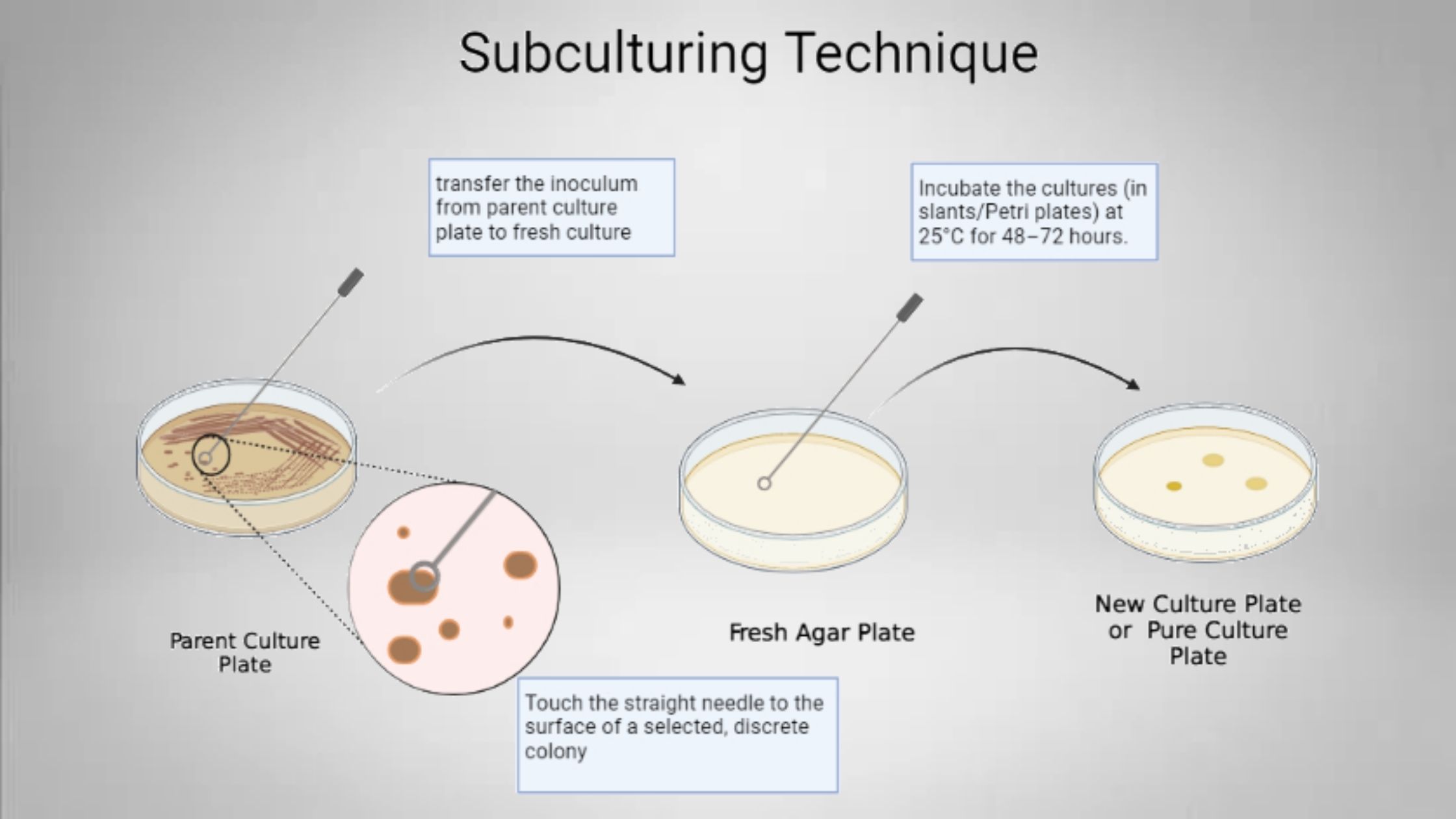
Subculturing Technique In Agar Slant/Agar Plate
Overview of Subculturing Technique In microbiology, subculture is defined as a new cell or microbiological culture, which is prepared by transferring a few or all cells to a fresh growth medium from an old culture or a previous culture. In a single word, the transfer of cells from a previous culture to a fresh or … Read more