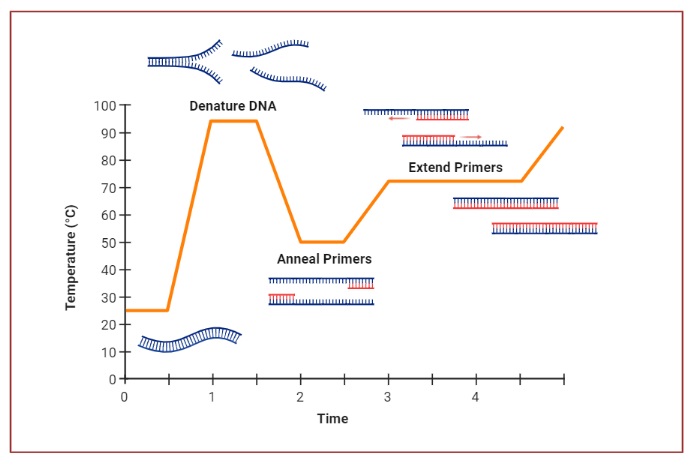
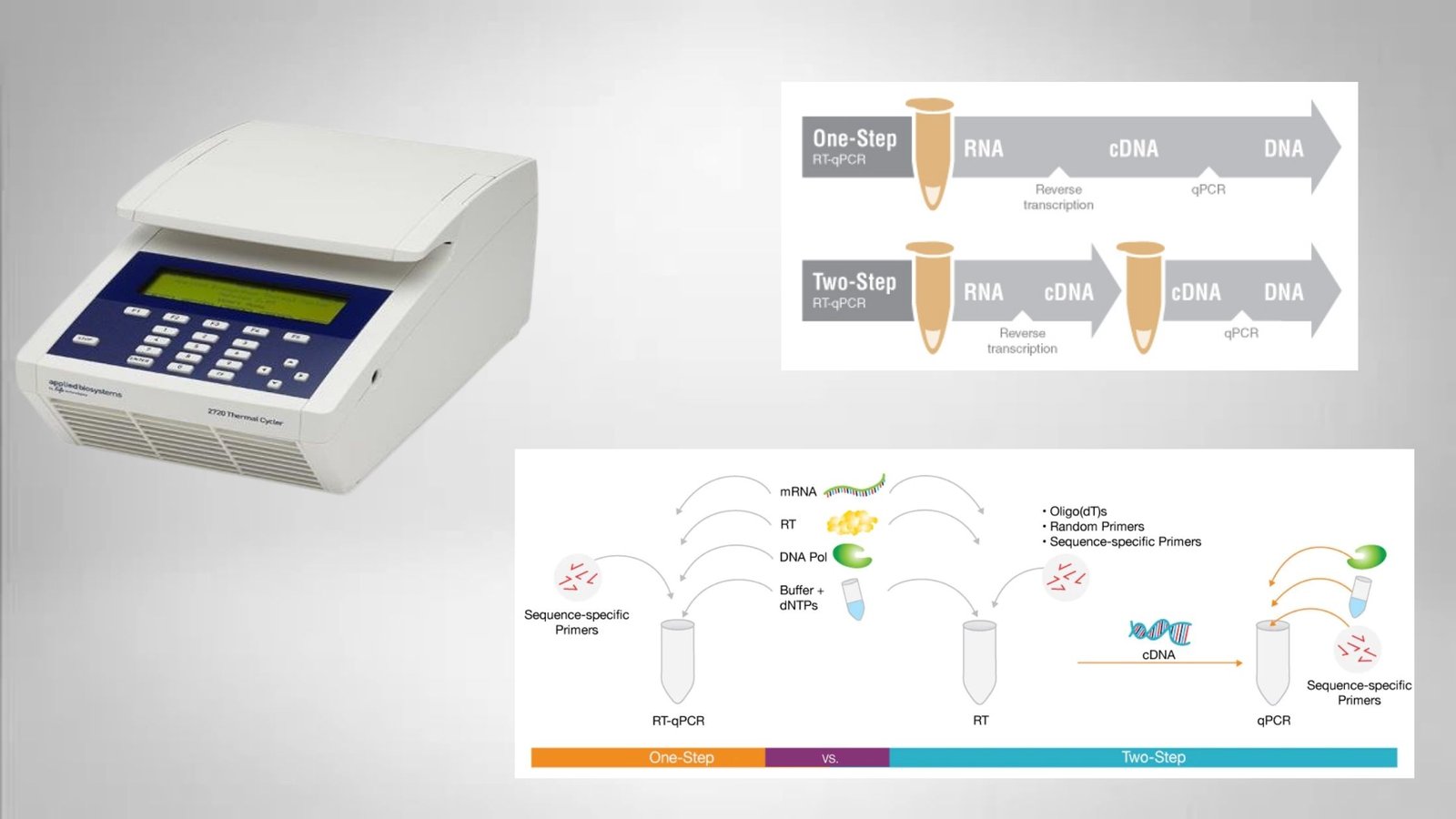
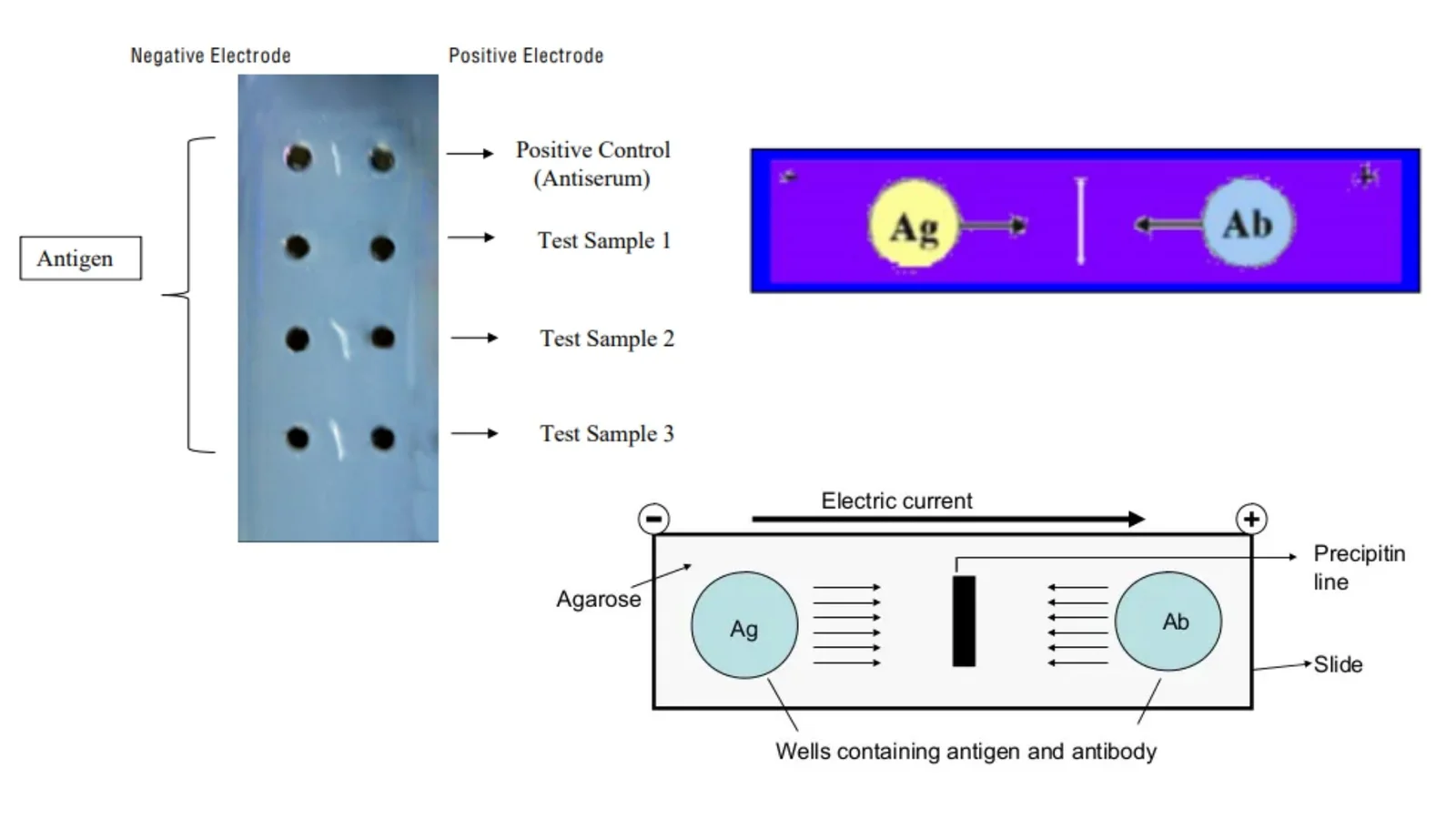
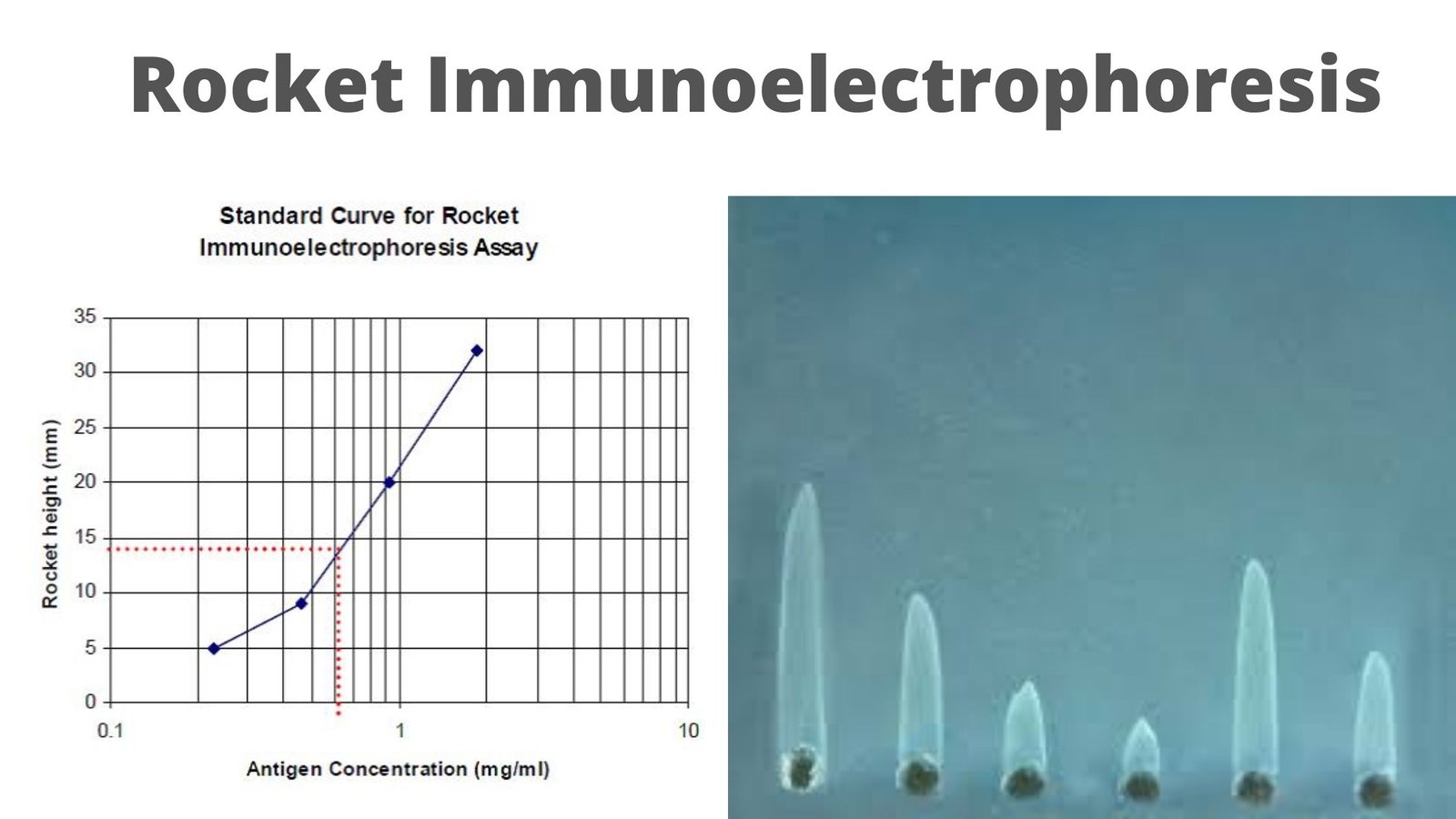
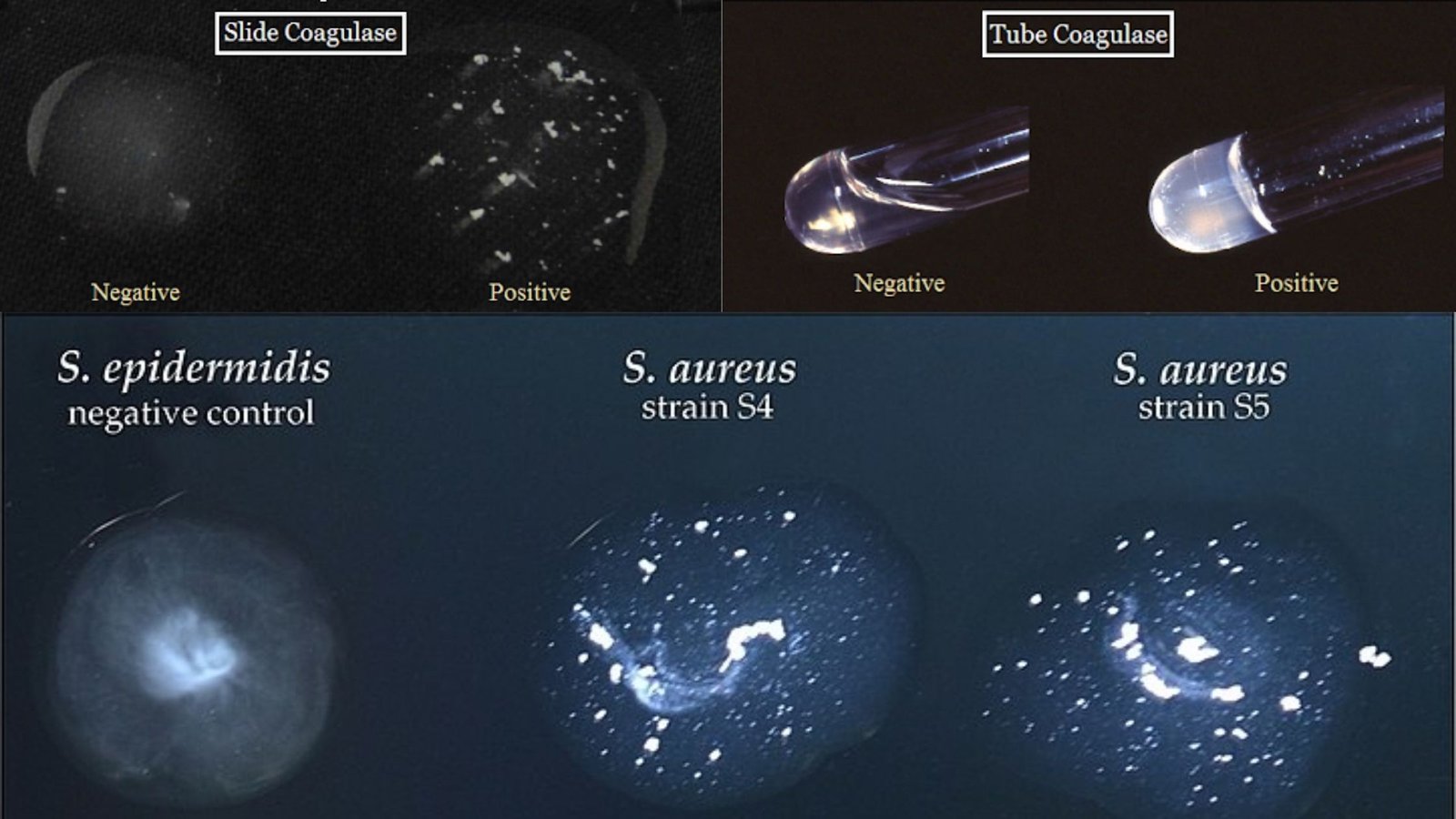
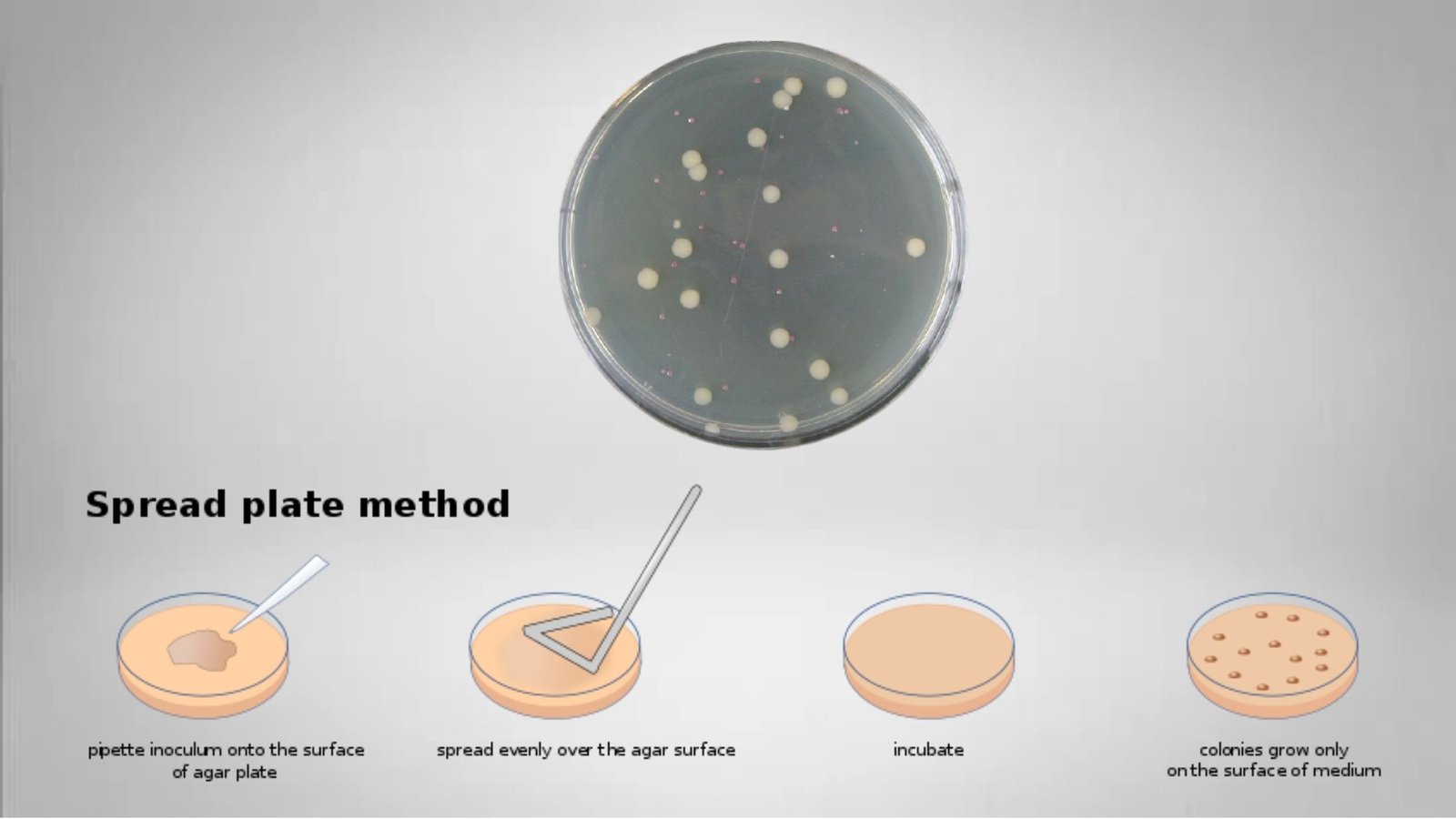
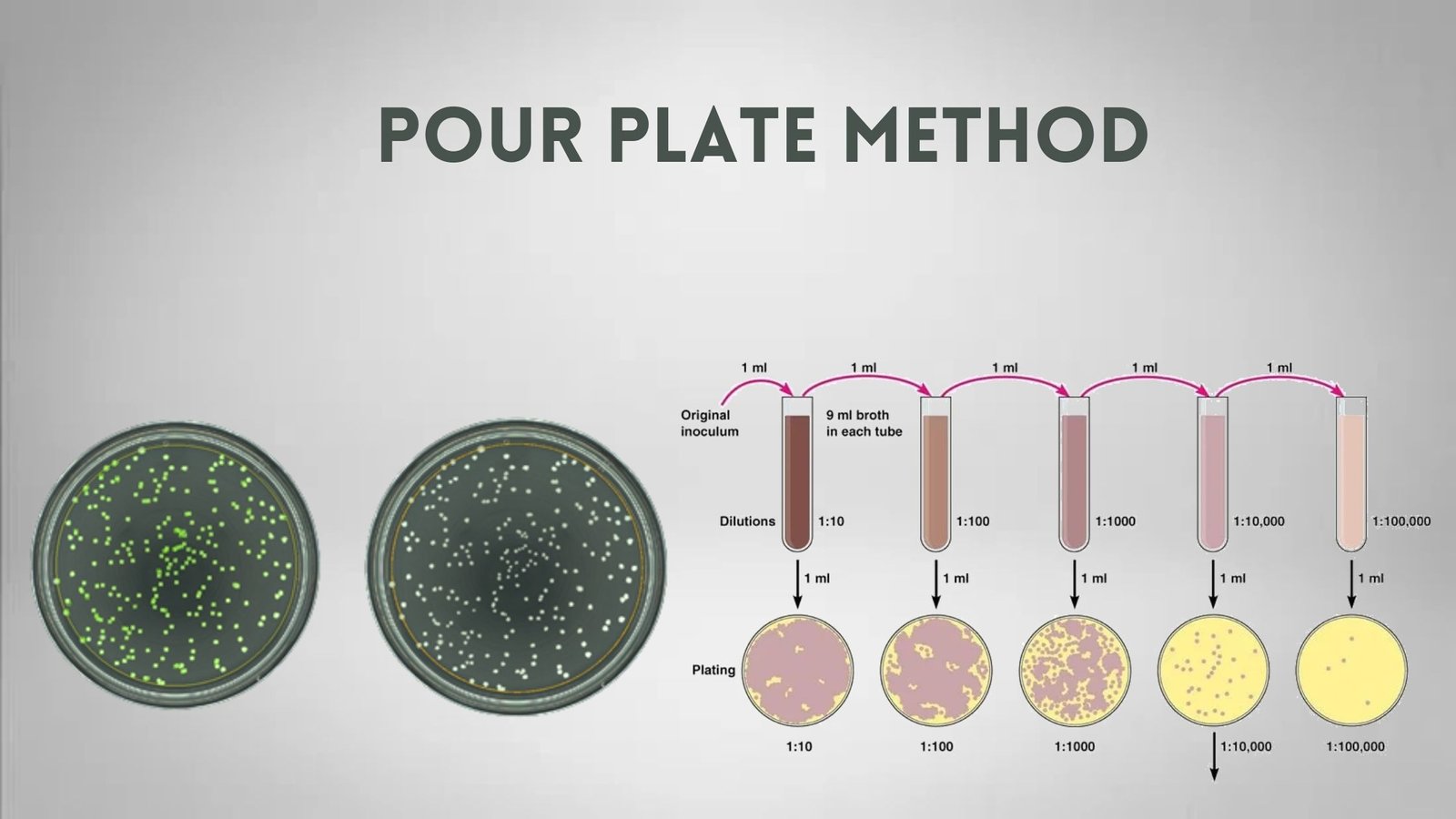
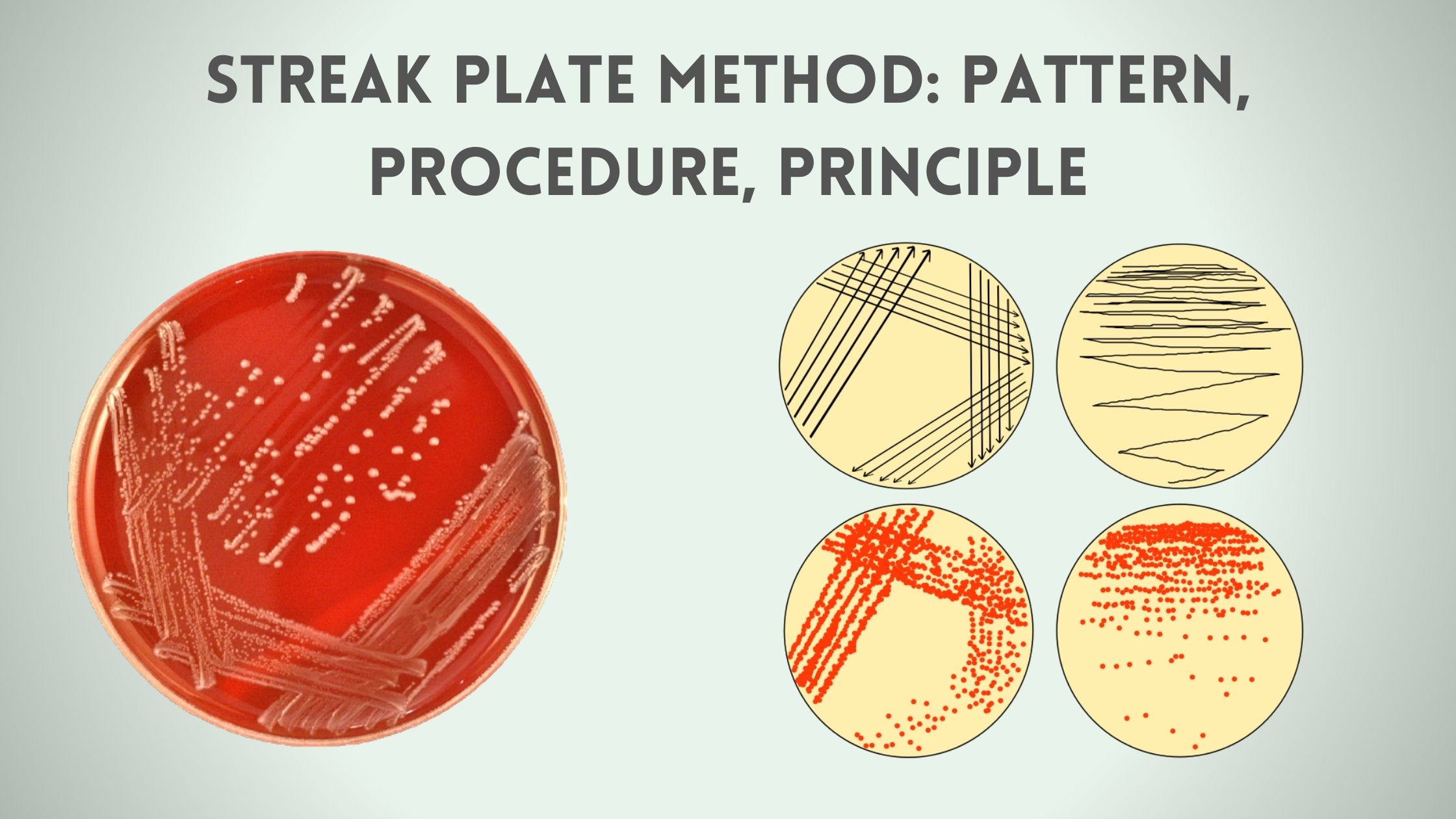
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – Definition, Steps, Principle, Application
Polymerase chain reaction or PCR is a laboratory technique that is used to make multiple copies (millions or billions!) of a specific region of DNA in vitro (in a test tube rather than an organism).