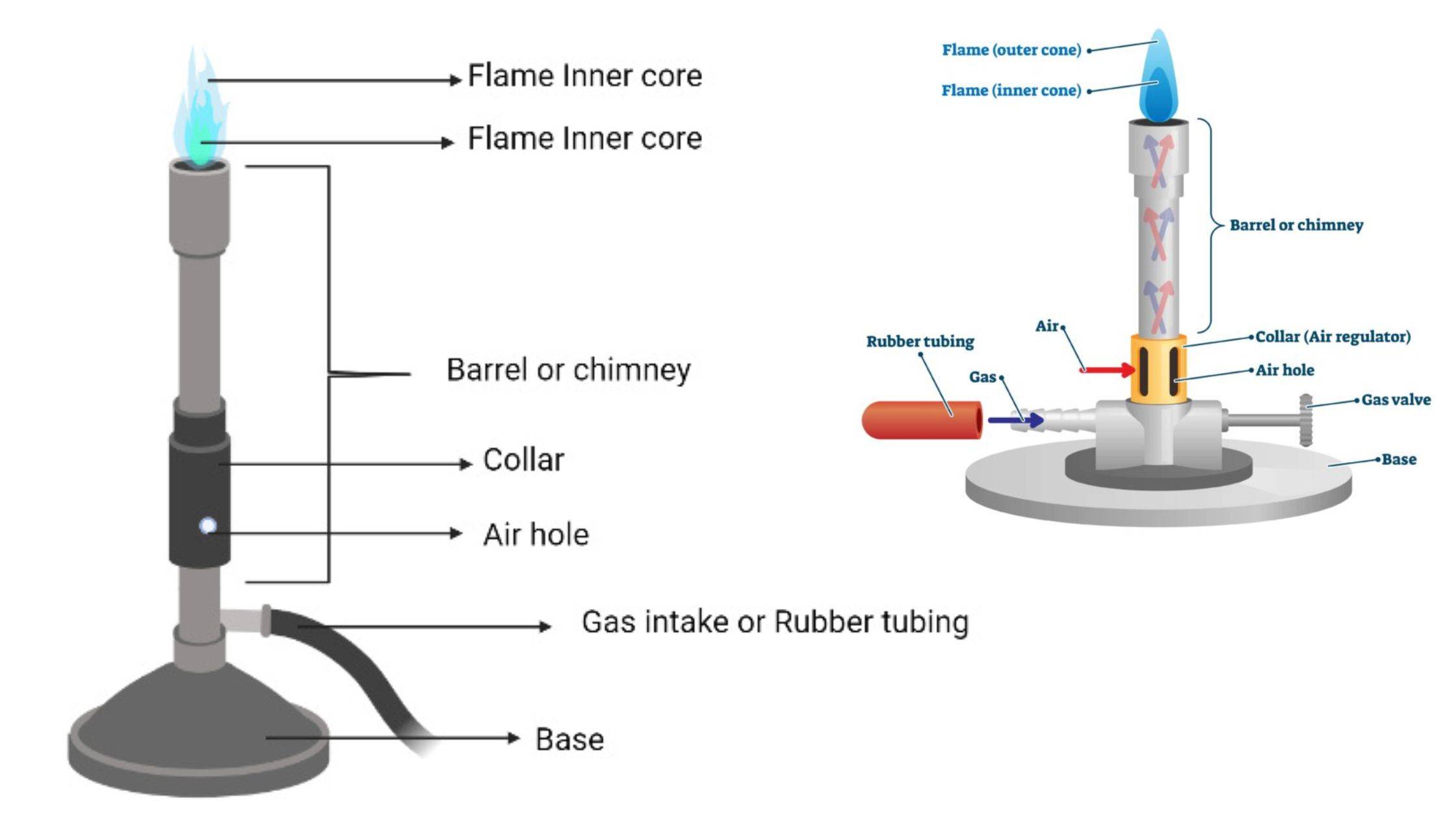
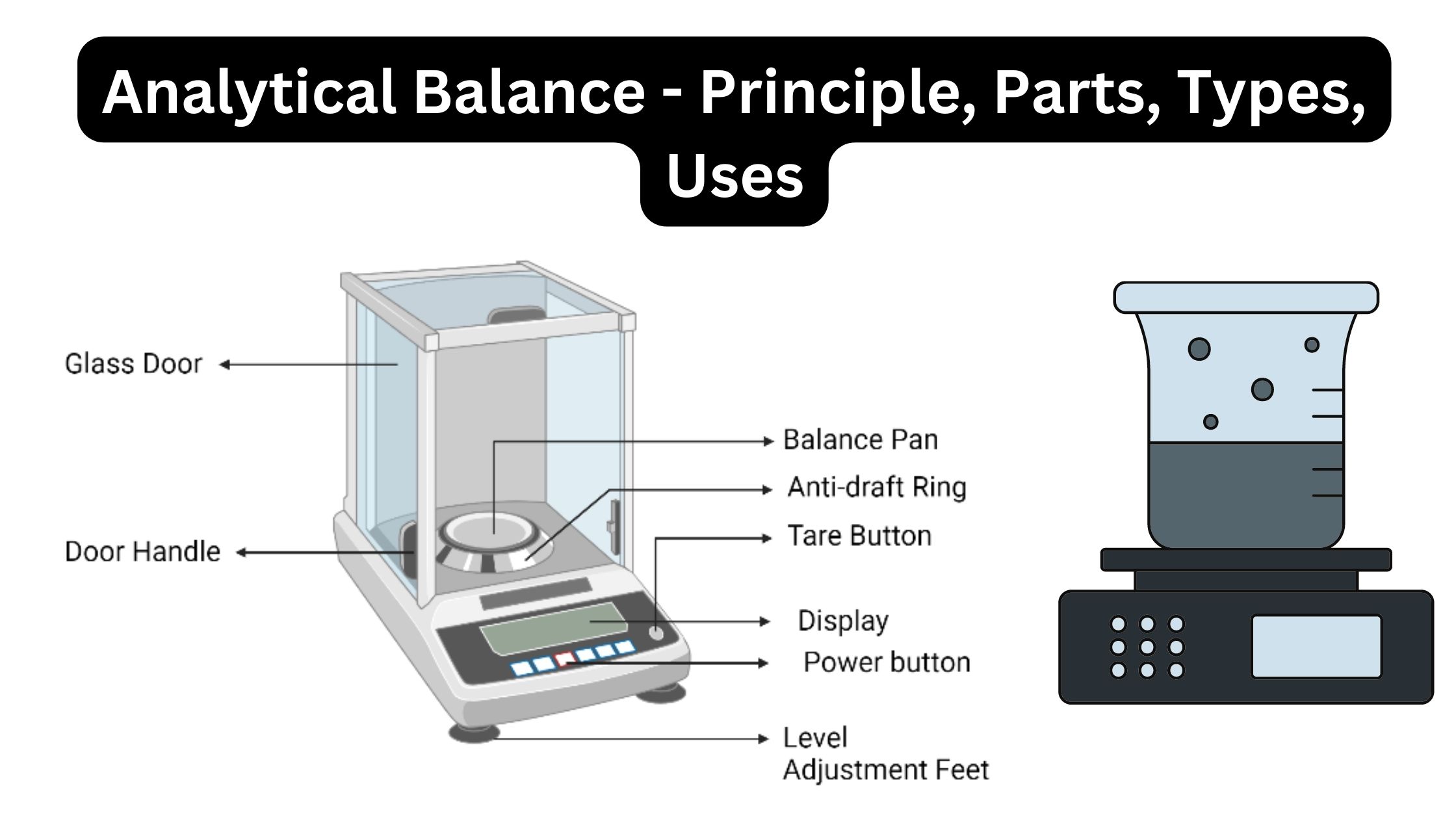
Bunsen Burner – Definition, Principle, Parts, Functions
What is a Bunsen Burner? Definition of Bunsen Burner A Bunsen burner is a laboratory gas burner that produces a controlled flame for scientific experiments and research purposes. Principle of Bunsen burner The principle of Bunsen burner based on the combustion of gas with air before ignition, which produce a safe and controllable flame for … Read more