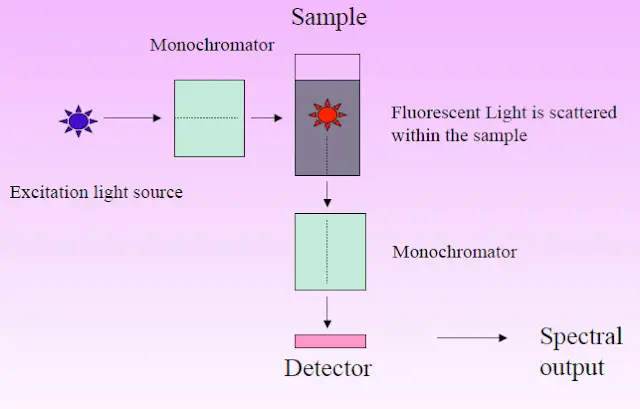
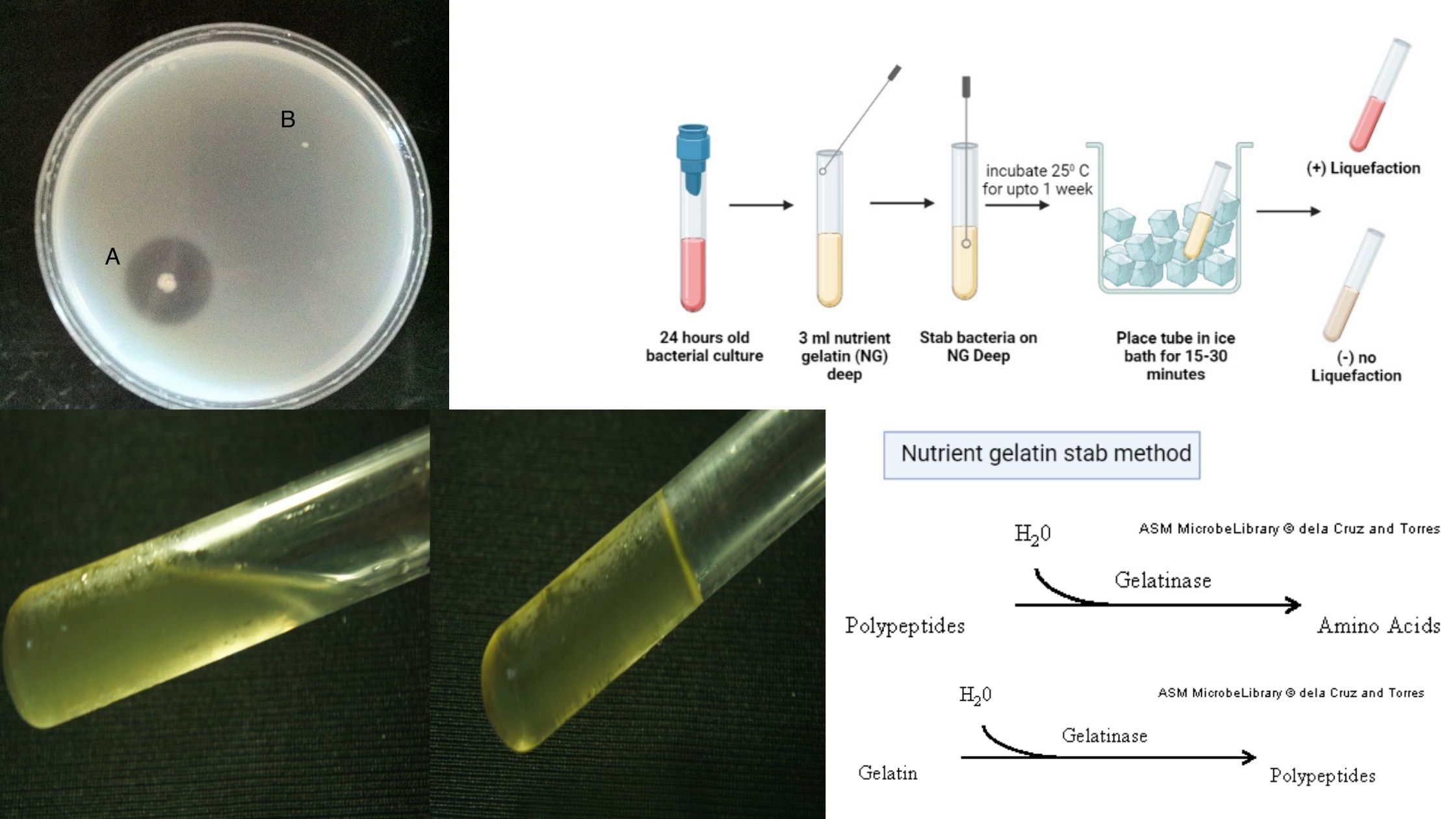
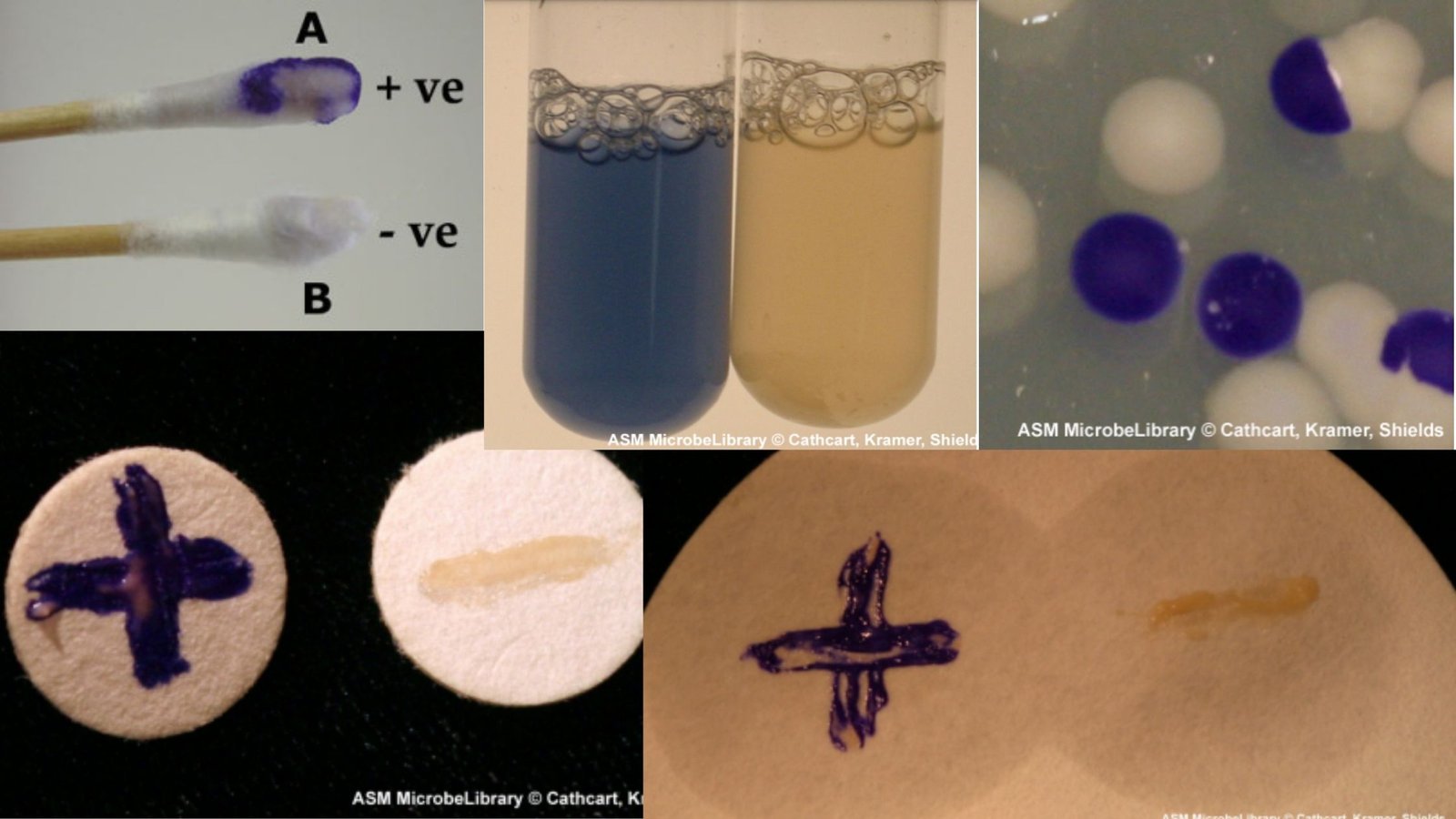
IMViC Test – Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses, Examples
What is IMViC test? The IMViC test is a group of biochemical tests which is used for the identification and differentiation of bacteria belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae. It is mainly used to distinguish fecal coliform bacteria from non-fecal coliform bacteria. The term IMViC is an acronym which stands for Indole, Methyl Red, Voges–Proskauer and … Read more