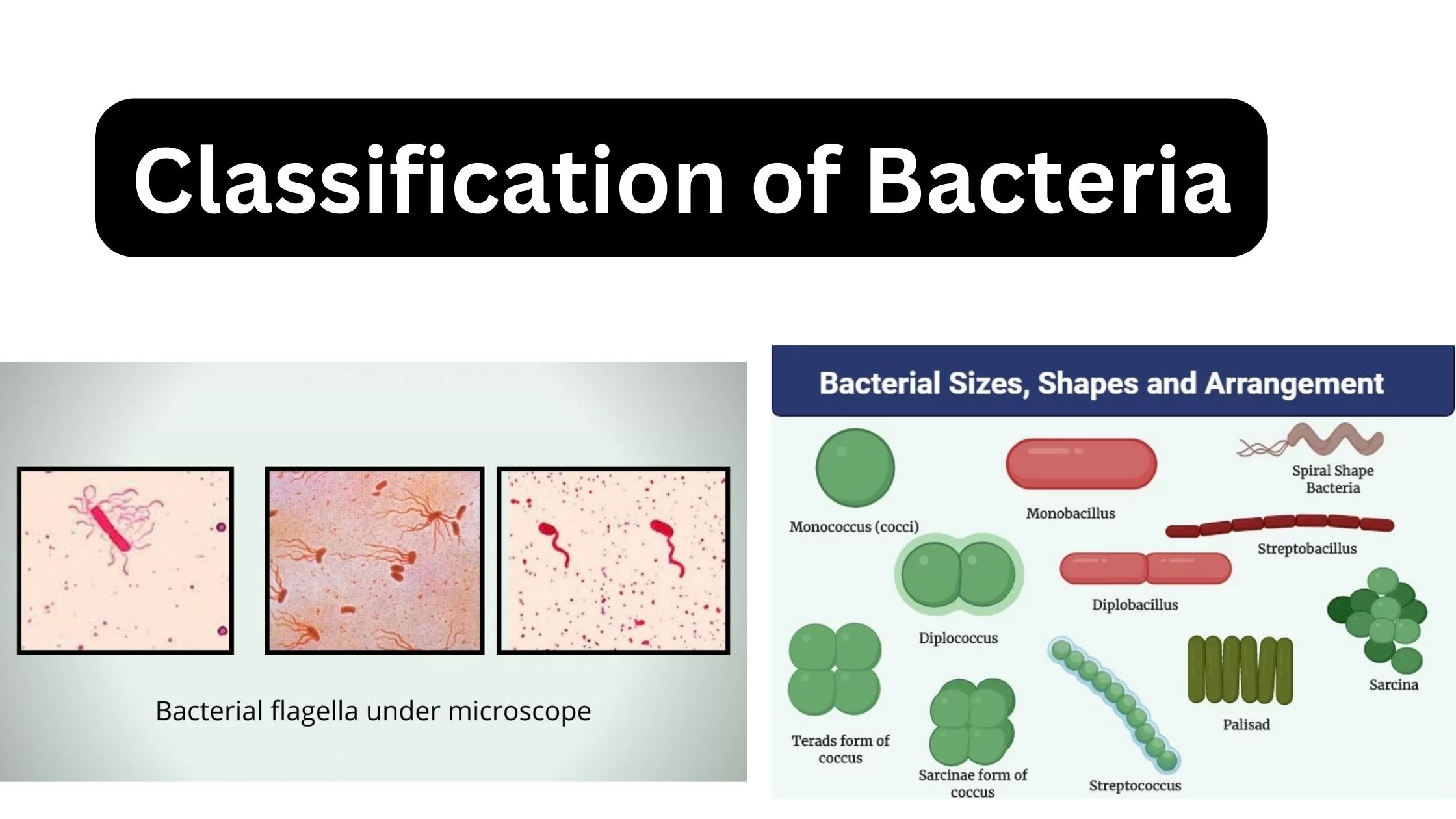
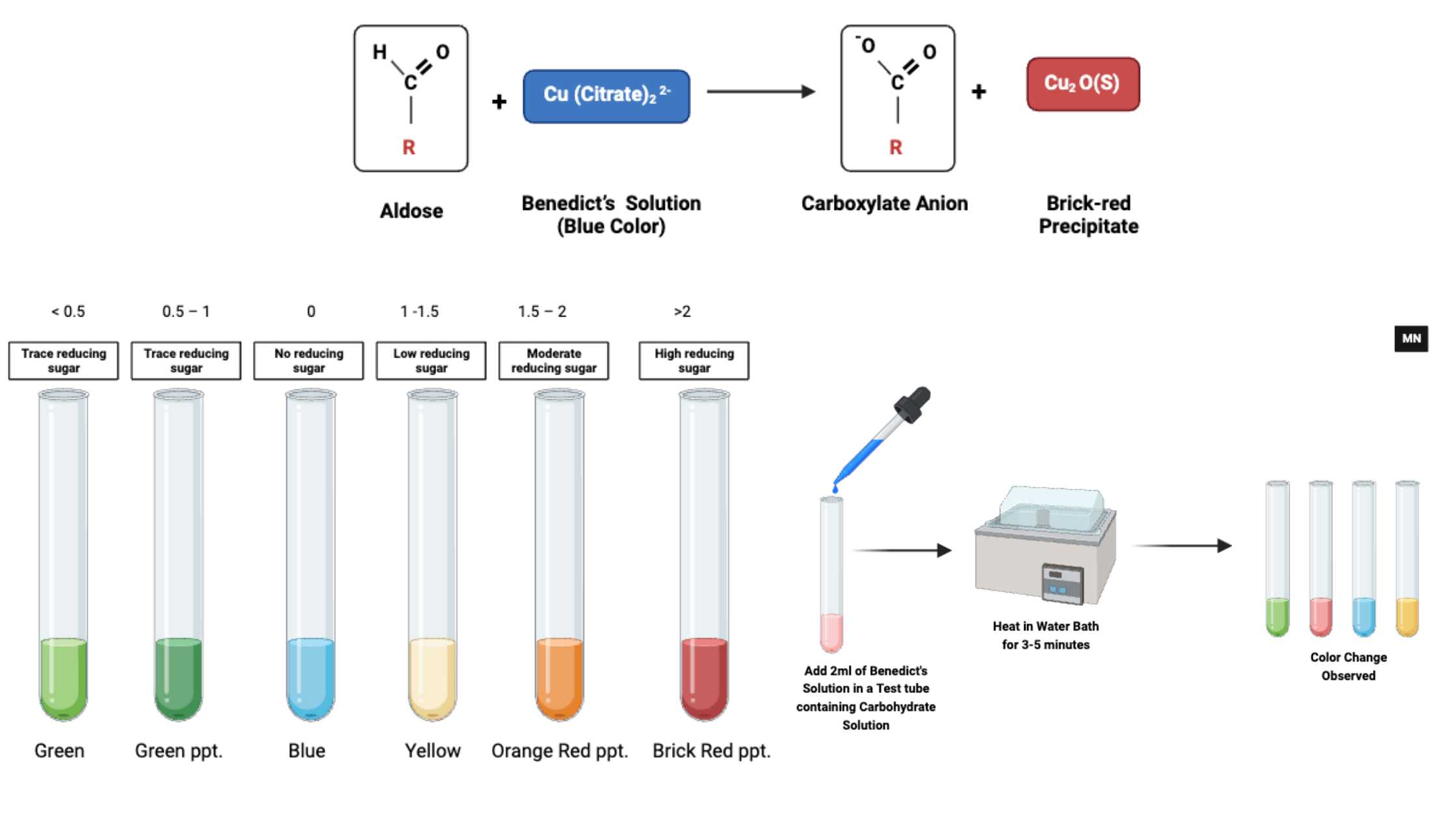
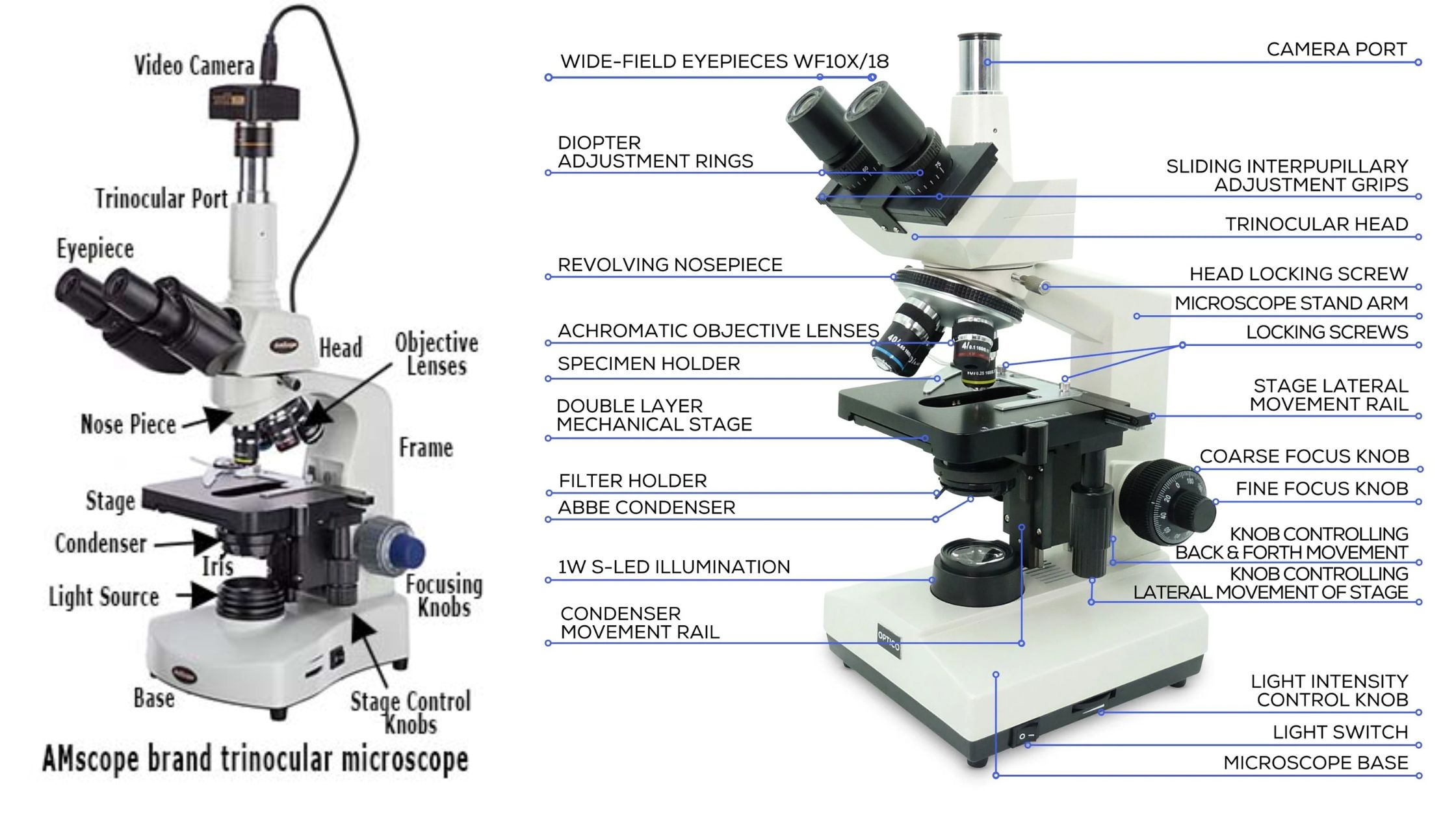
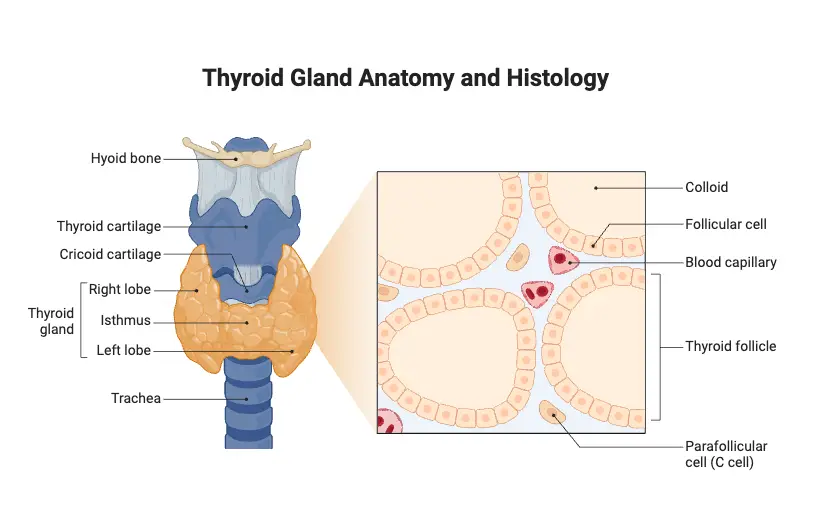
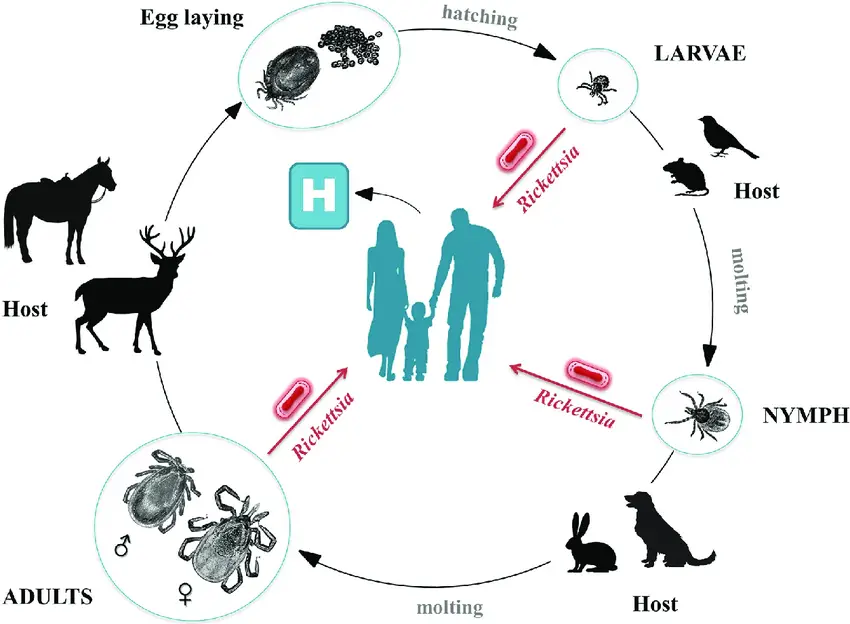
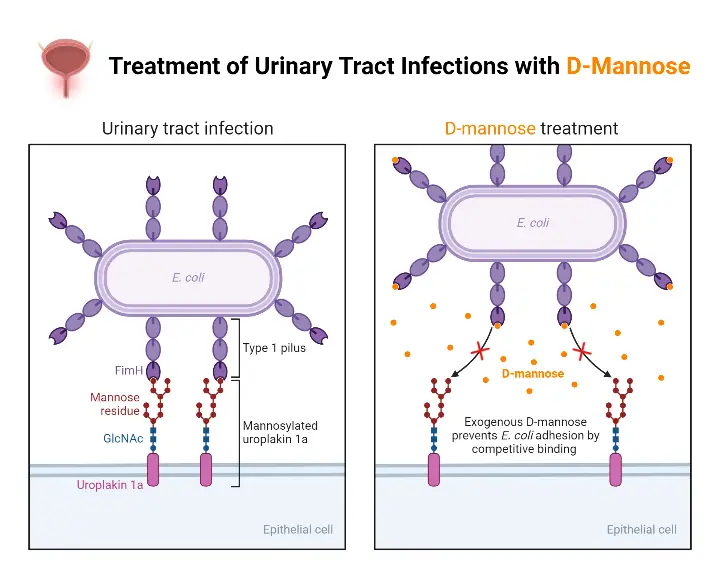
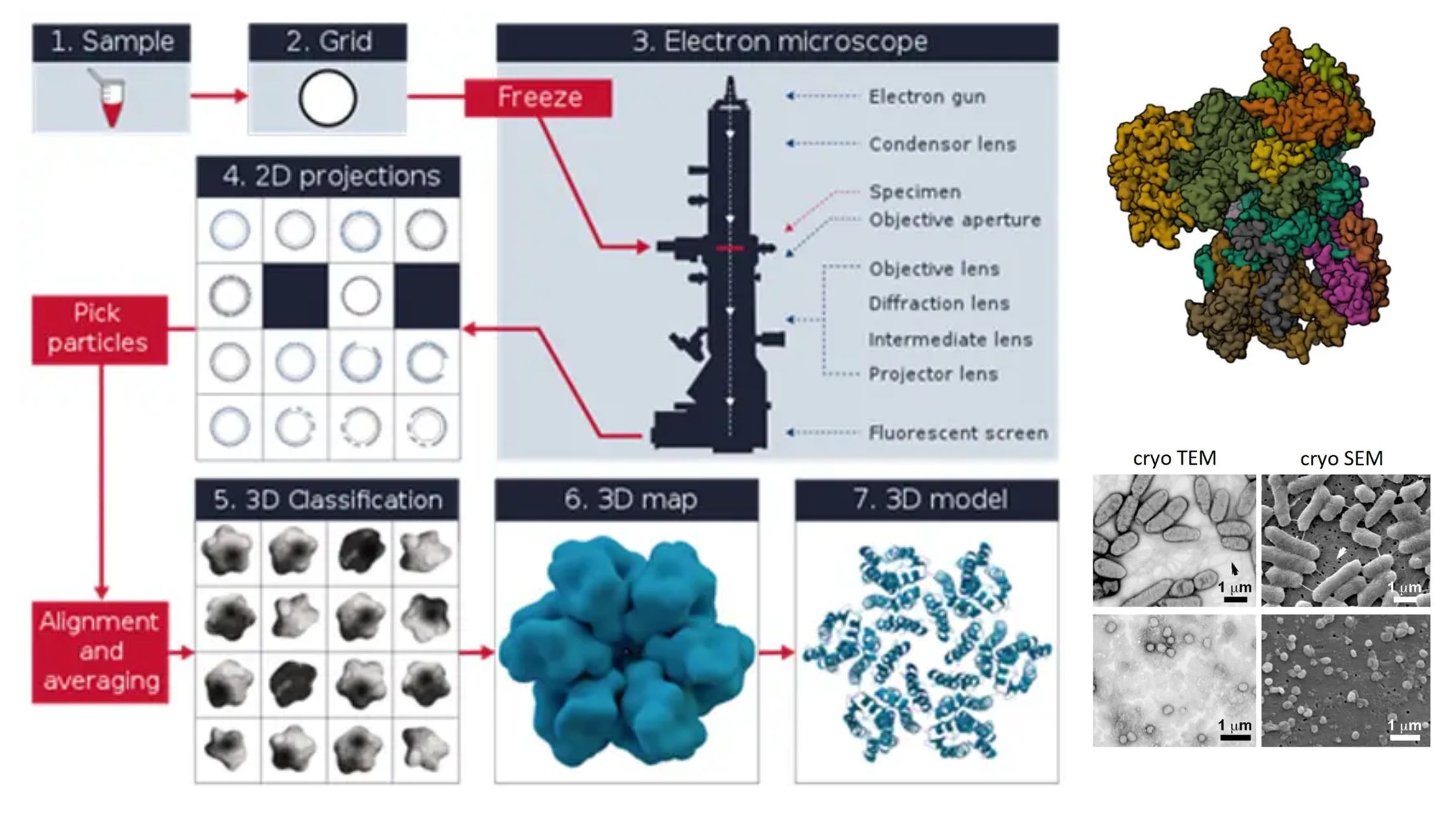
Culture Media – Definition, Types, Composition, Use, Examples
When it comes to culturing bacteria, it is crucial to create the same environmental and nutritional conditions as those found in the natural environment. The majority of culture mediums contain water, which is a major source of carbon and energy and nitrogen. It also contains trace elements, as well as some growth factors. In addition, the pH as well as oxygen tension and Osmolarity must also be considered. Some of the components of media for culture include: Although tap water is appropriate for the use of culture media, it shouldn’t be used in the event that it contains a significant amounts of minerals. In these instances the use of demineralised or distillated water is recommended.