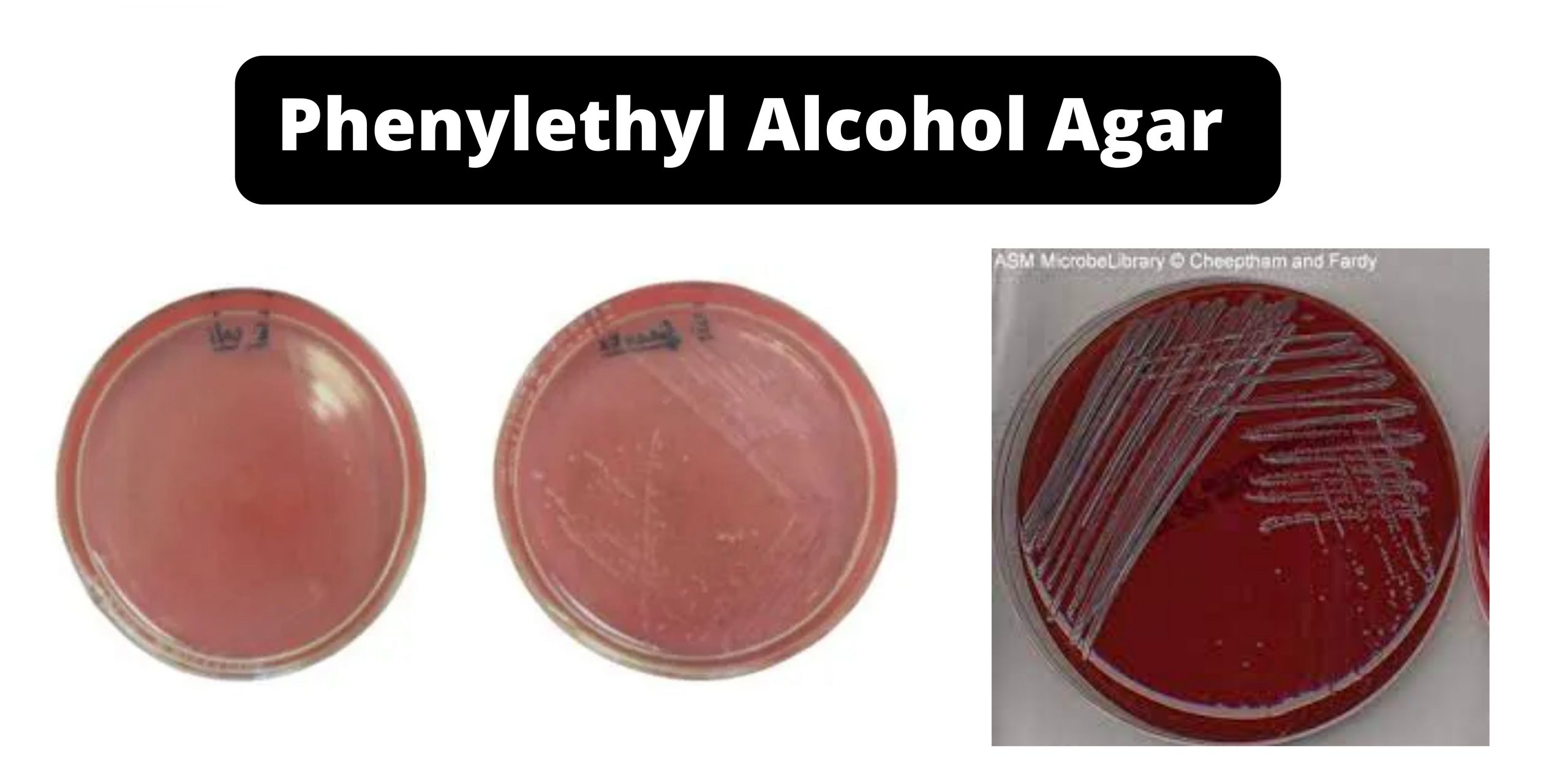
Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar – Composition, Preparation, Uses, Limitation
A selective medium called phenylethyl alcohol (PEA), is used to cultivate Gram positive organisms, especially cocci, in a sample containing pathogens. Phenylethyl alcohol is the active ingredient that inhibits or significantly reduces growth of Gram-negative organisms.