Pedigree Method – Procedure, Applications, Advantages, Disadvantages
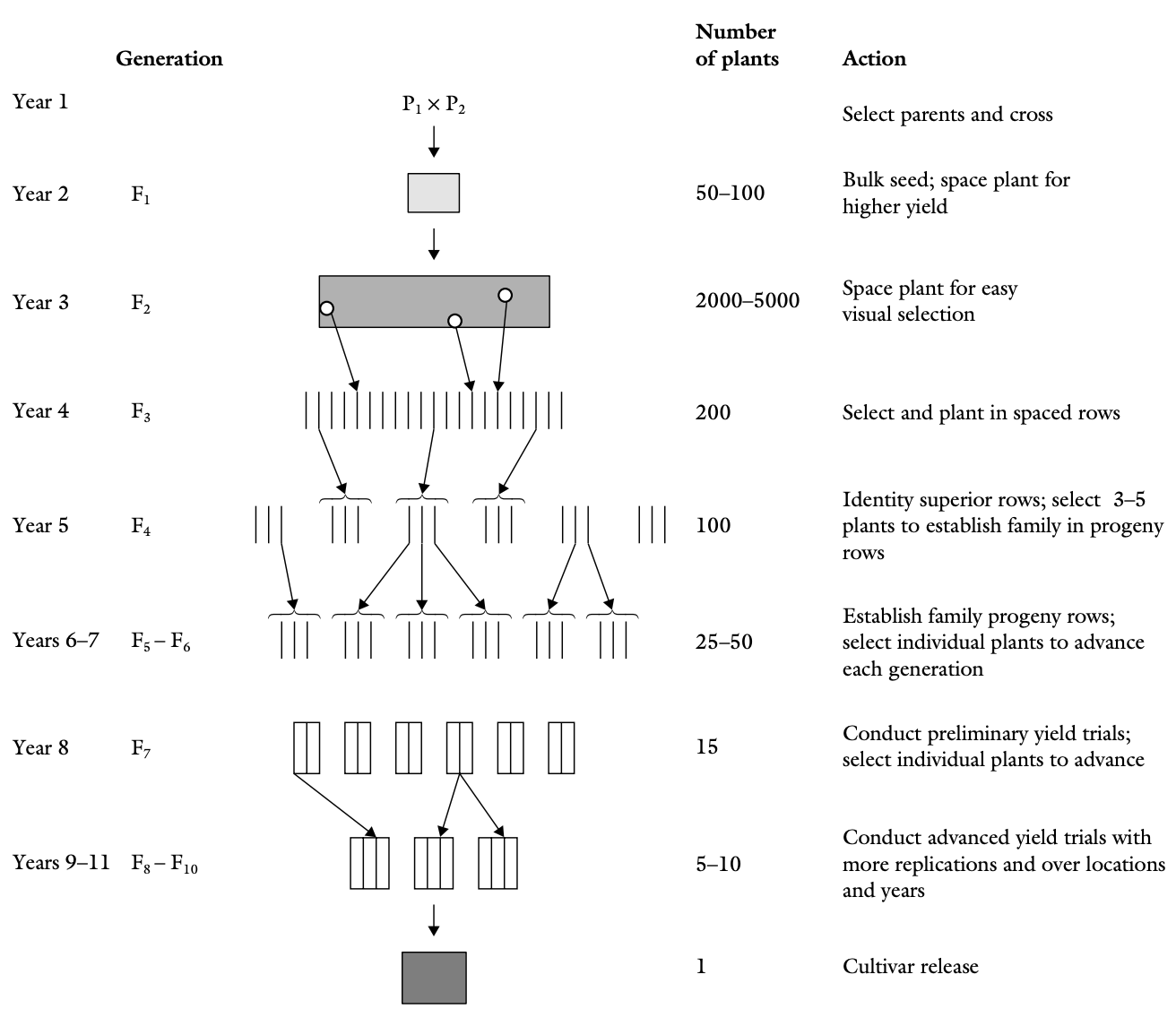
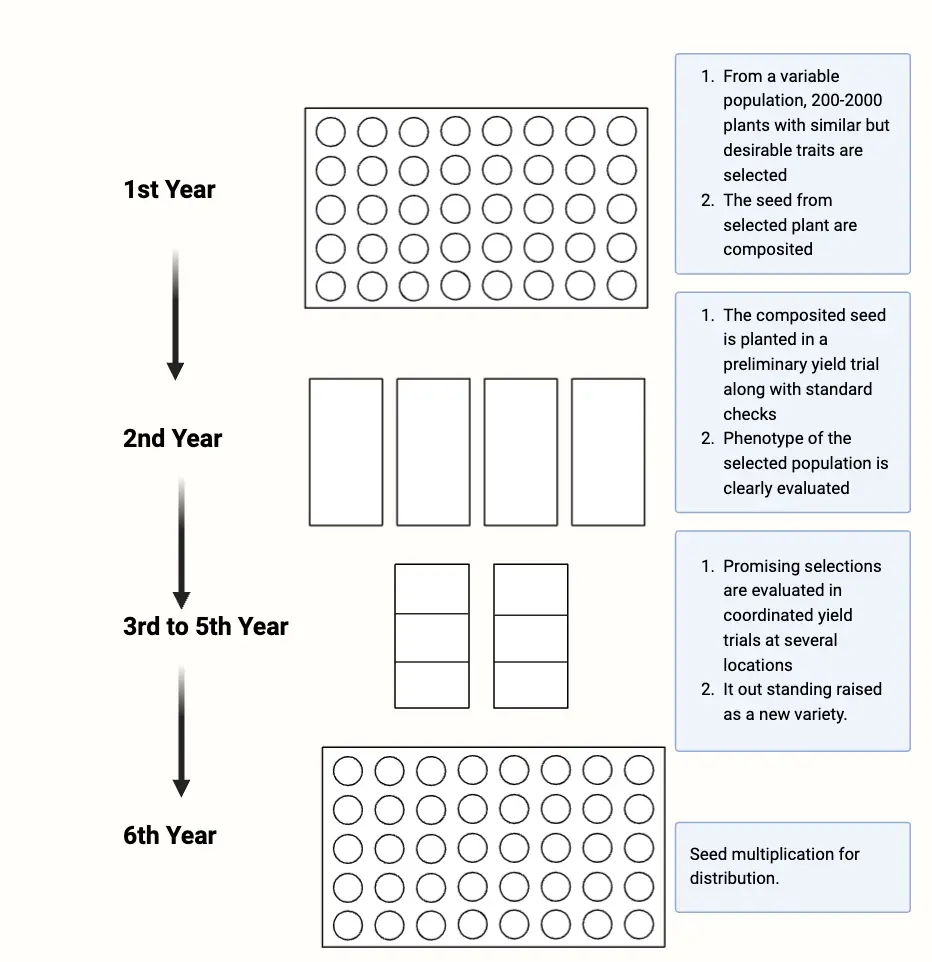
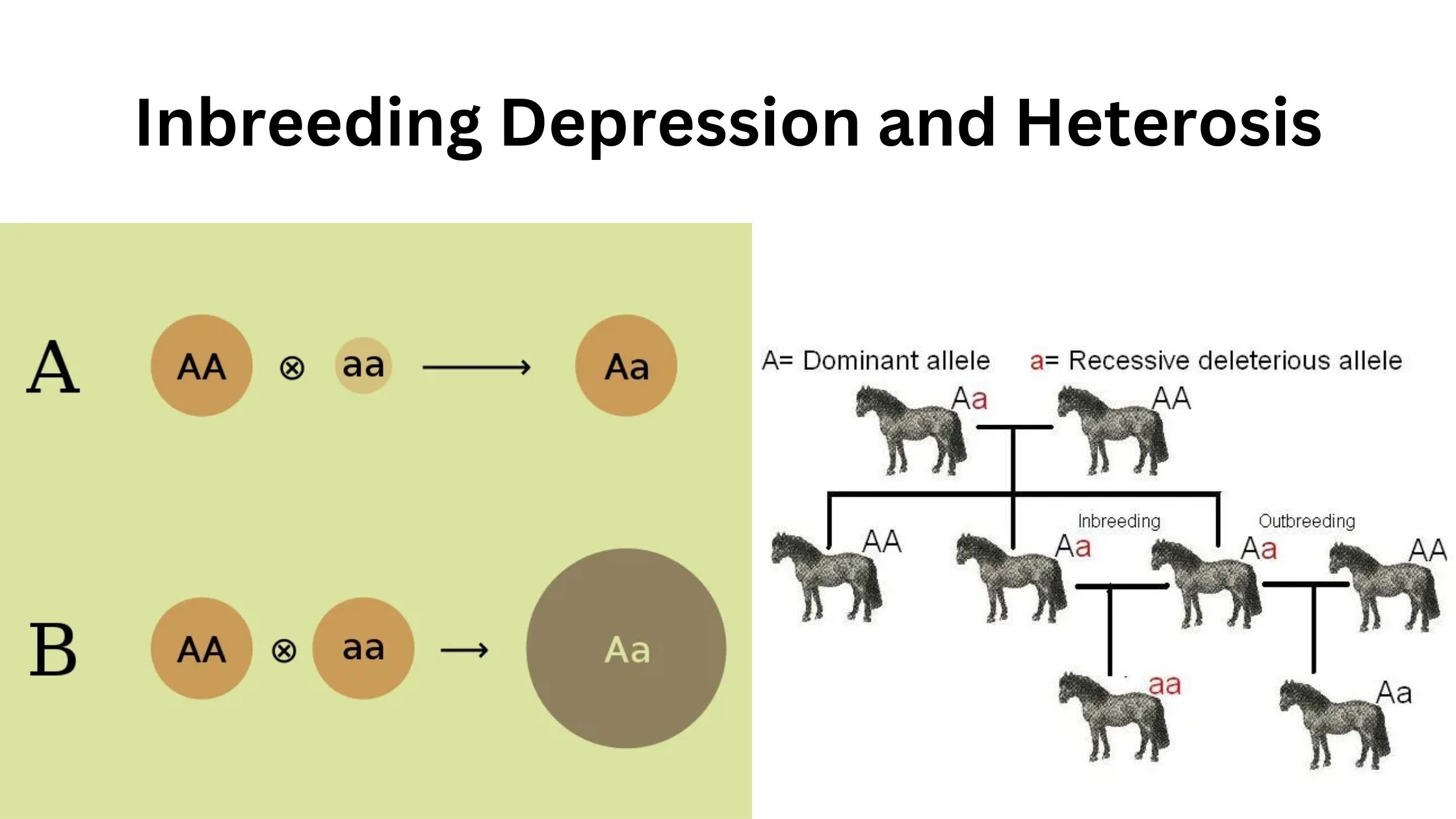
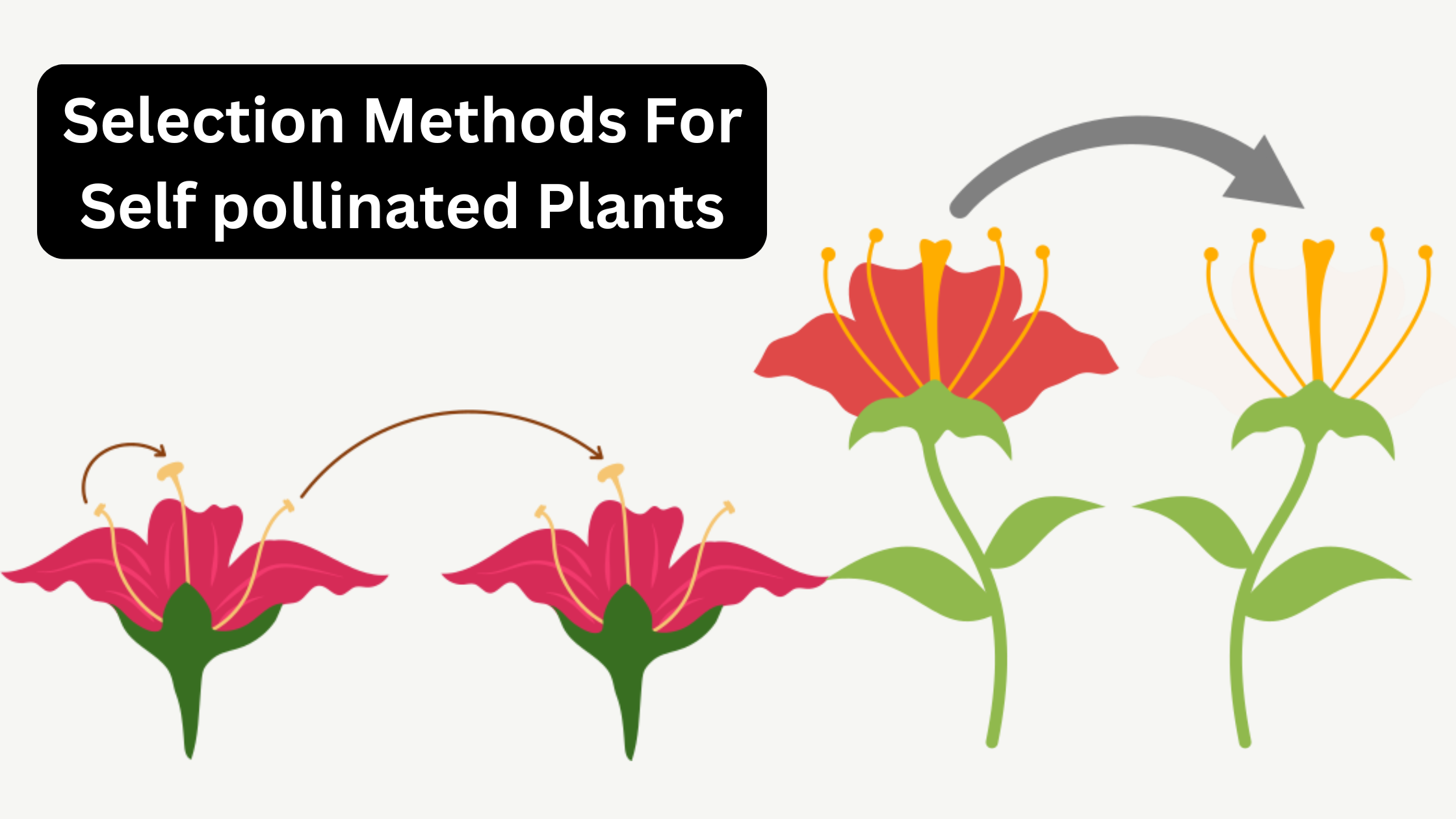
What is Pedigree Method? Definition of Pedigree Method The pedigree method is a plant breeding technique where individual plants from segregating generations are selected and documented through detailed pedigree records. This method aims to develop genetically uniform pureline varieties by maintaining and selecting plants until progenies exhibit no further genetic variation. Procedure for the Pedigree … Read more