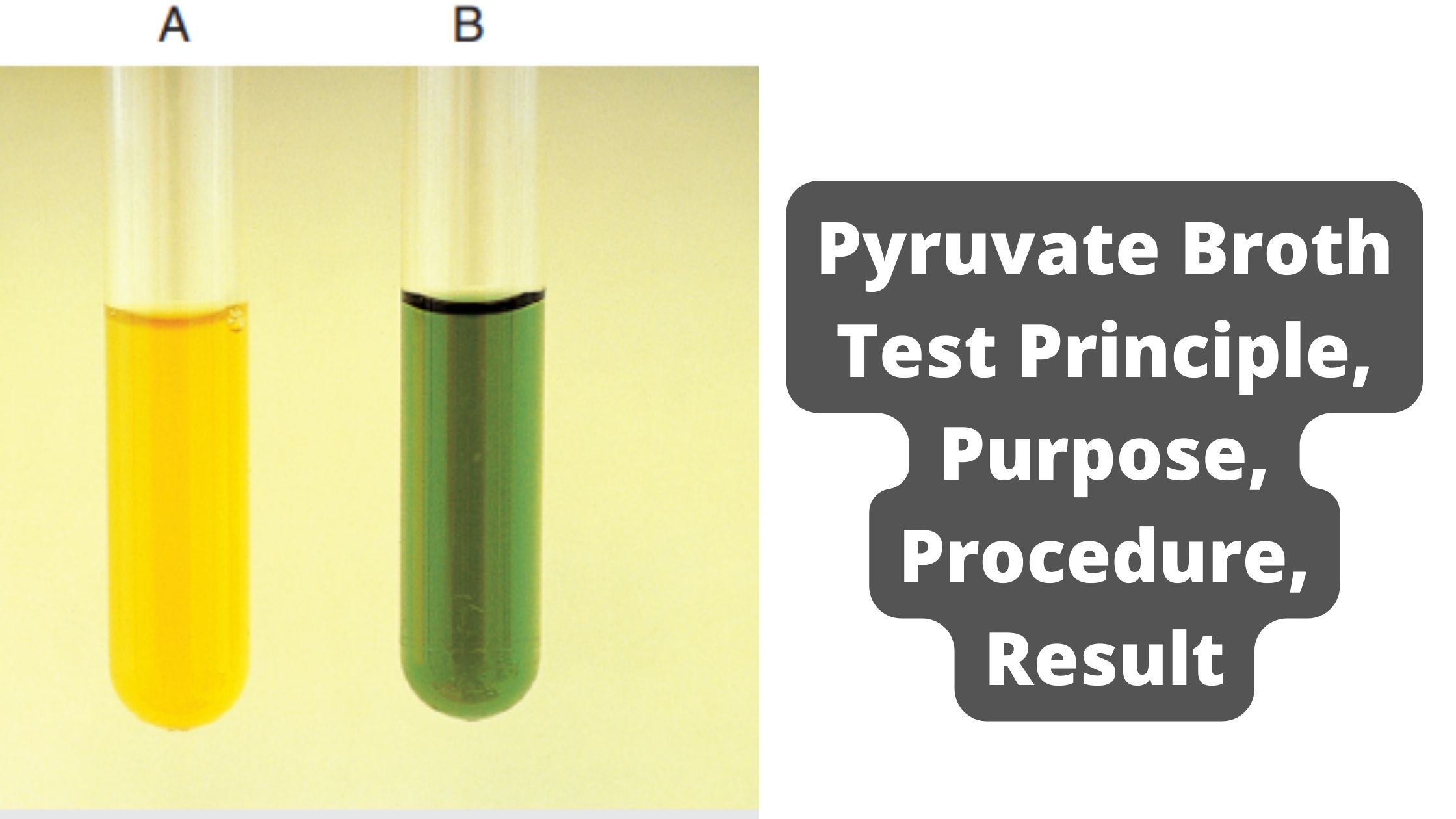
Pyruvate Broth Test – Principle, Purpose, Procedure, Result
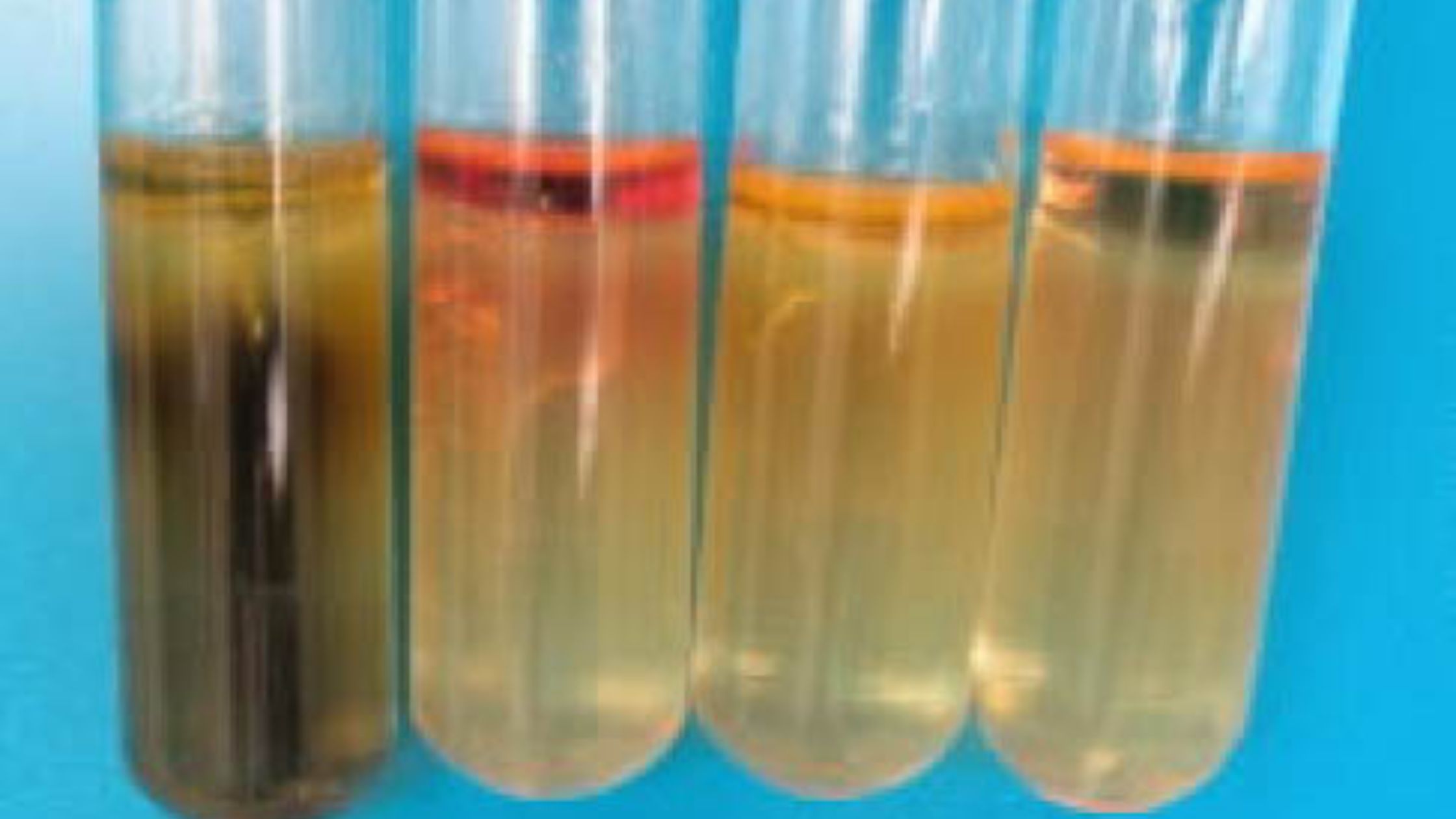
Pyruvate Broth Test is a biochemical test that is used in microbiology for identification and differentiation of certain bacteria. It is mainly used for differentiating species of Enterococcus group. It is the process in which ability of organism to utilize sodium pyruvate as a sole source of energy is determined. The medium used in this … Read more