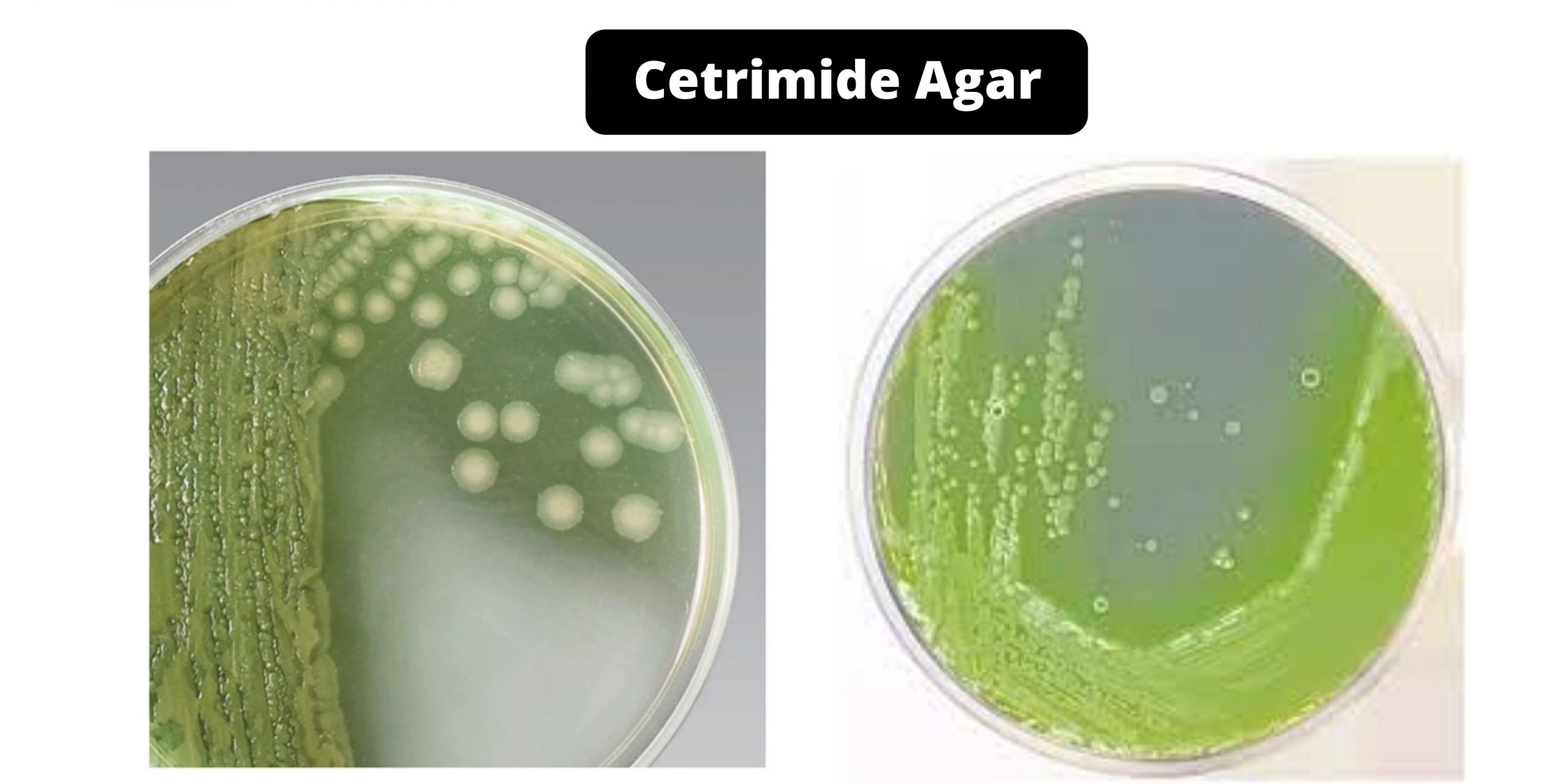
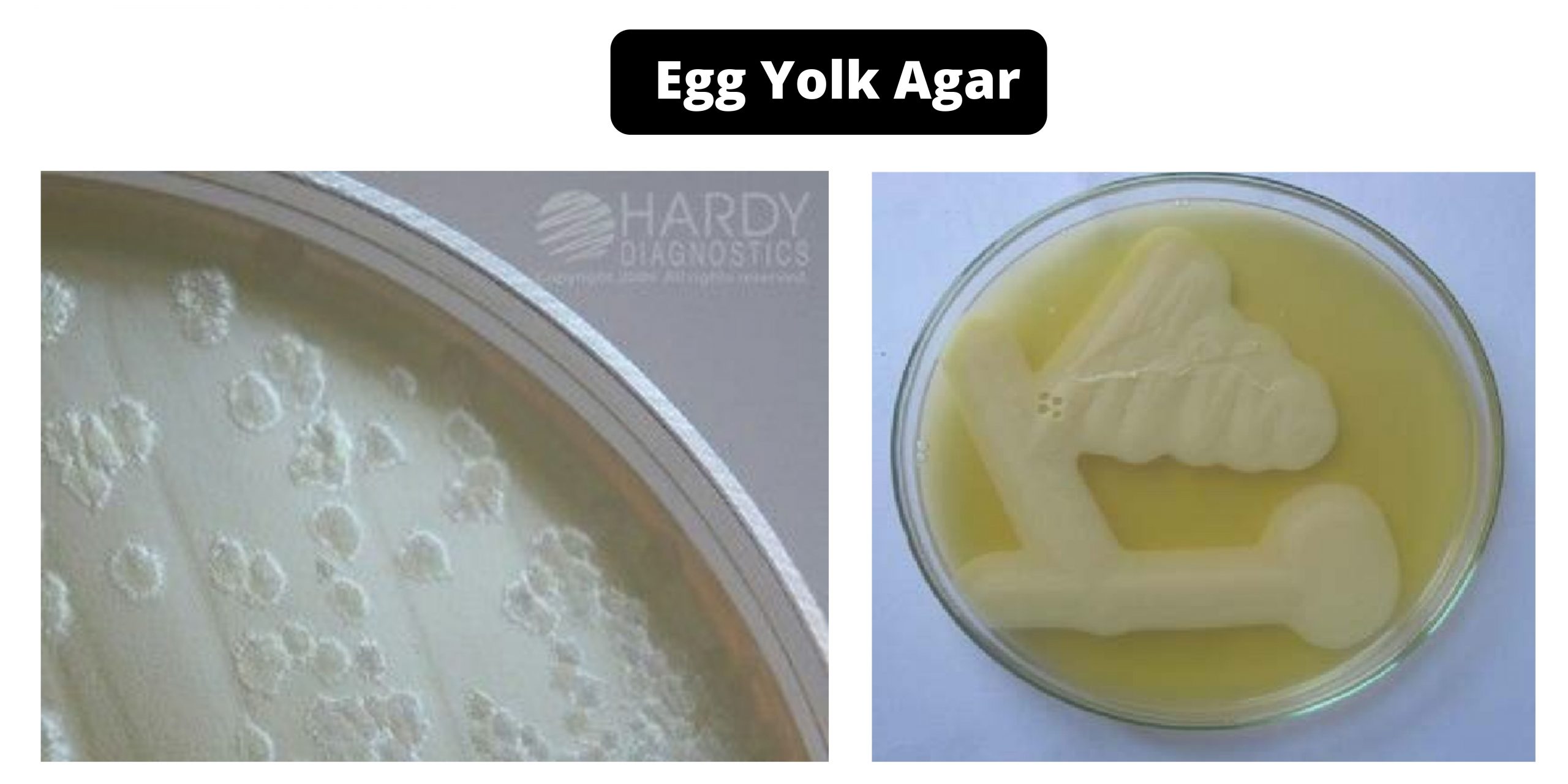
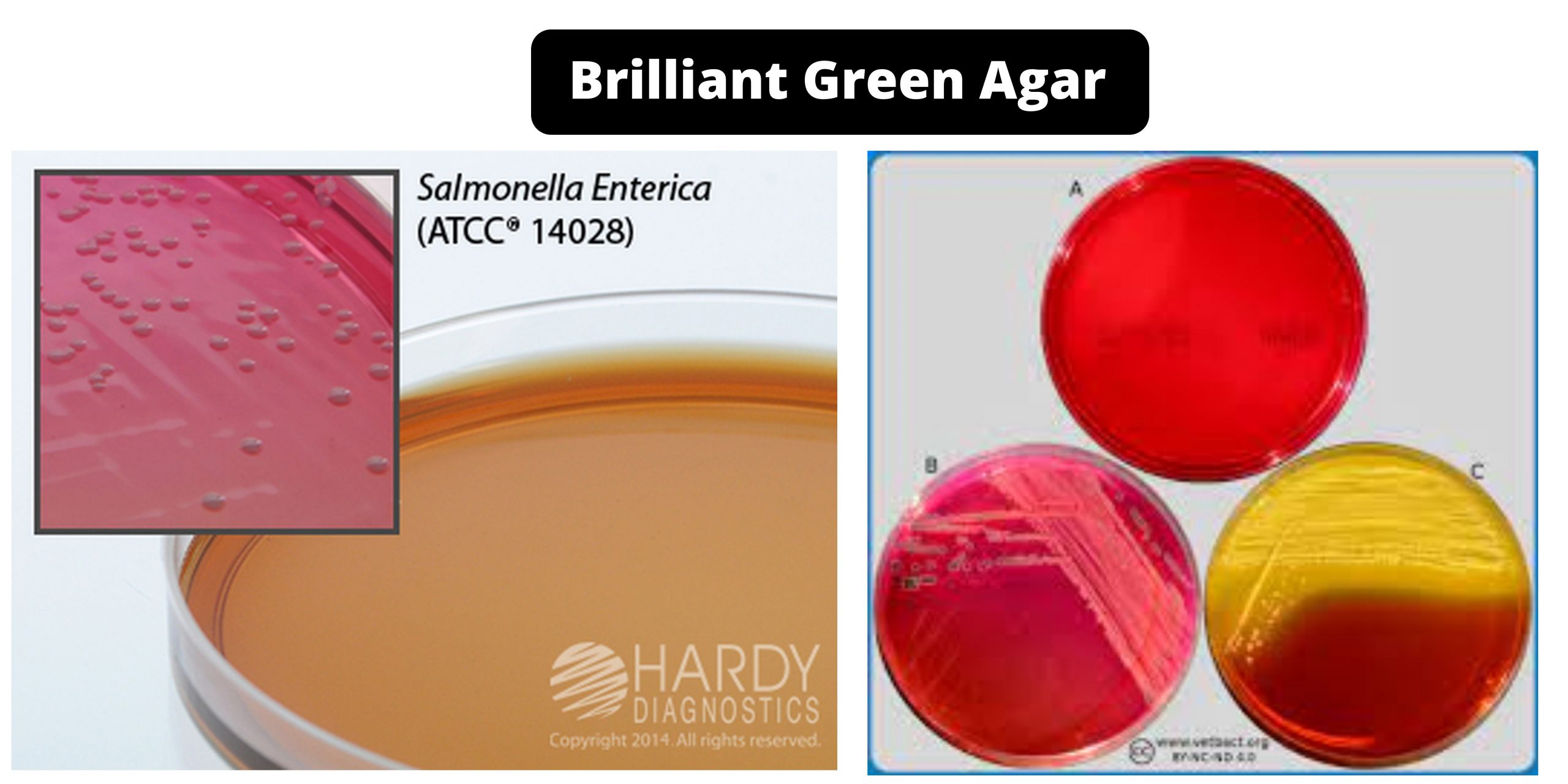
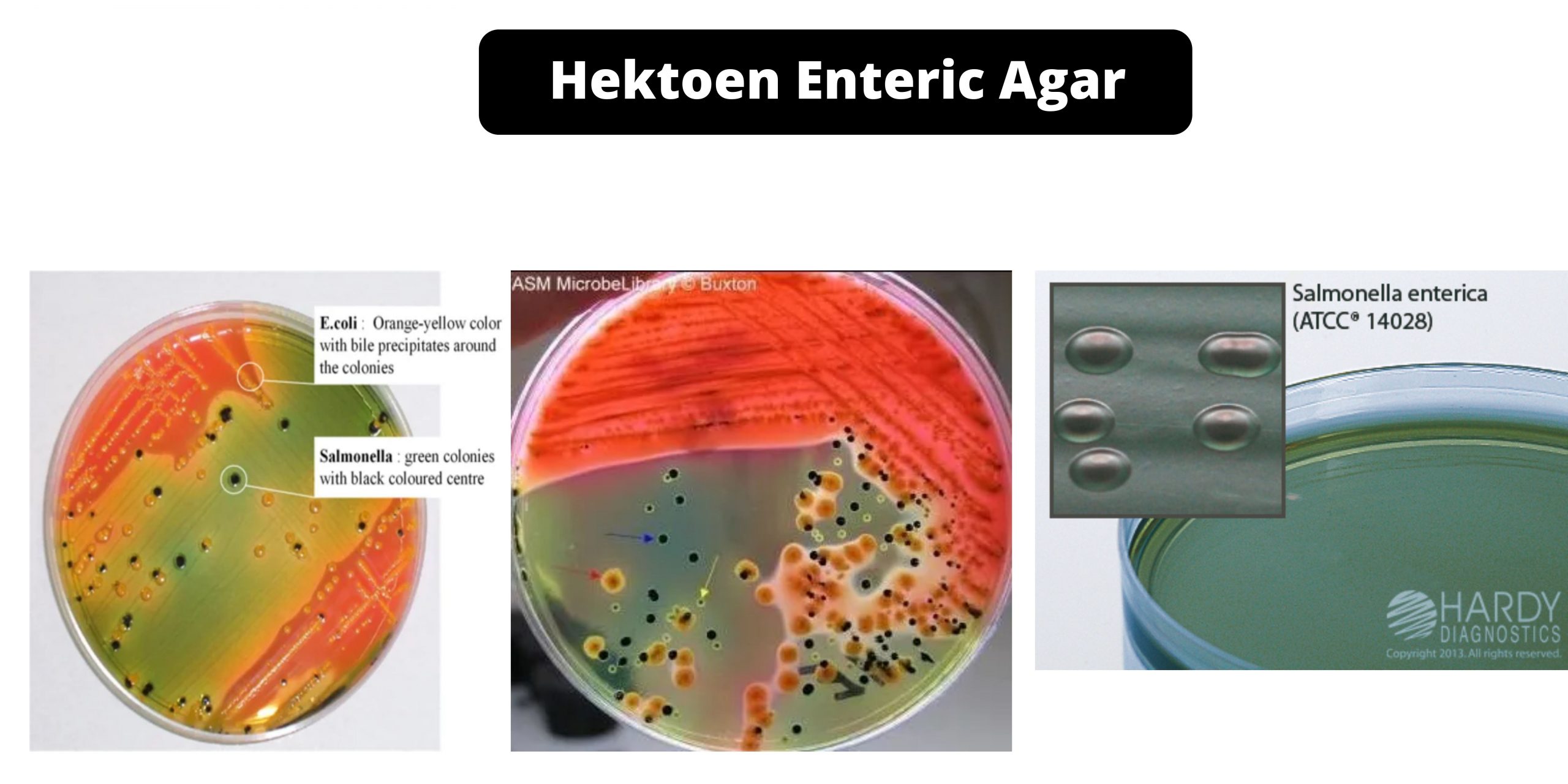
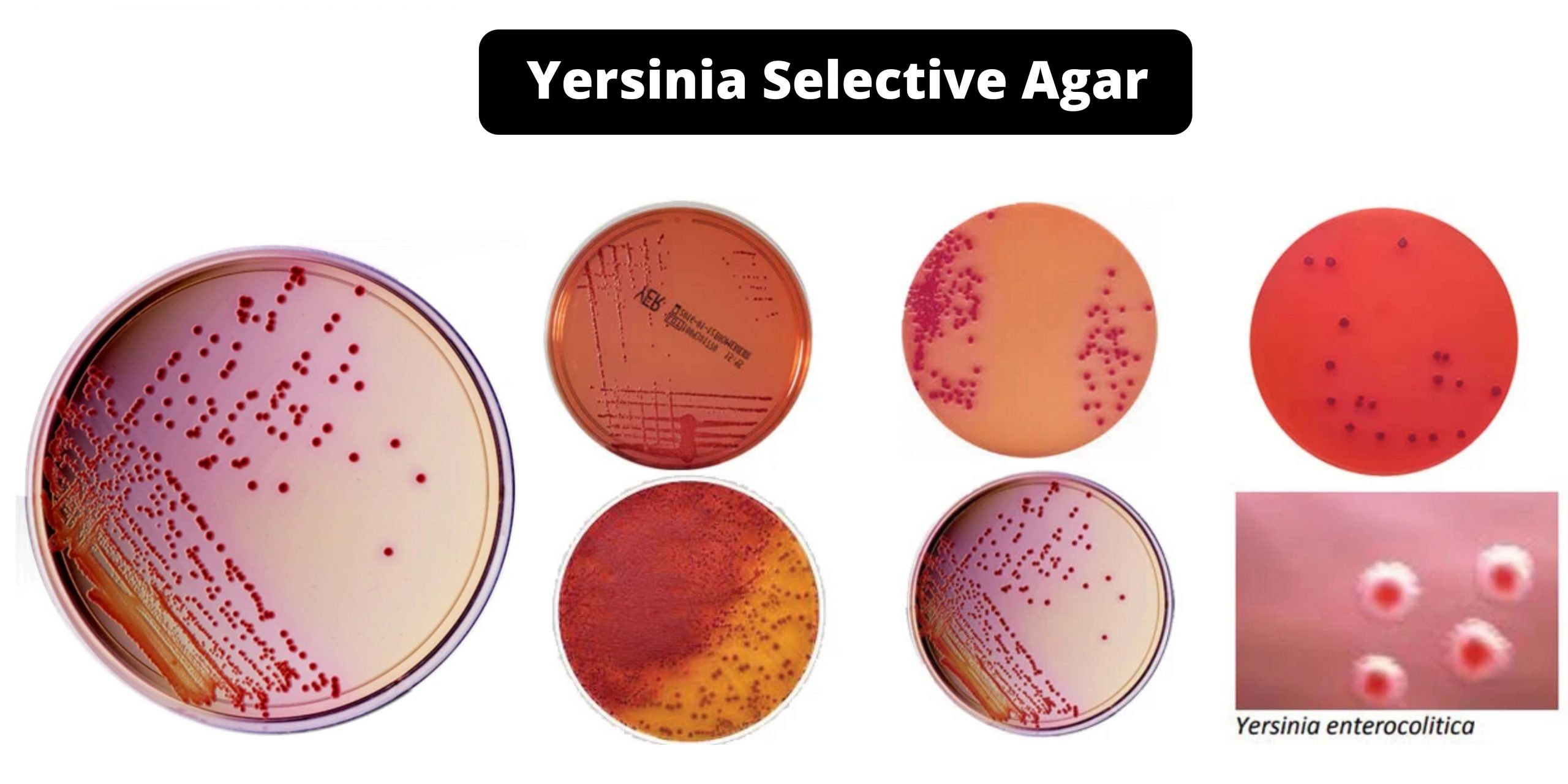
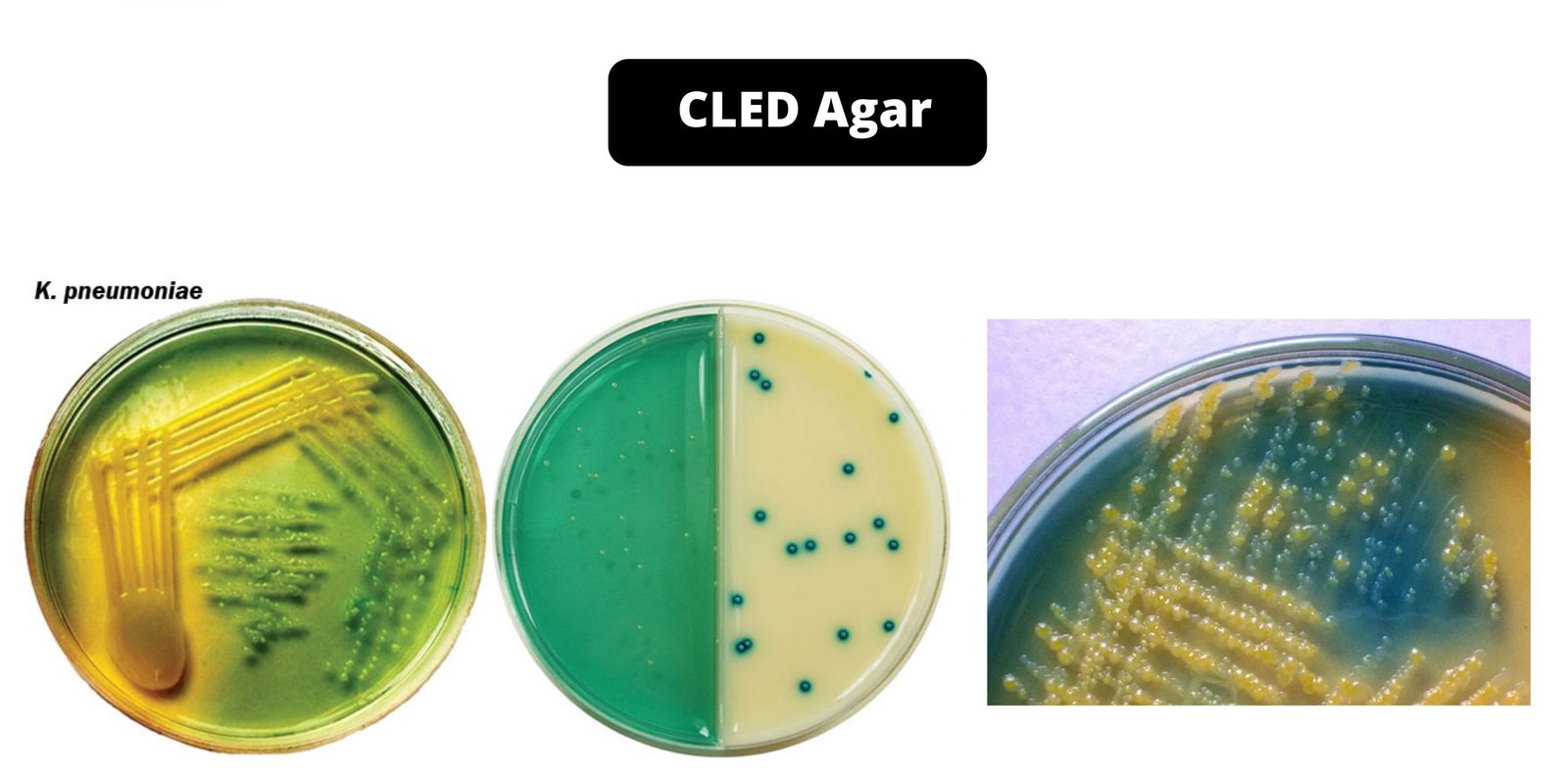
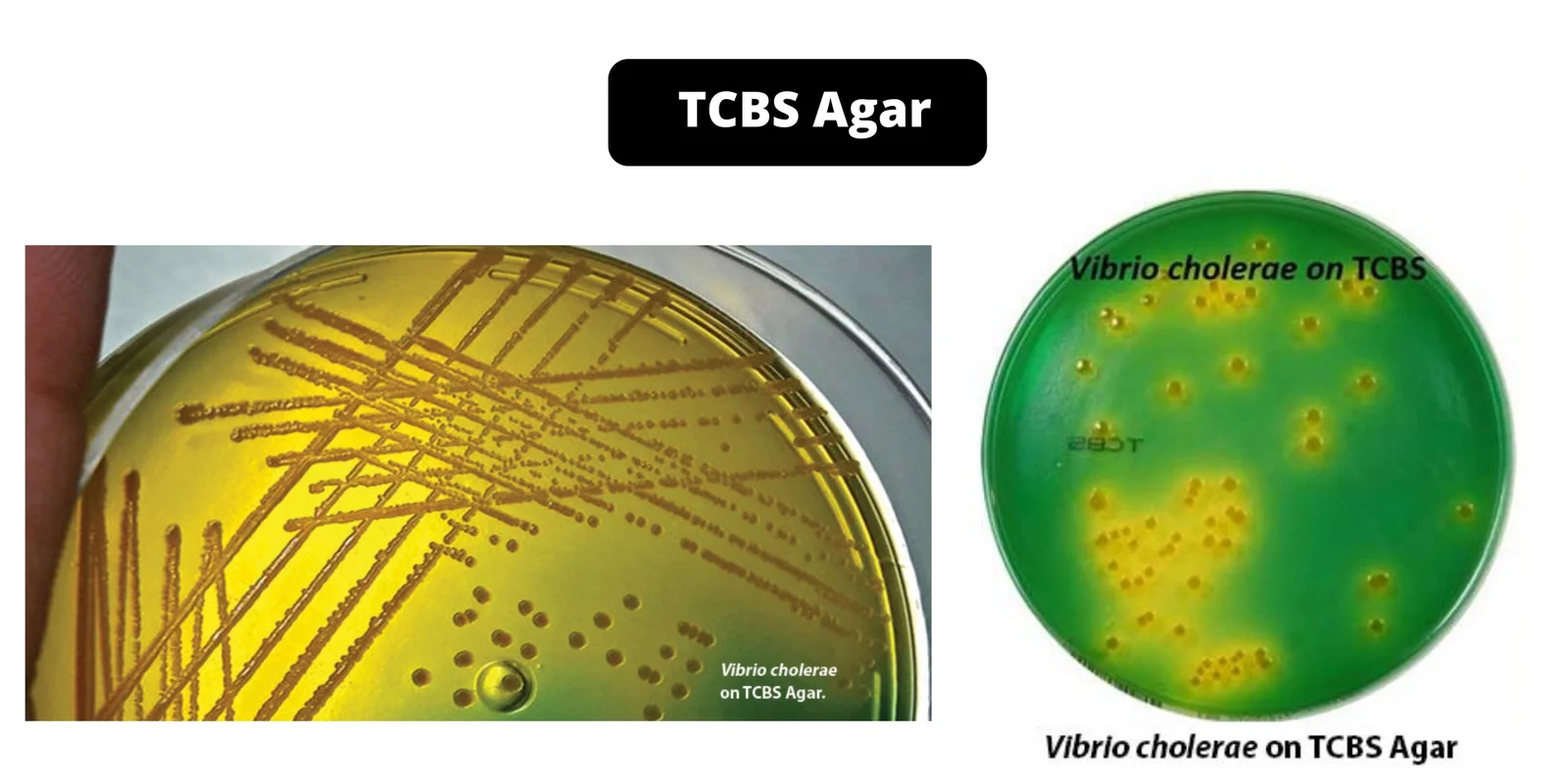
Cetrimide Agar – Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
Cetrimide, a quaternary salt of ammonium, acts as a detergent that lowers the surface tension at the point-of-contact. It also has precipitant, complexing, and denaturing effects upon bacterial membrane proteins. It has inhibitory properties on many microorganisms, including Pseudomonas species that are not Pseudomonas. Lowburry was the first to develop cetrimide agar. It is a modified version of Tech Agar (developed in King et al. For the selective inhibition other than Pseudomonas, aeruginosa, 0.1% cetrimide (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide), was added. Cetrimide agar can be used to presumptive identify and selectively isolate Pseudomonas.aeruginosa species from both clinical and nonclinical specimens.