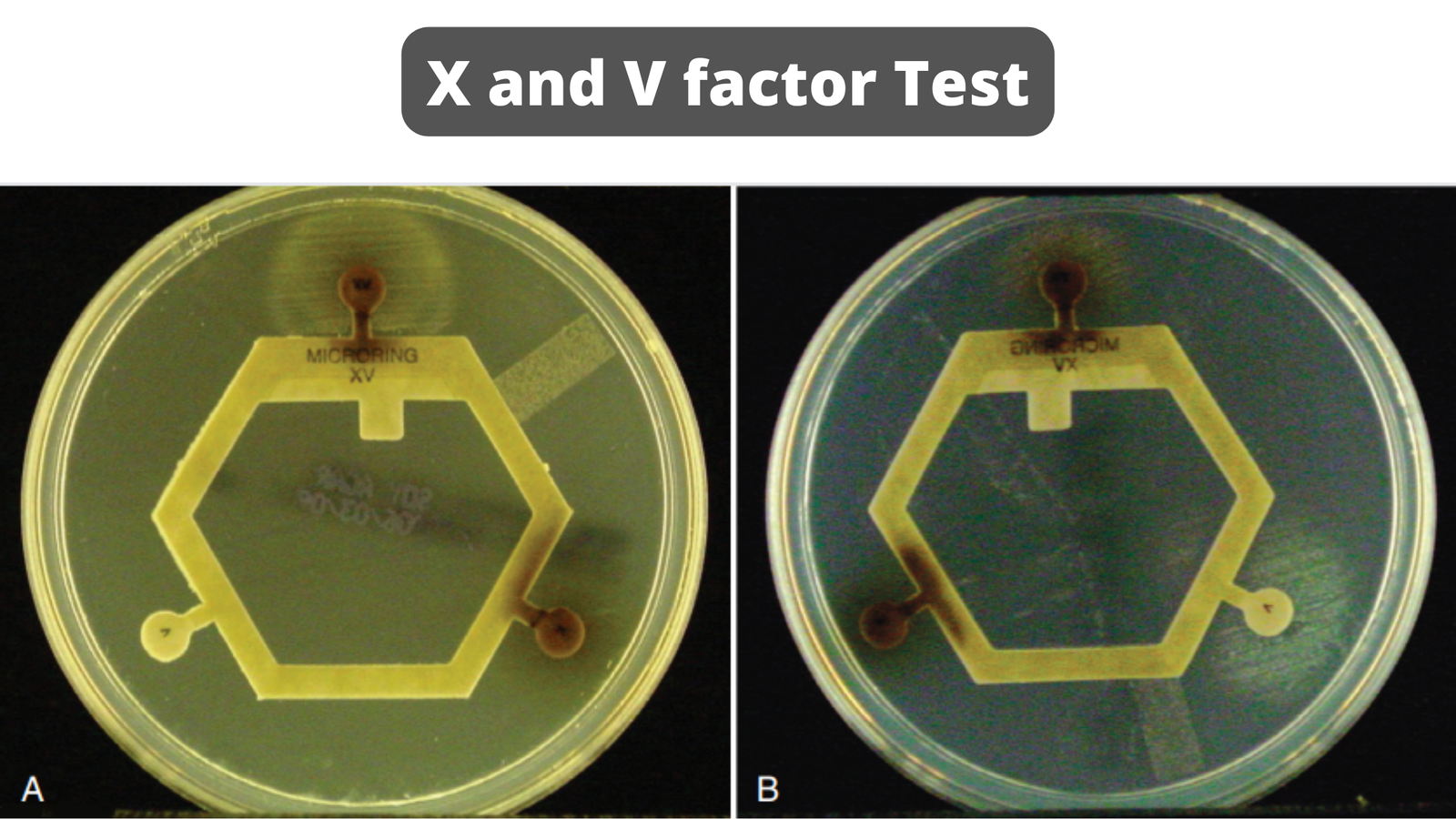
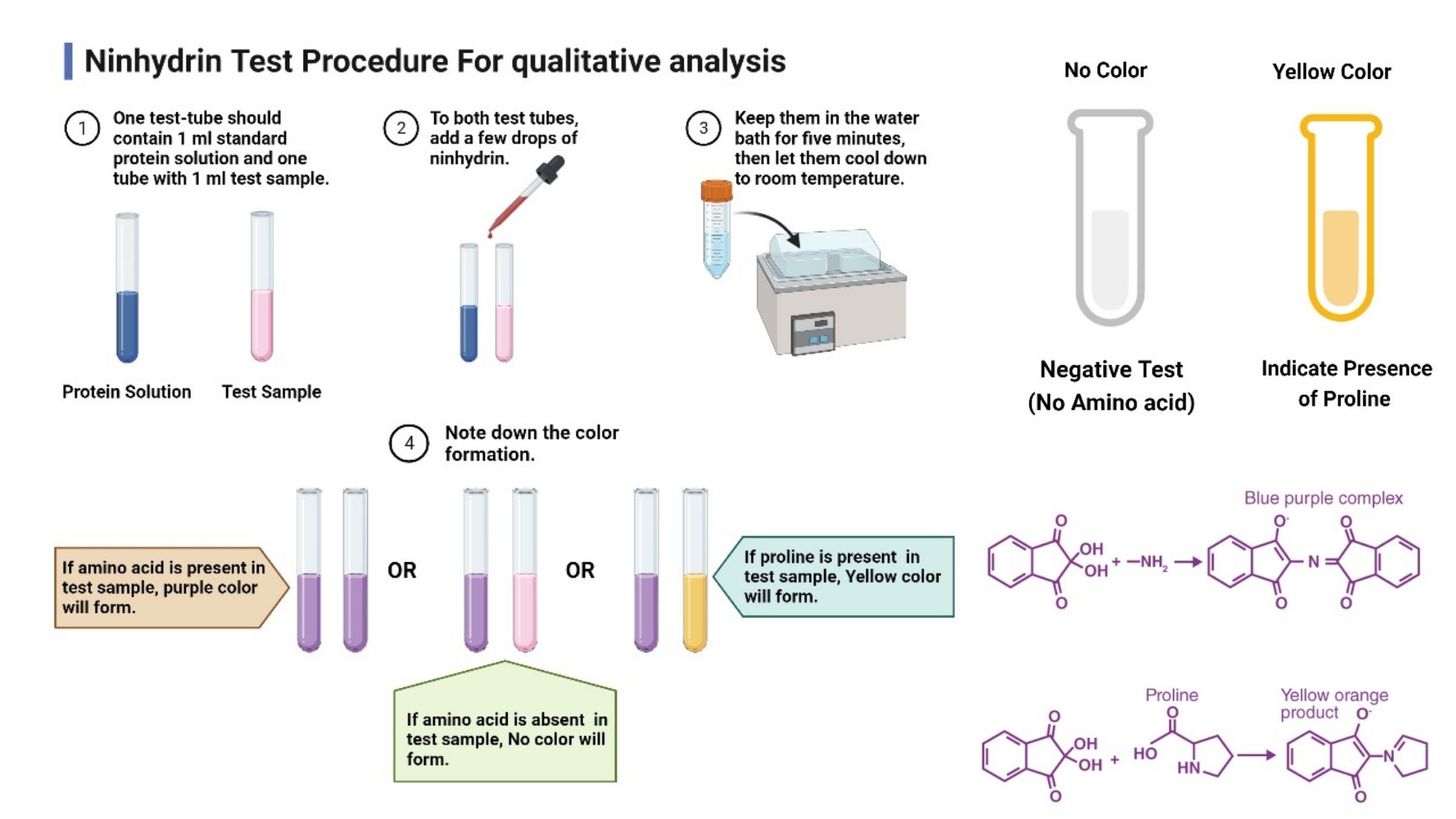
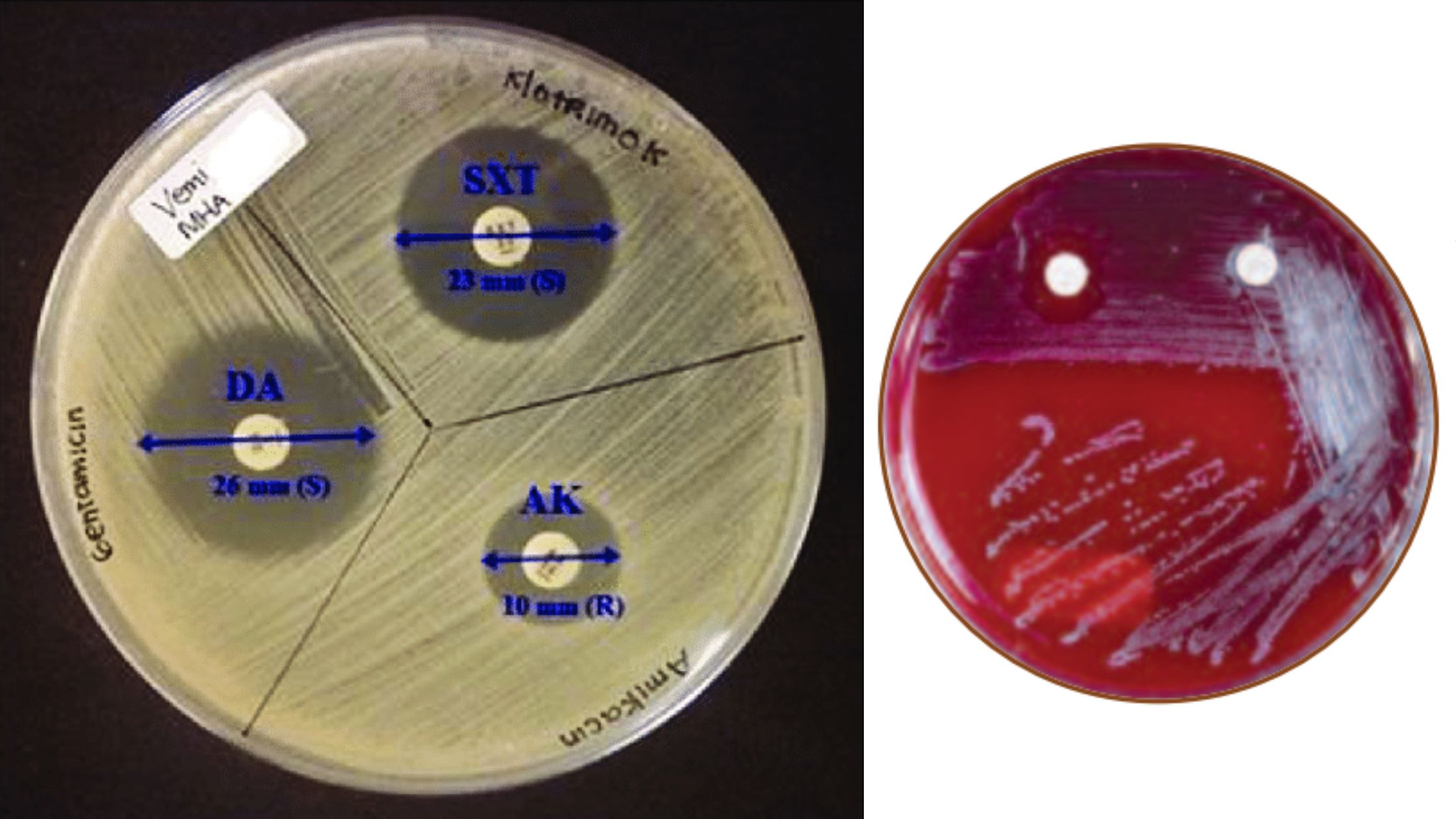
X and V factor Test – Principle, Purpose, Procedure, Result
Some bacteria make substances that other bacteria need to grow. The X factor and the V factor are two such substances. The heat-stable X-factor can be protoporphyrin IX, hemin, or other iron-containing porphyrins. It can be found in red blood cells and outside of them in the blood. The heat-sensitive V-factor may be nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), and it is mostly found inside red blood cells. The X and V factor test or a disc test can be used to find out if a bacterium depends on its X factor or its V factor. The results can help identify the bacteria.