Nelson-Somogyi method – Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
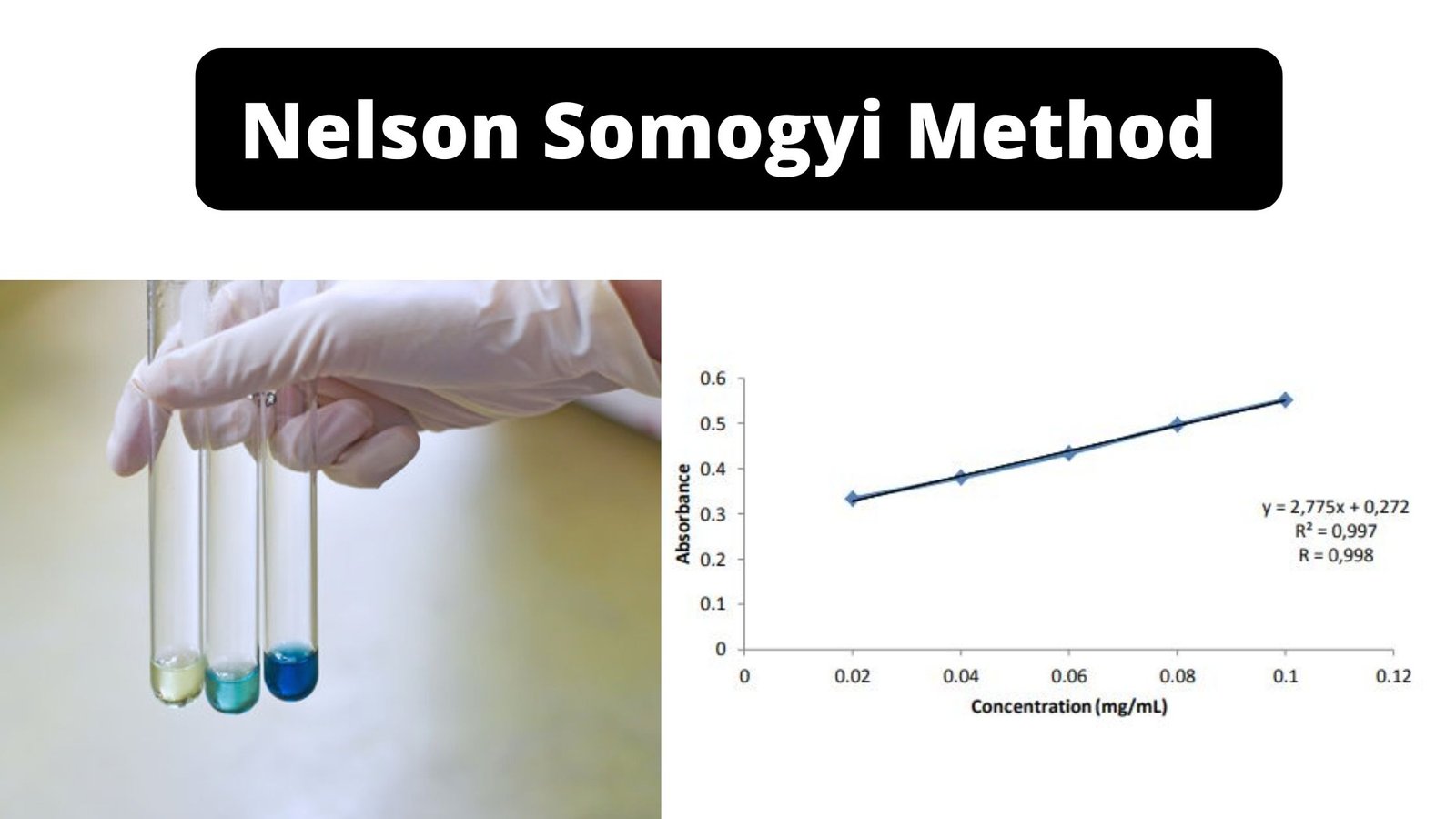
Nelson–Somogyi method is a classical colorimetric method used for the quantitative determination of reducing sugars such as glucose and fructose. It is a highly sensitive method and is commonly used in biochemical and carbohydrate analysis. It is considered as a standard method because the estimation is based on stoichiometric reduction reaction and gives accurate measurement … Read more