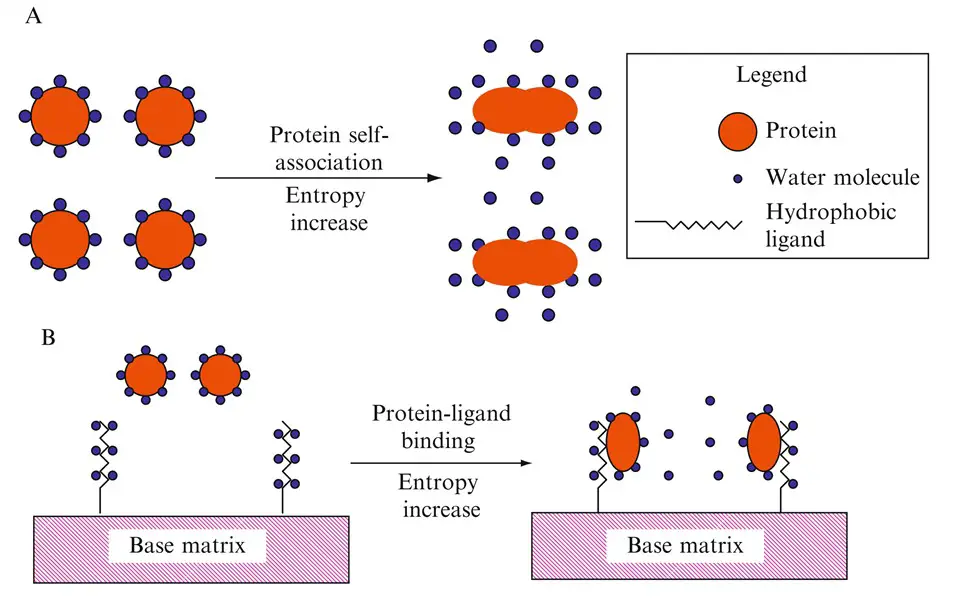
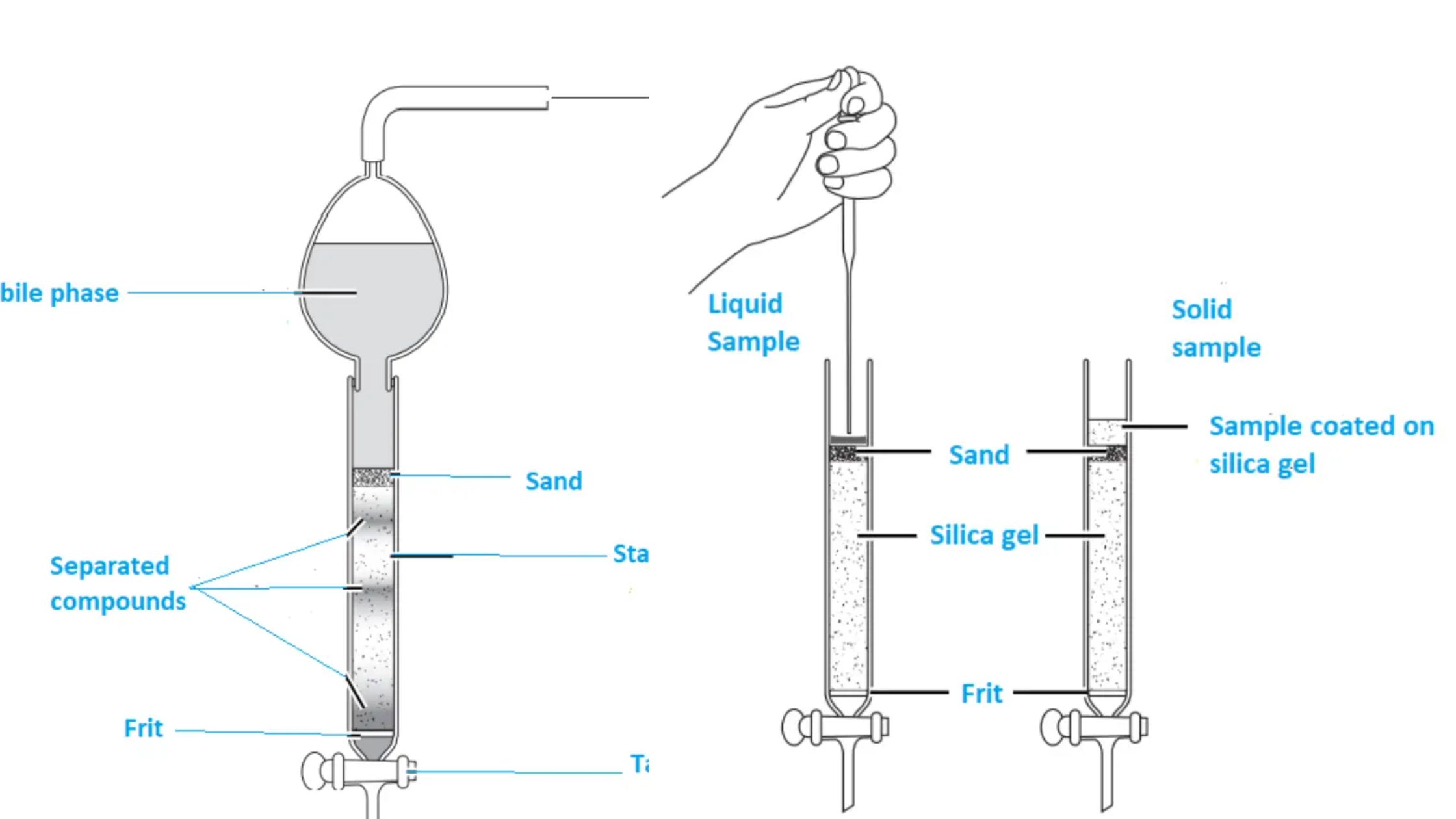
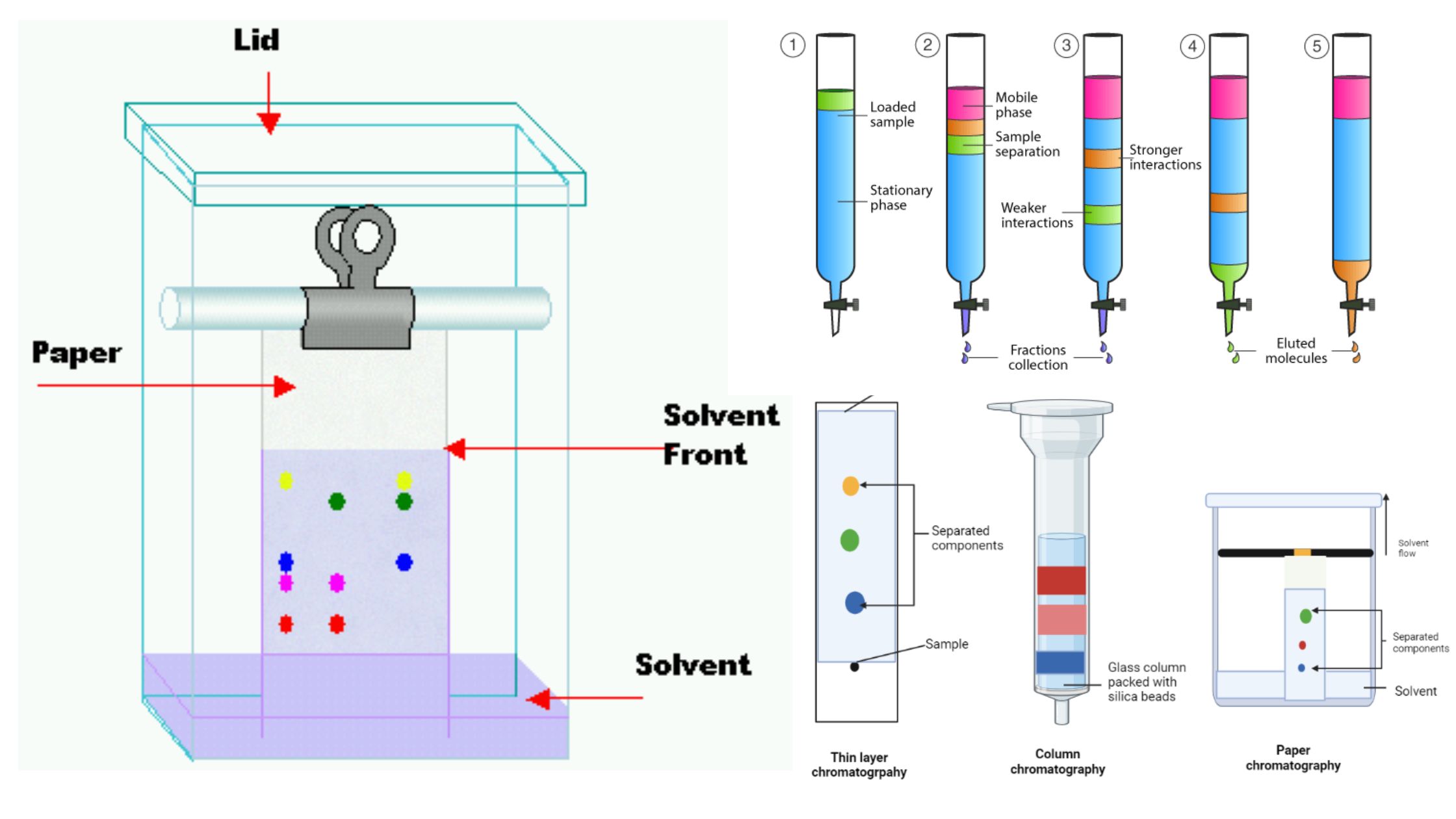
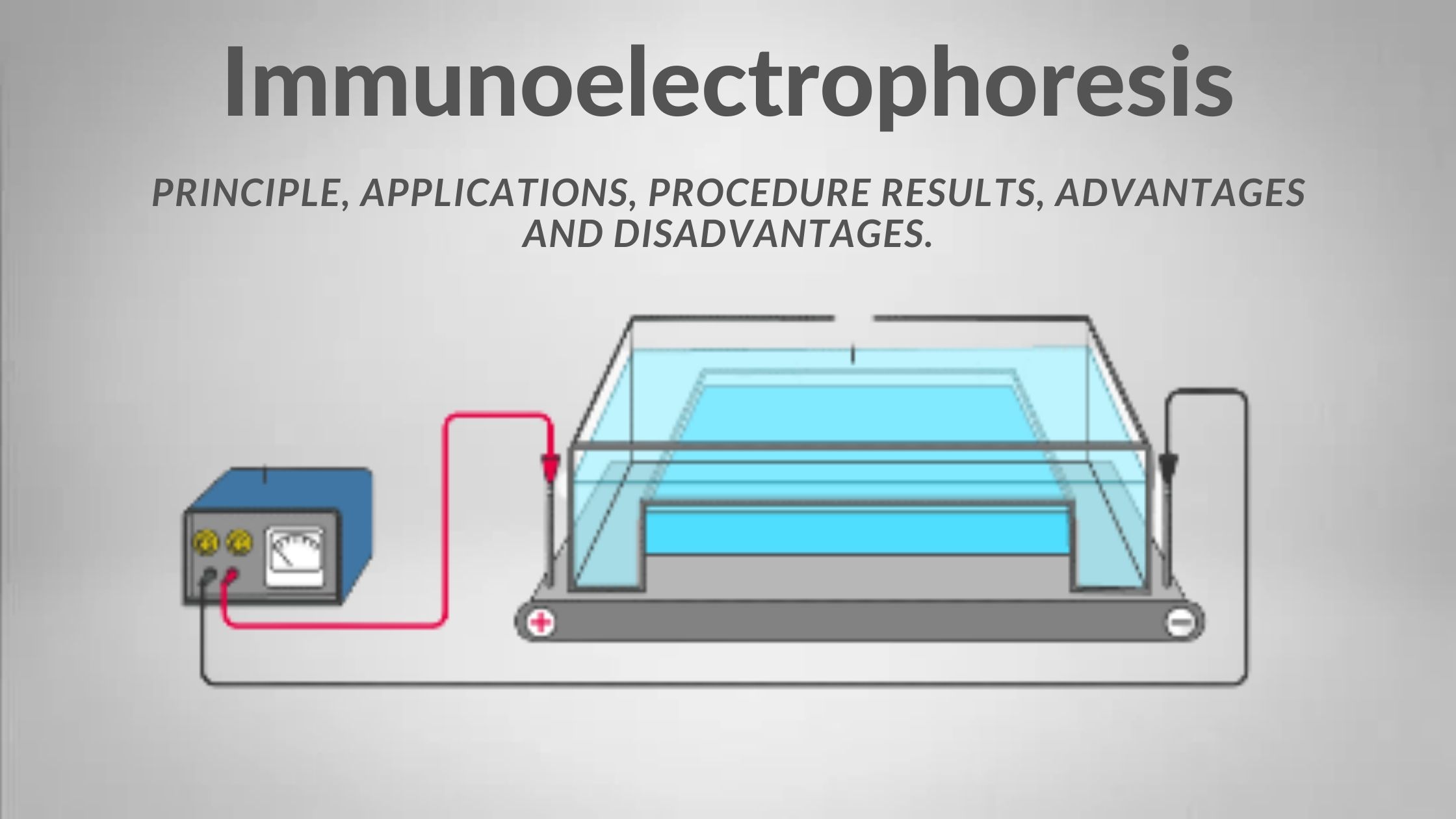
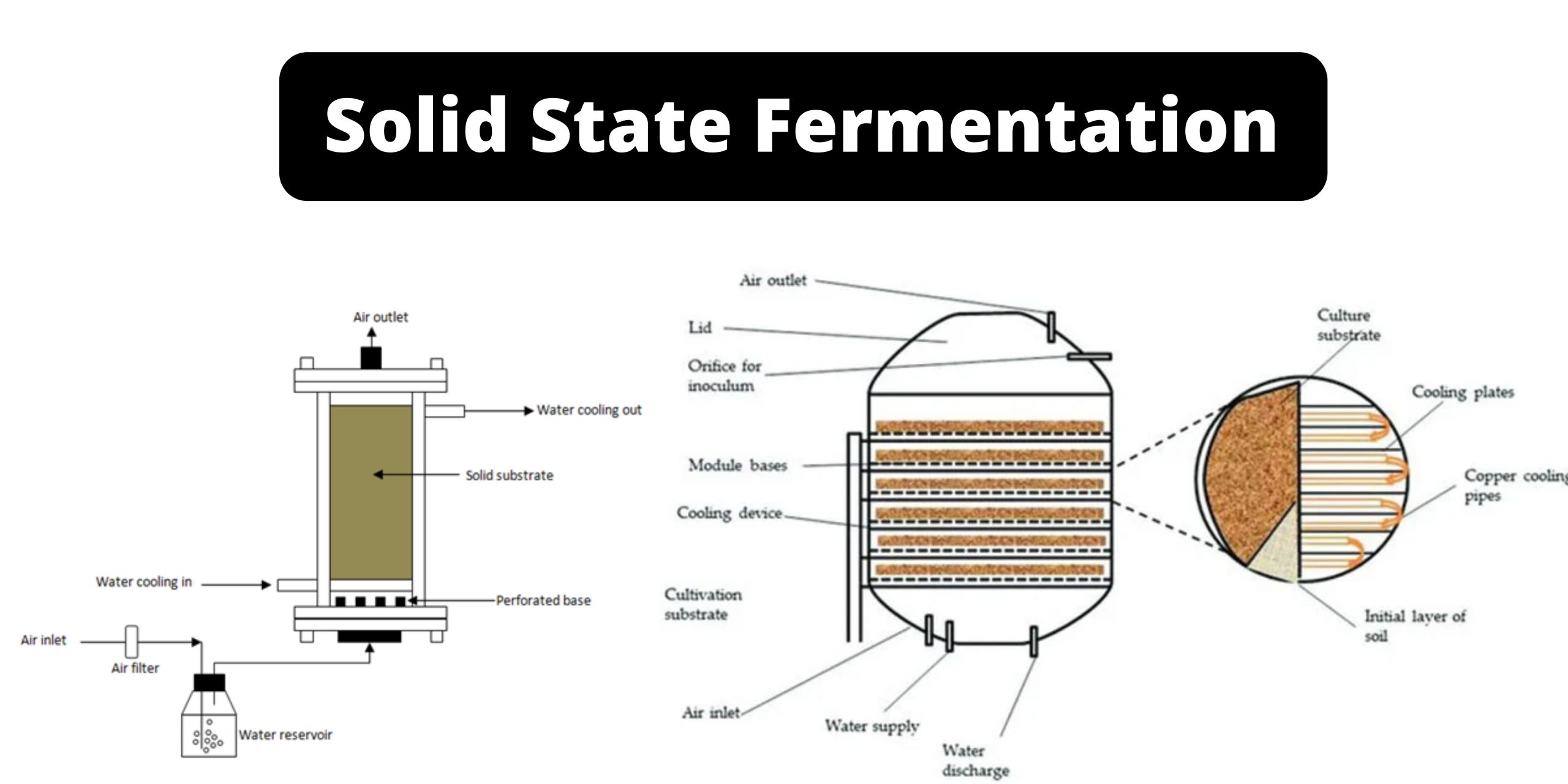
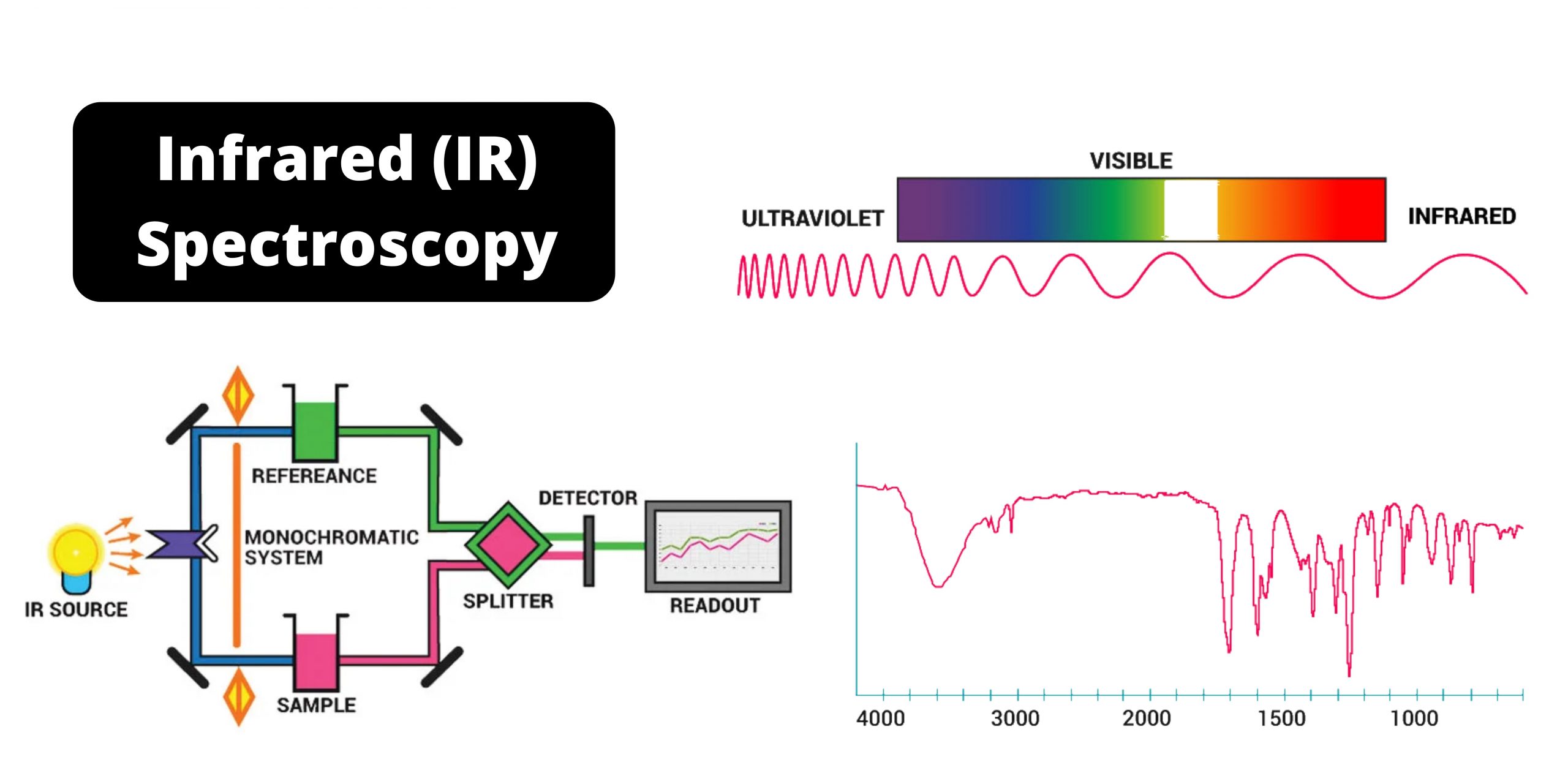
Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC)
What is Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC)? Principle of Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) Protocol of Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) Factors that Affect Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) Uses of Hydrophobic interaction chromatography Advantages of Hydrophobic interaction chromatography Limitations of Hydrophobic interaction chromatography FAQ