Bombardment (Biolistics) Method for Plant Cells – Principle, Requirement, Protocol
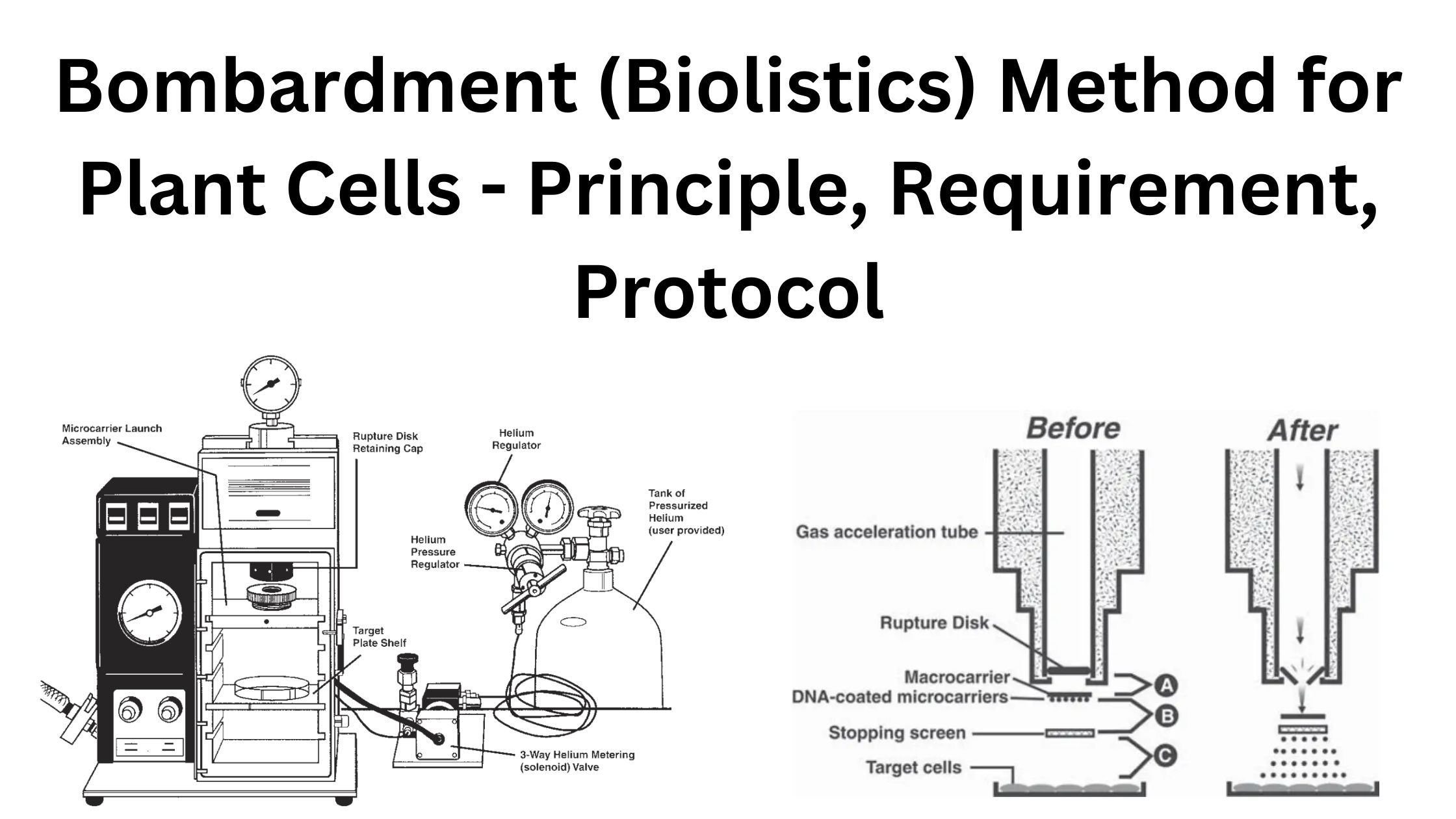
What is Bombardment (Biolistics) Method? Bombardment (Biolistics) method is a direct physical technique used to introduce foreign DNA into living cells. It is also referred to as the gene gun method. In this process, the desired DNA is first coated on very small and dense metal particles such as gold or tungsten. These DNA coated … Read more