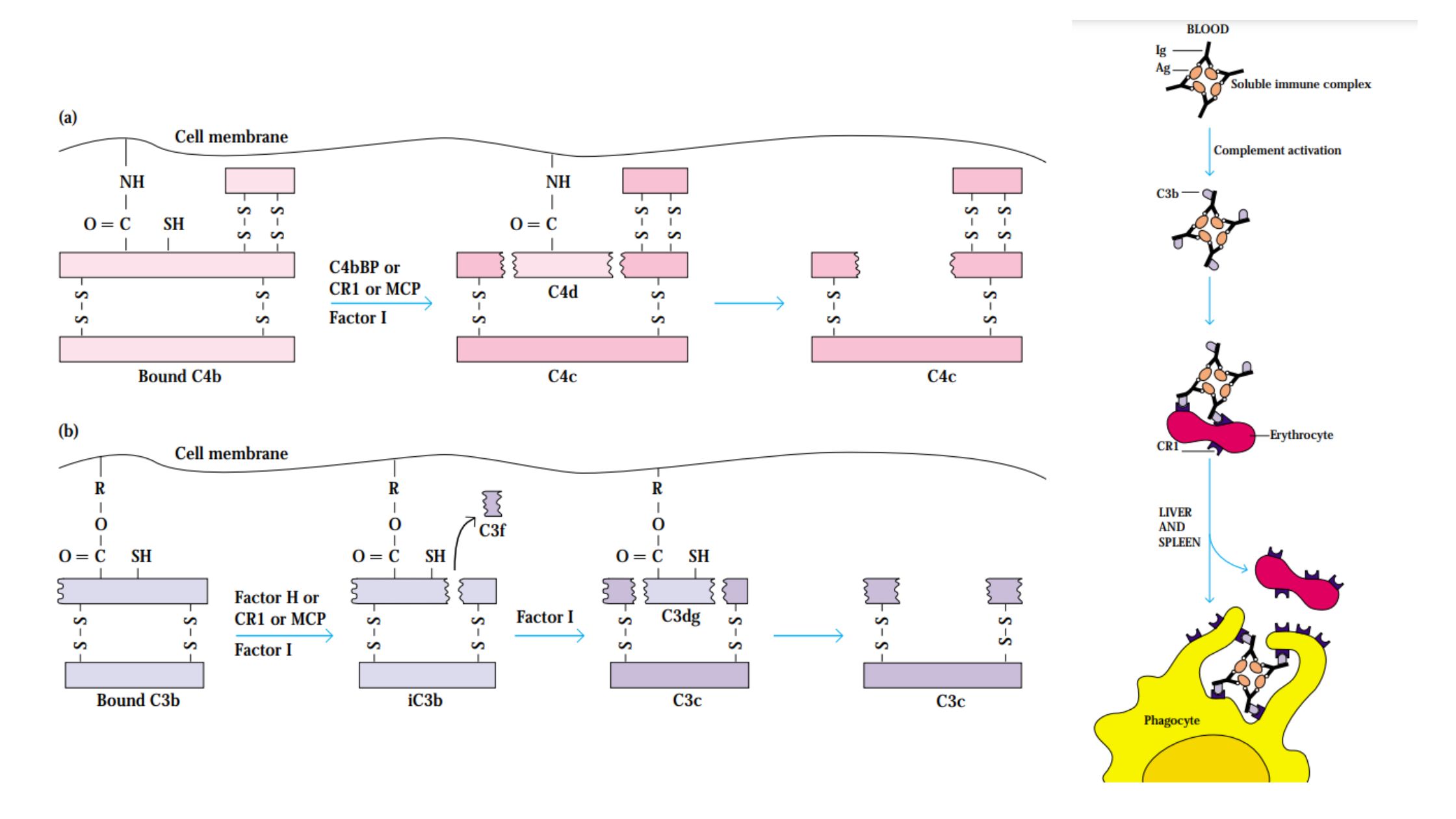
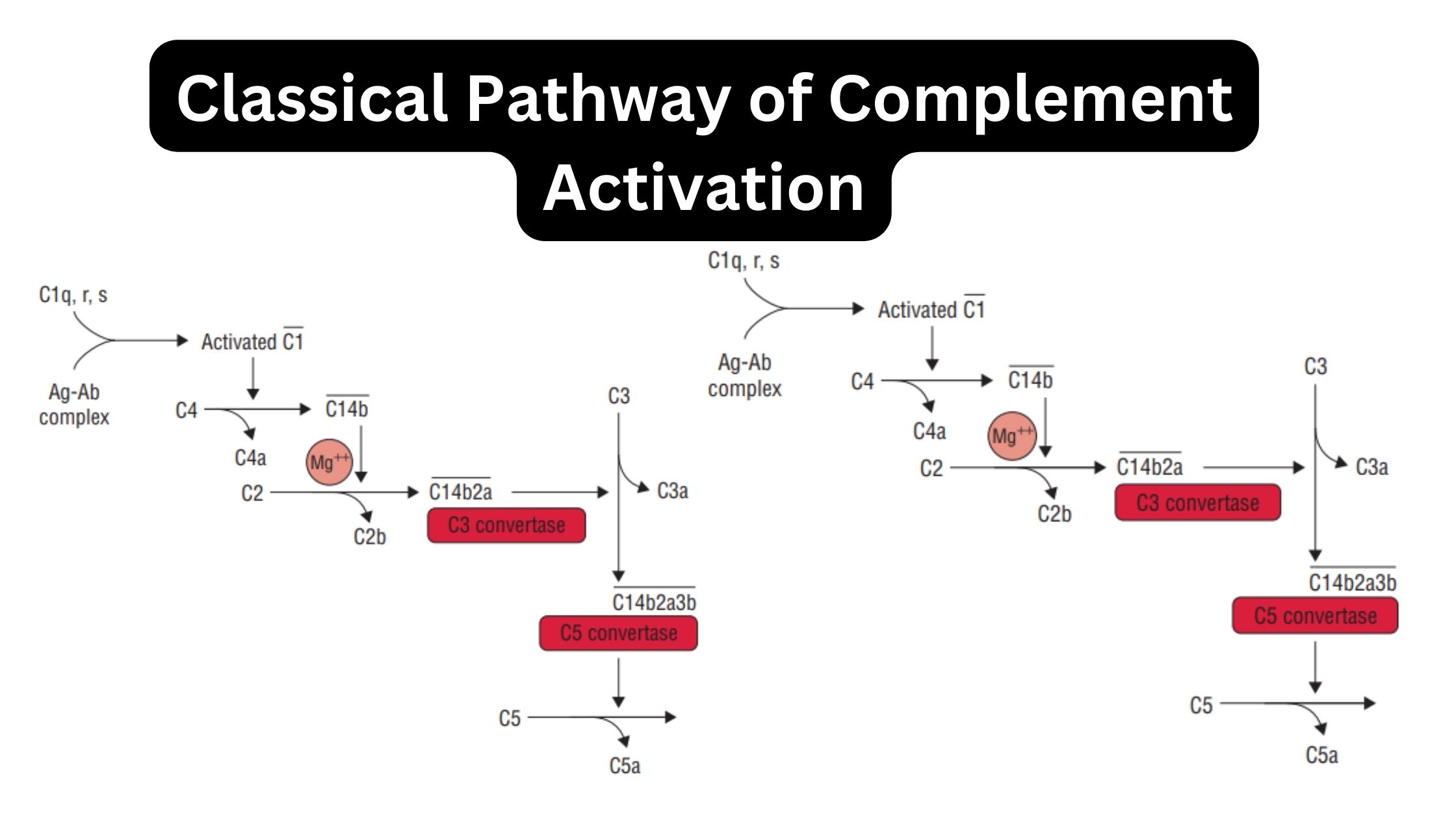
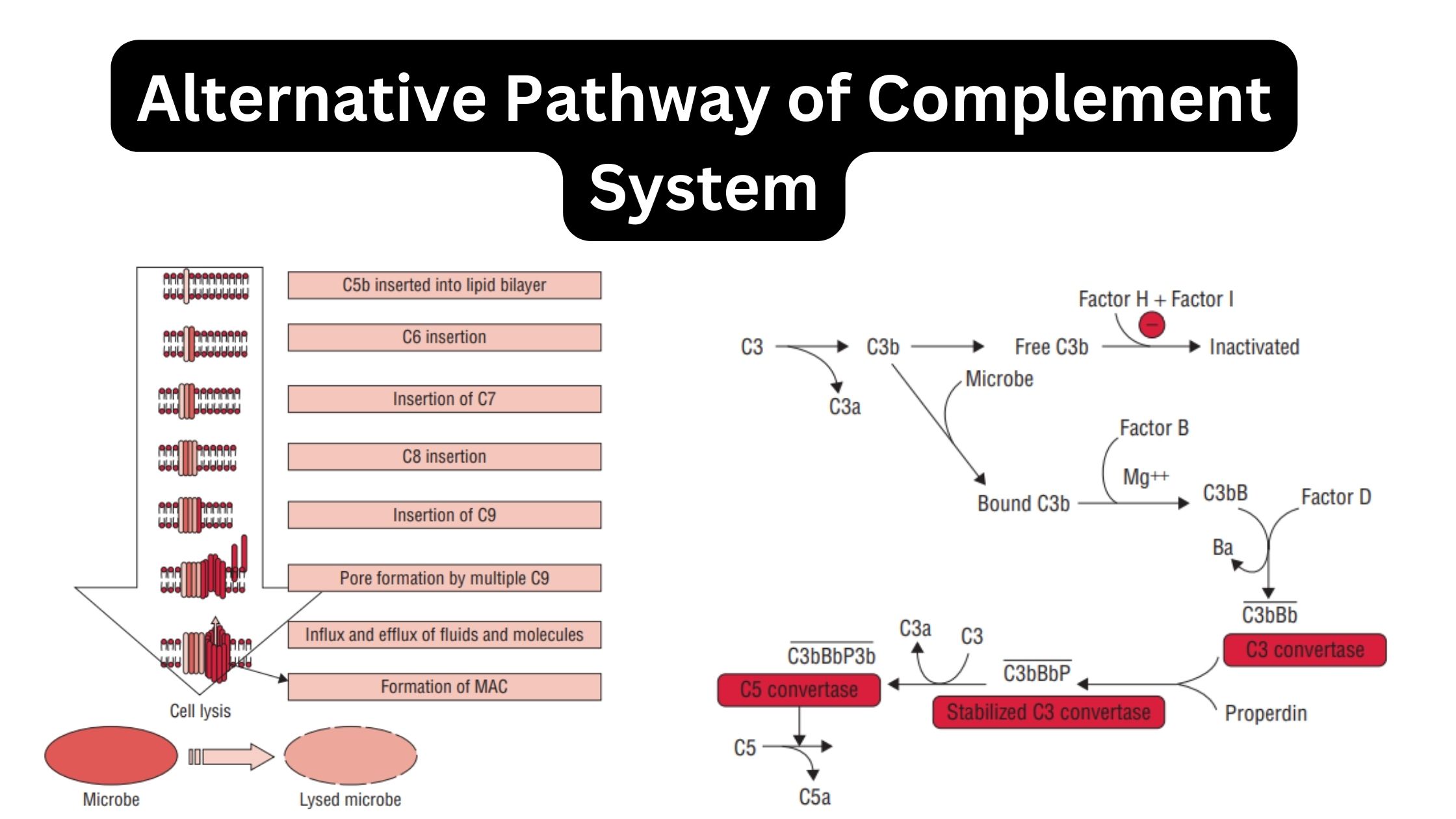
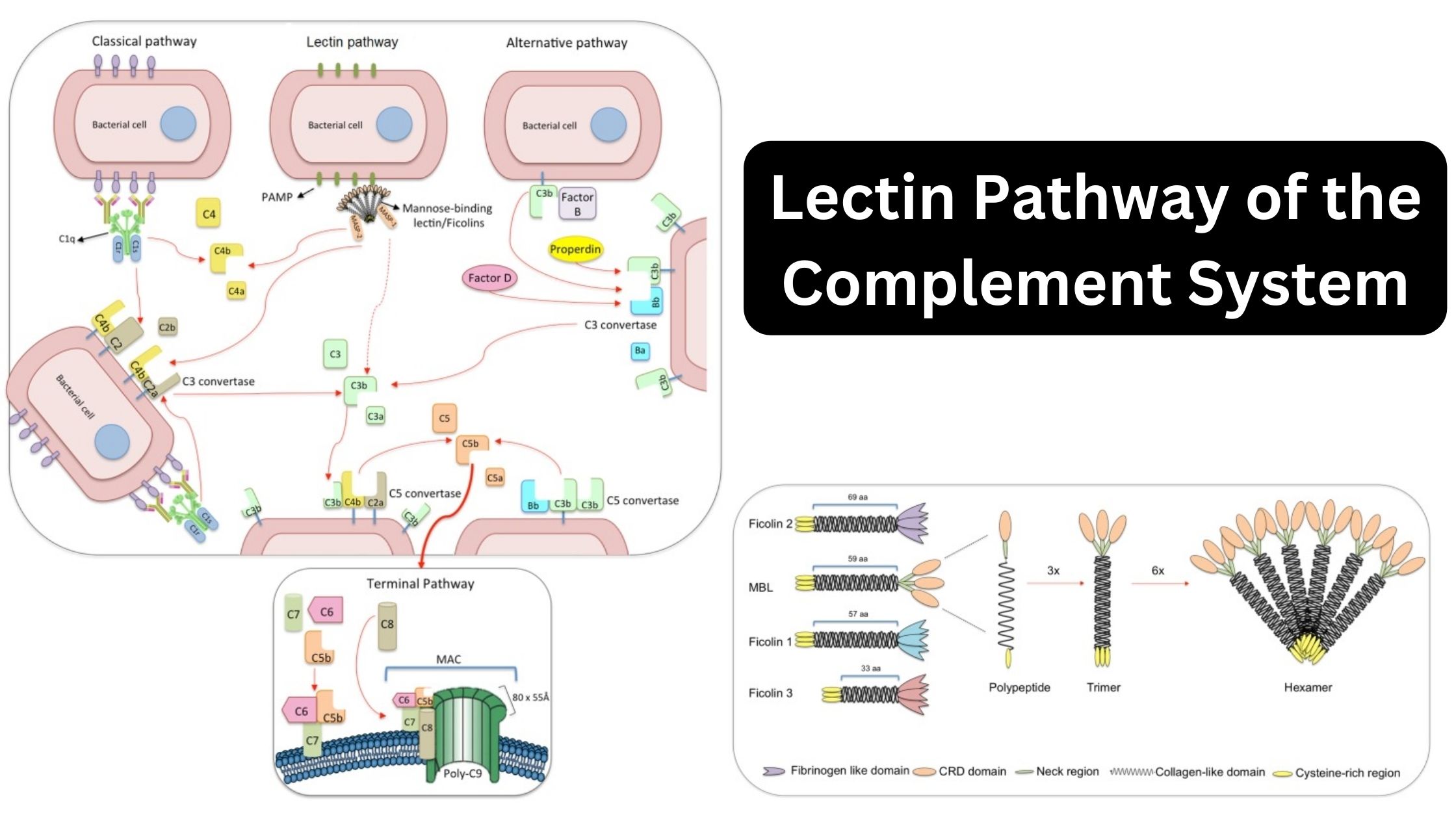
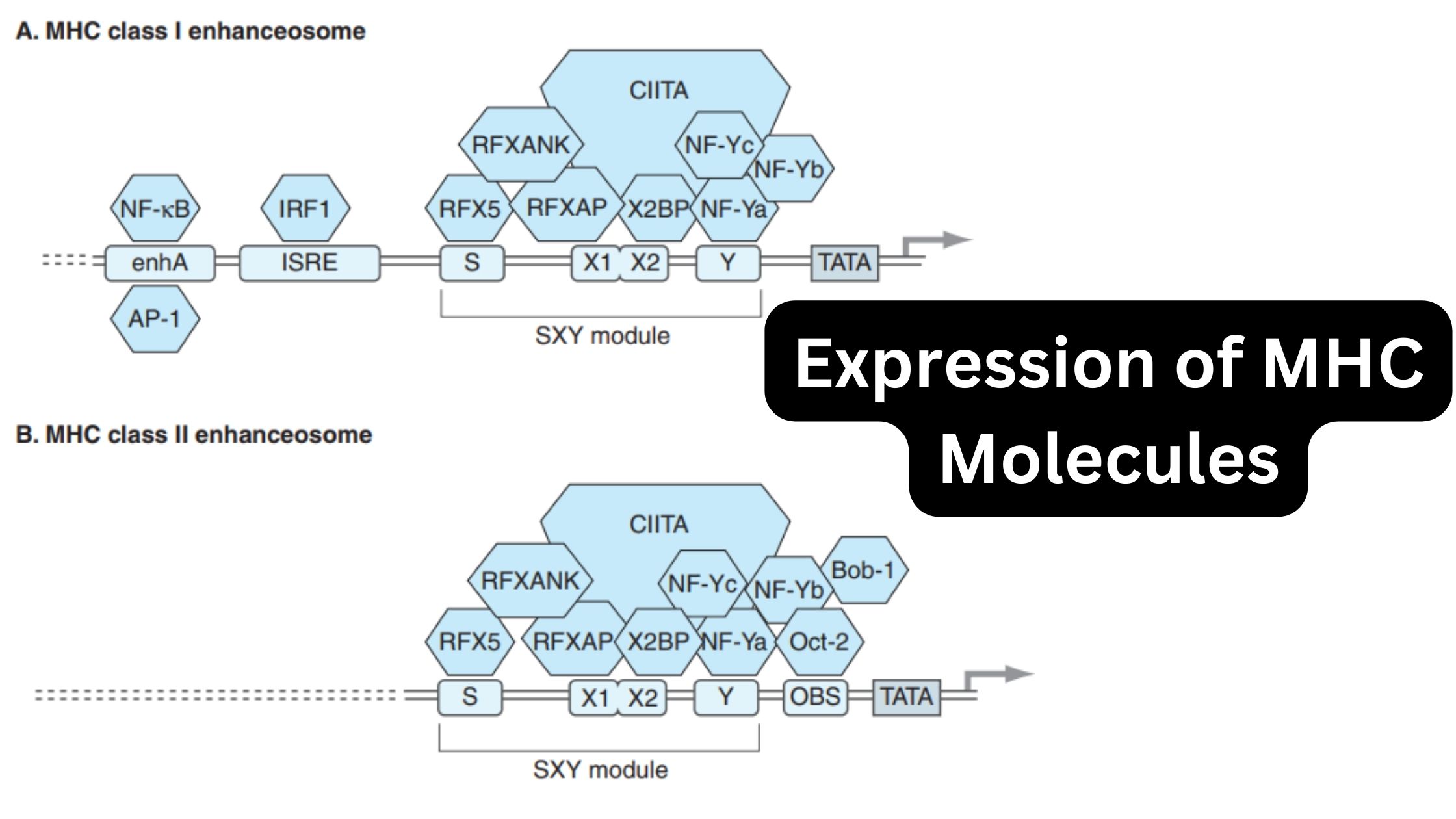
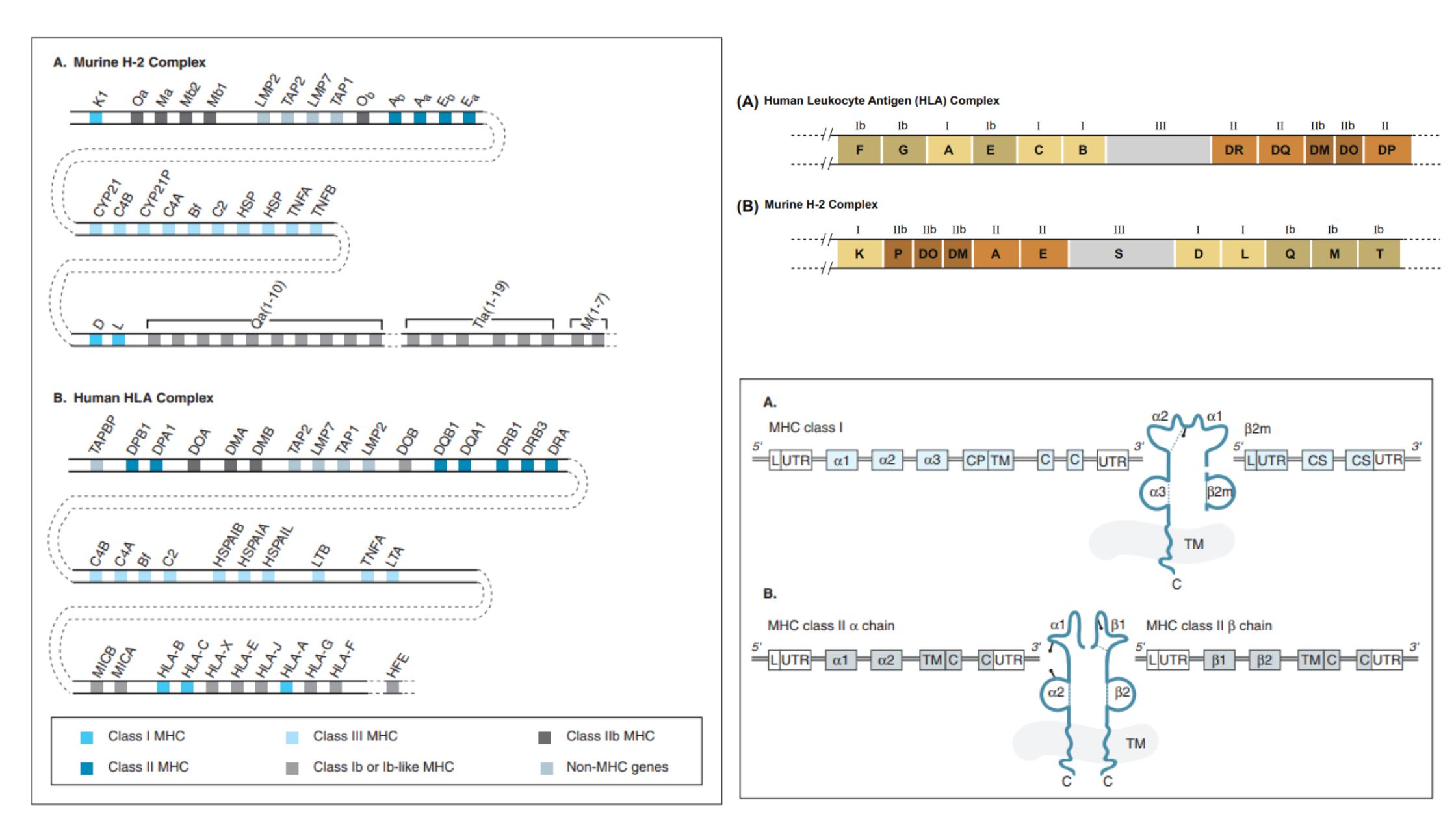
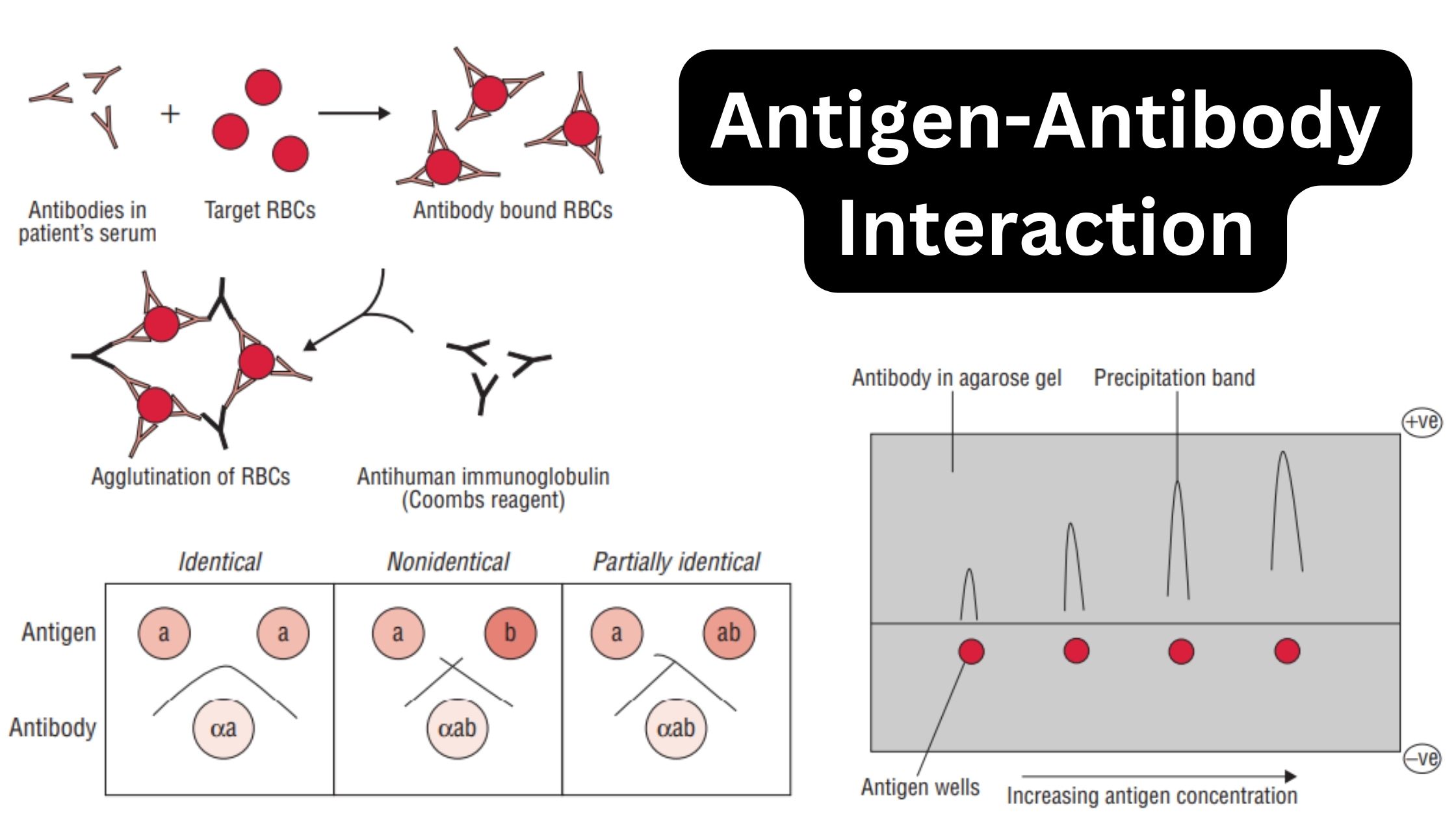
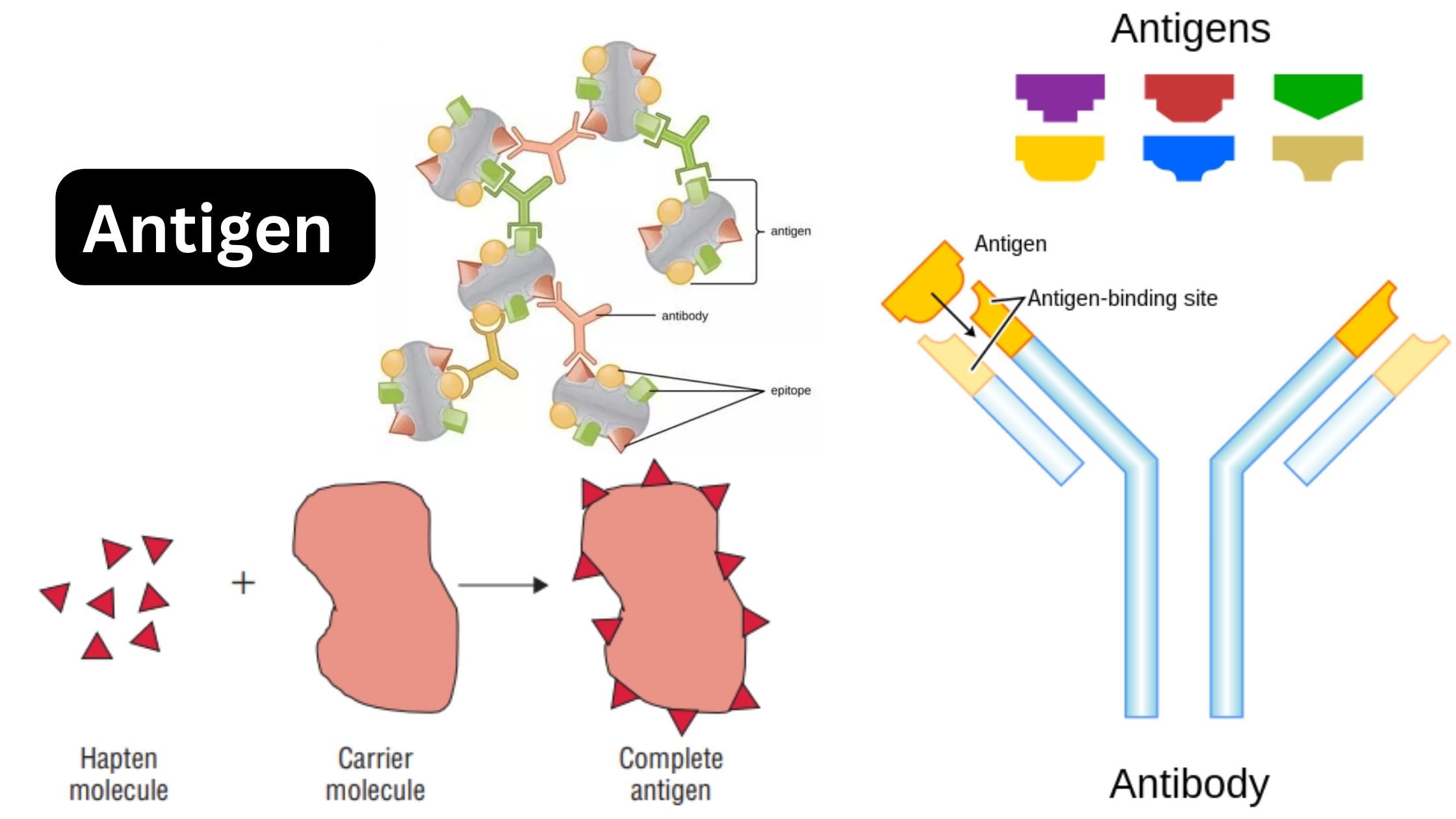
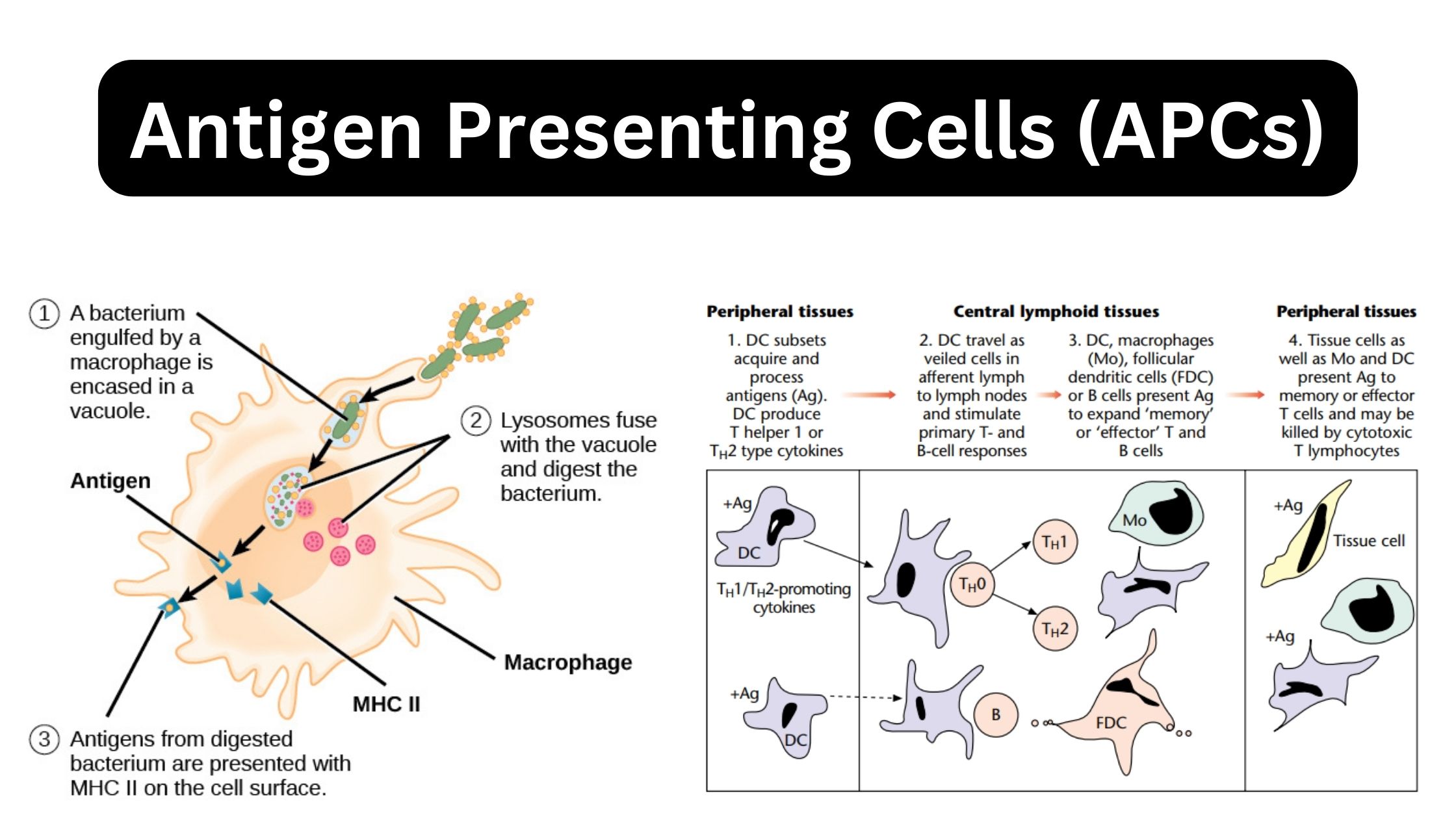
Biological Consequences of Complement Activation
The Membrane-Attack Complex Can Lyse a Broad Spectrum of Cells Cleavage Products of Complement Components Mediate Inflammation C3b and C4b Binding Facilitates Opsonization The Complement System Also Neutralizes Viral Infectivity The Complement System Clears Immune Complexes from Circulation Complement Deficiencies C1q, C1r, C1s, C4, and C2 Deficiencies C3 deficiencies Homozygous deficiencies Congenital deficiencies The majority … Read more