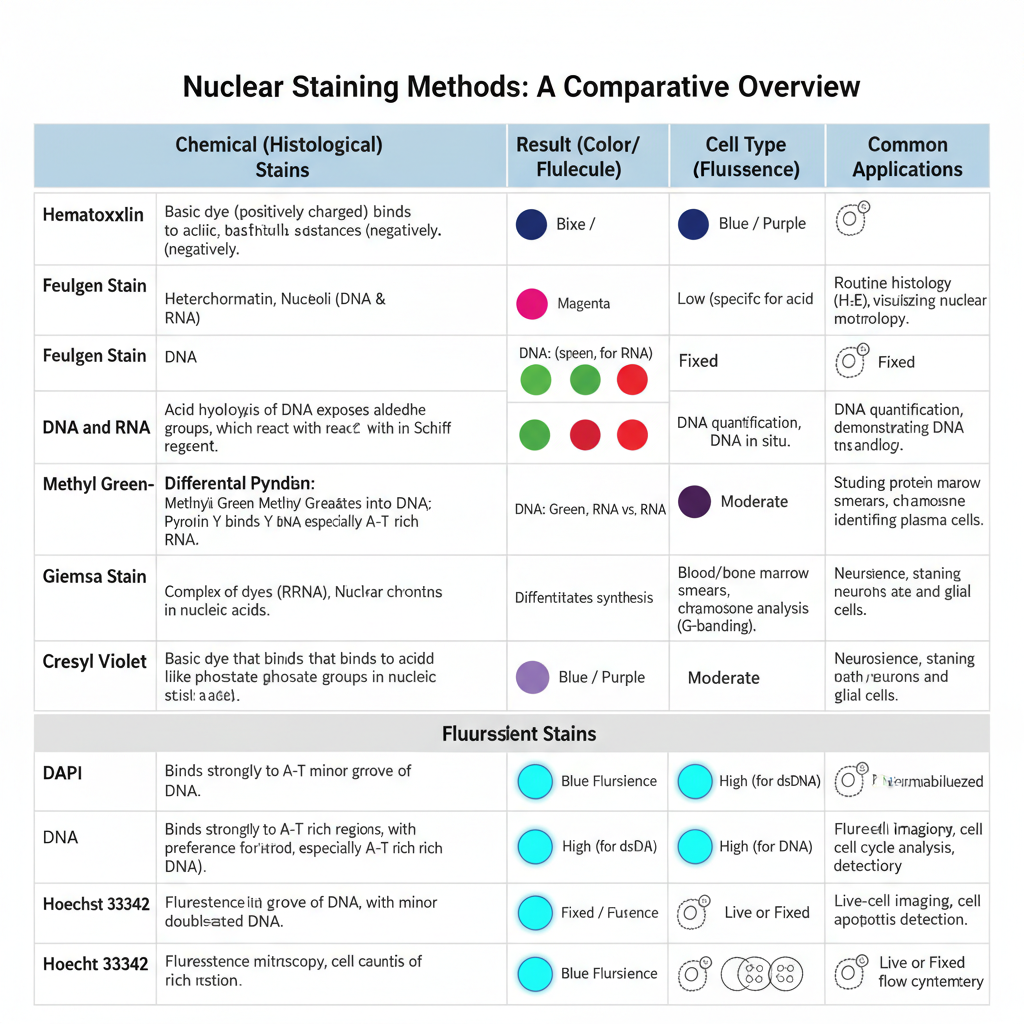
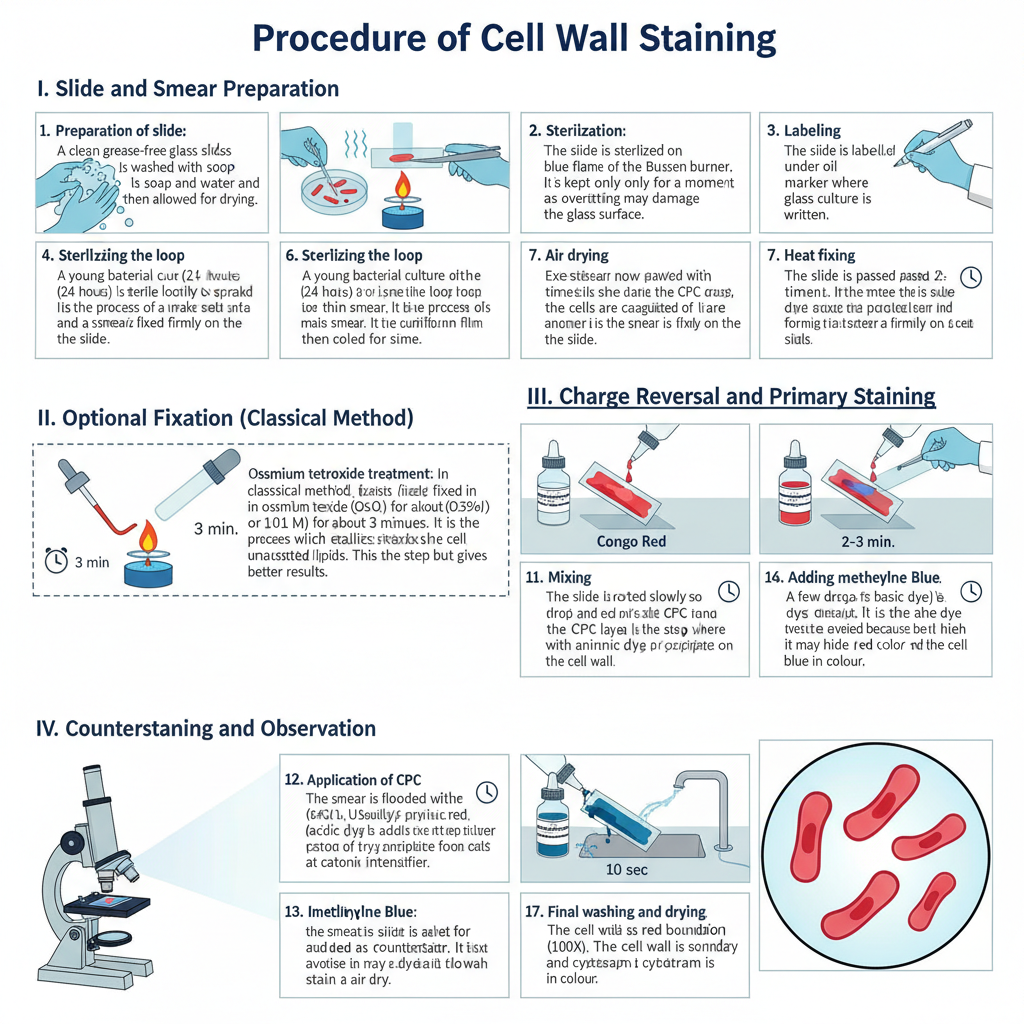
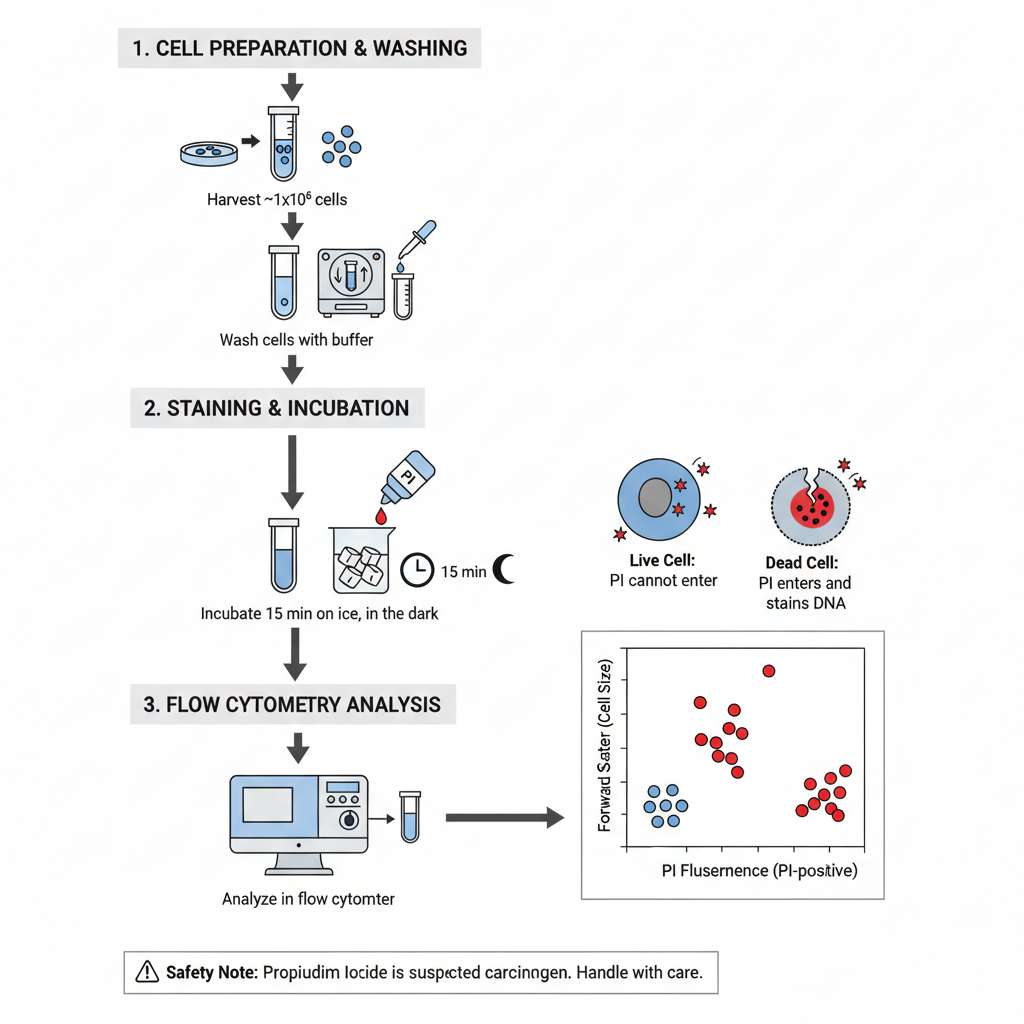
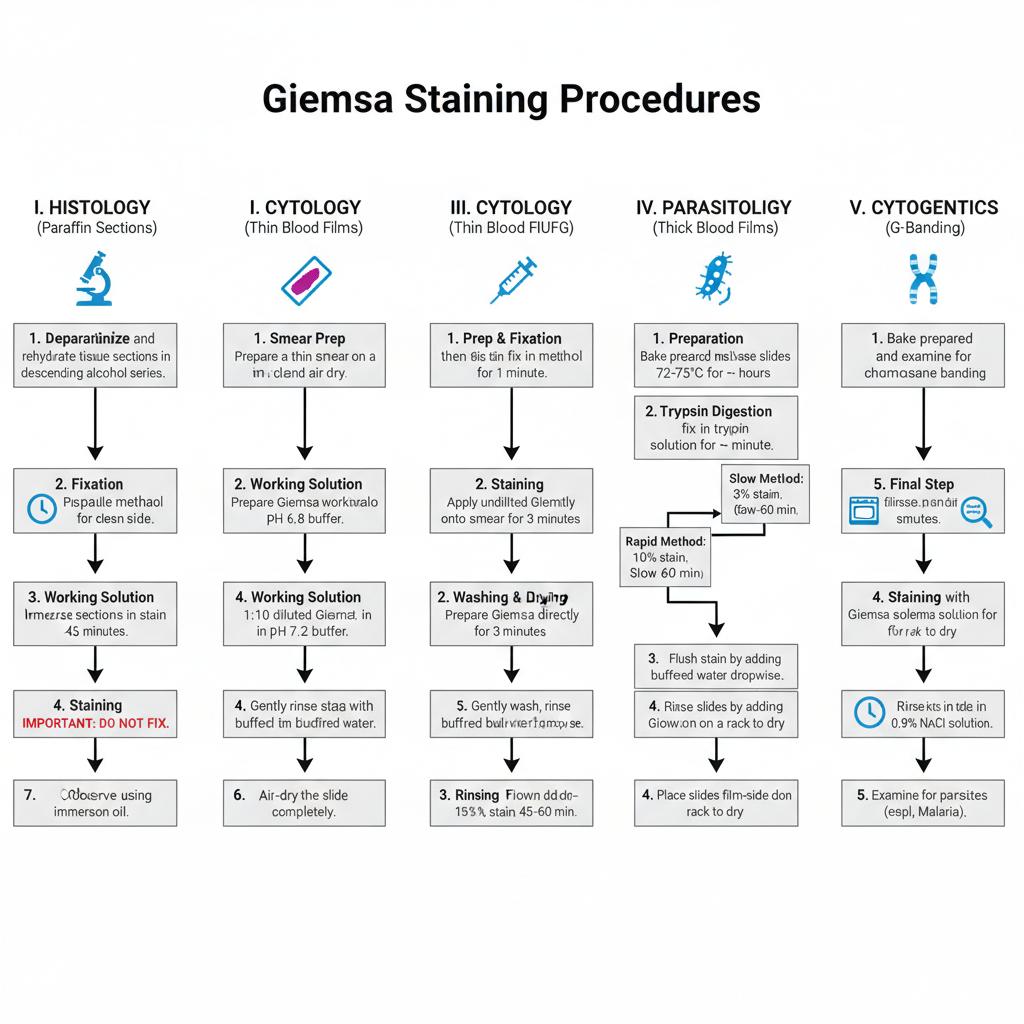
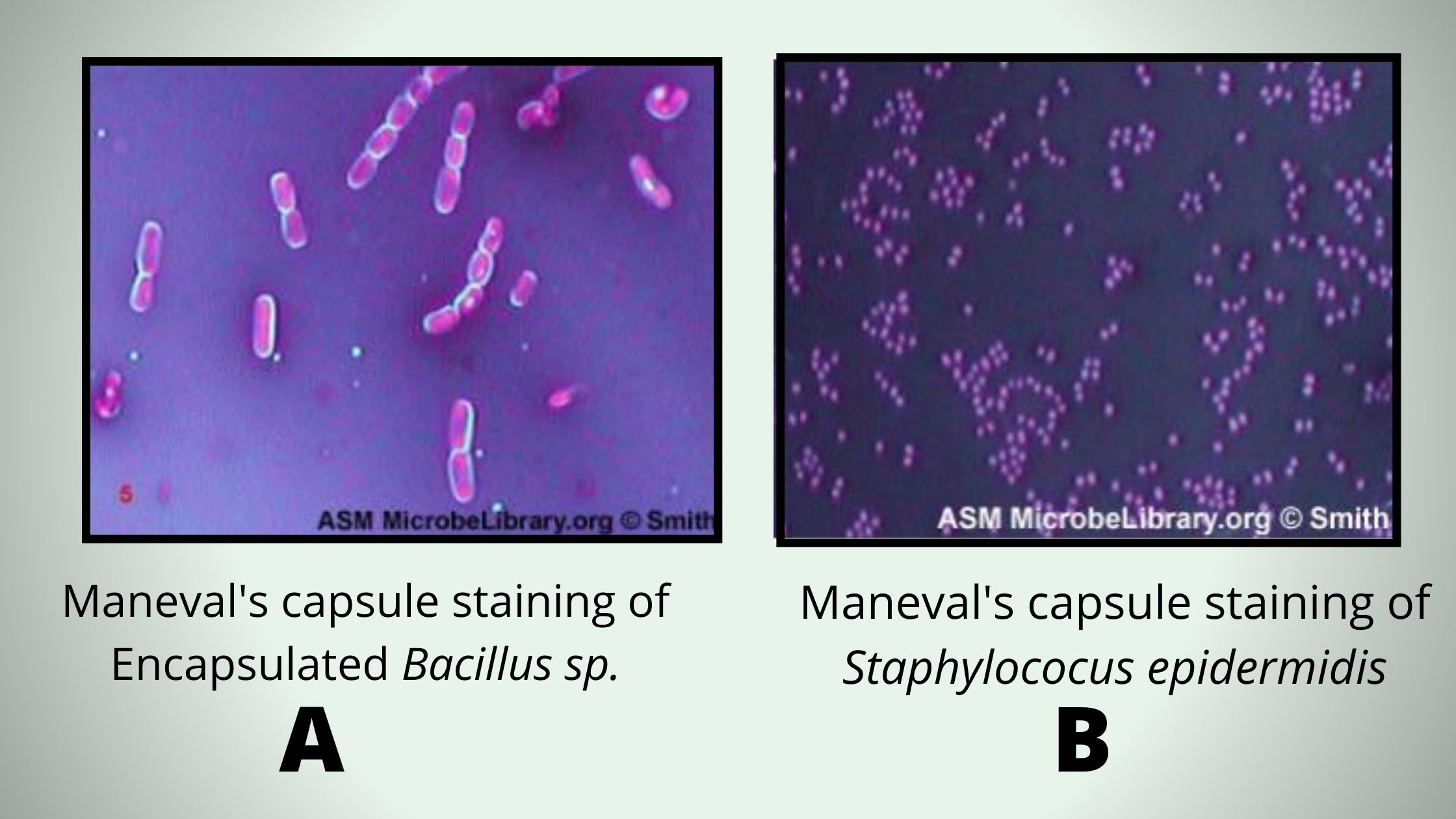
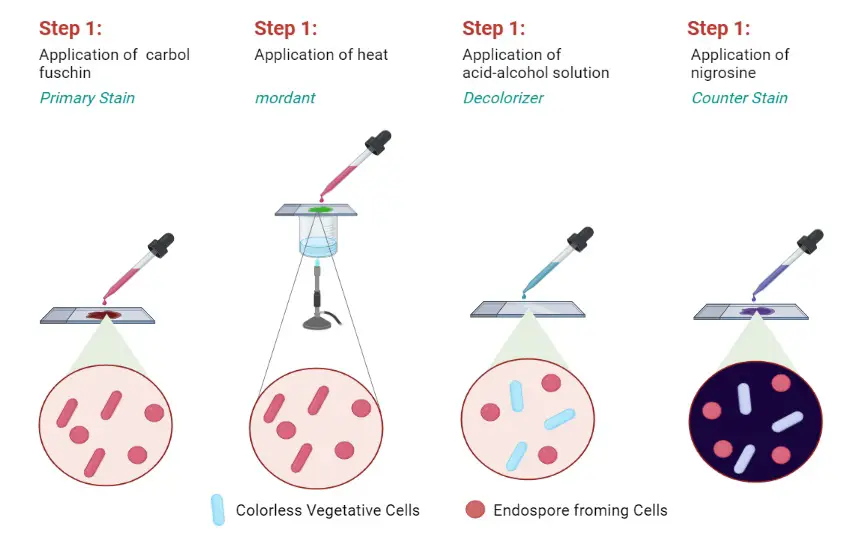
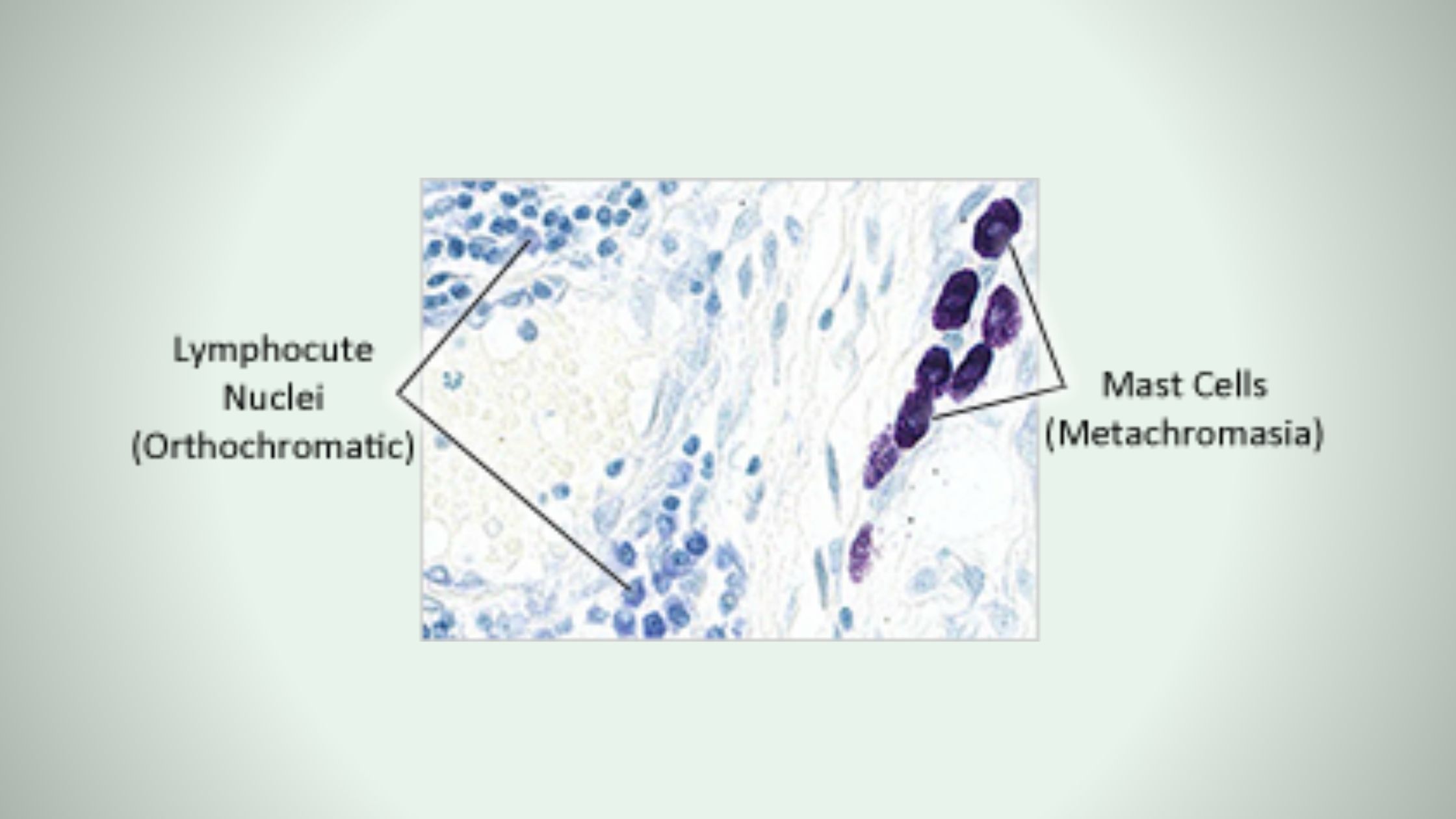
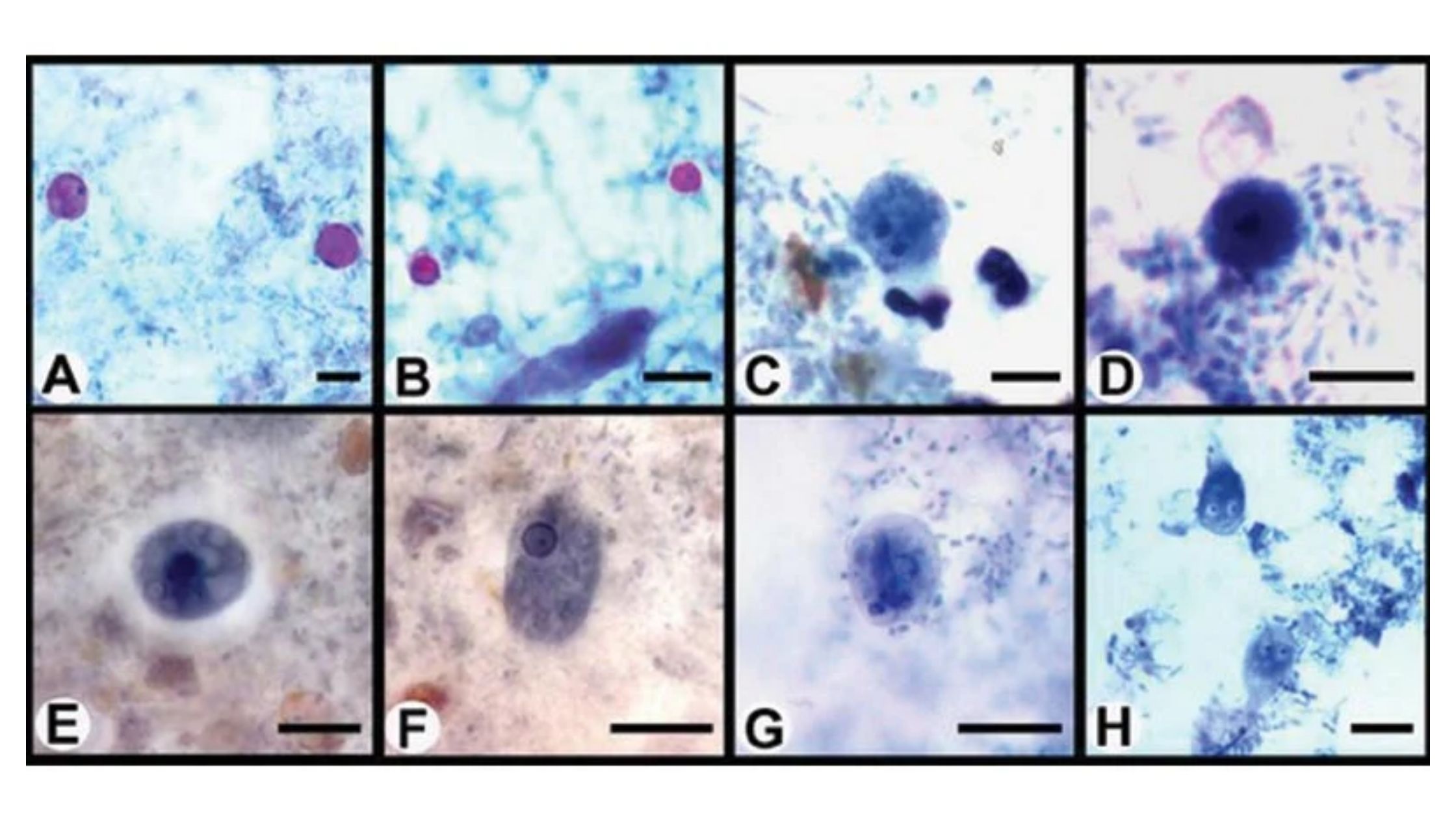
Nuclear Staining- Principle, Procedure, Uses
Nuclear staining is the process in which the nucleus of a cell is given artificial colour so that it becomes visible under microscope. It is the main method used in histology and cytology because the nucleus is naturally transparent and it needs specific dyes for proper contrast. The nucleus contains DNA and chromatin materials which … Read more