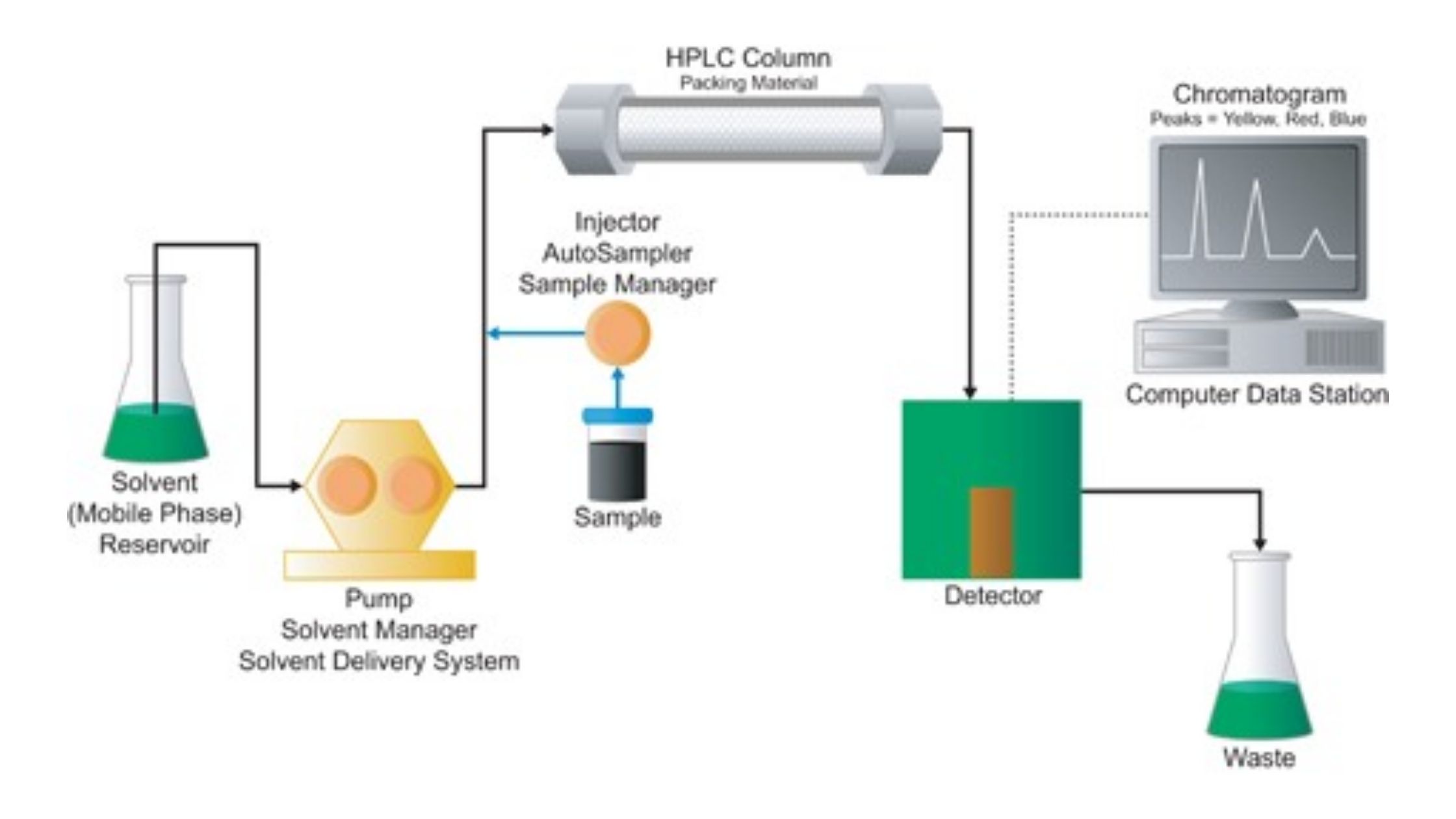
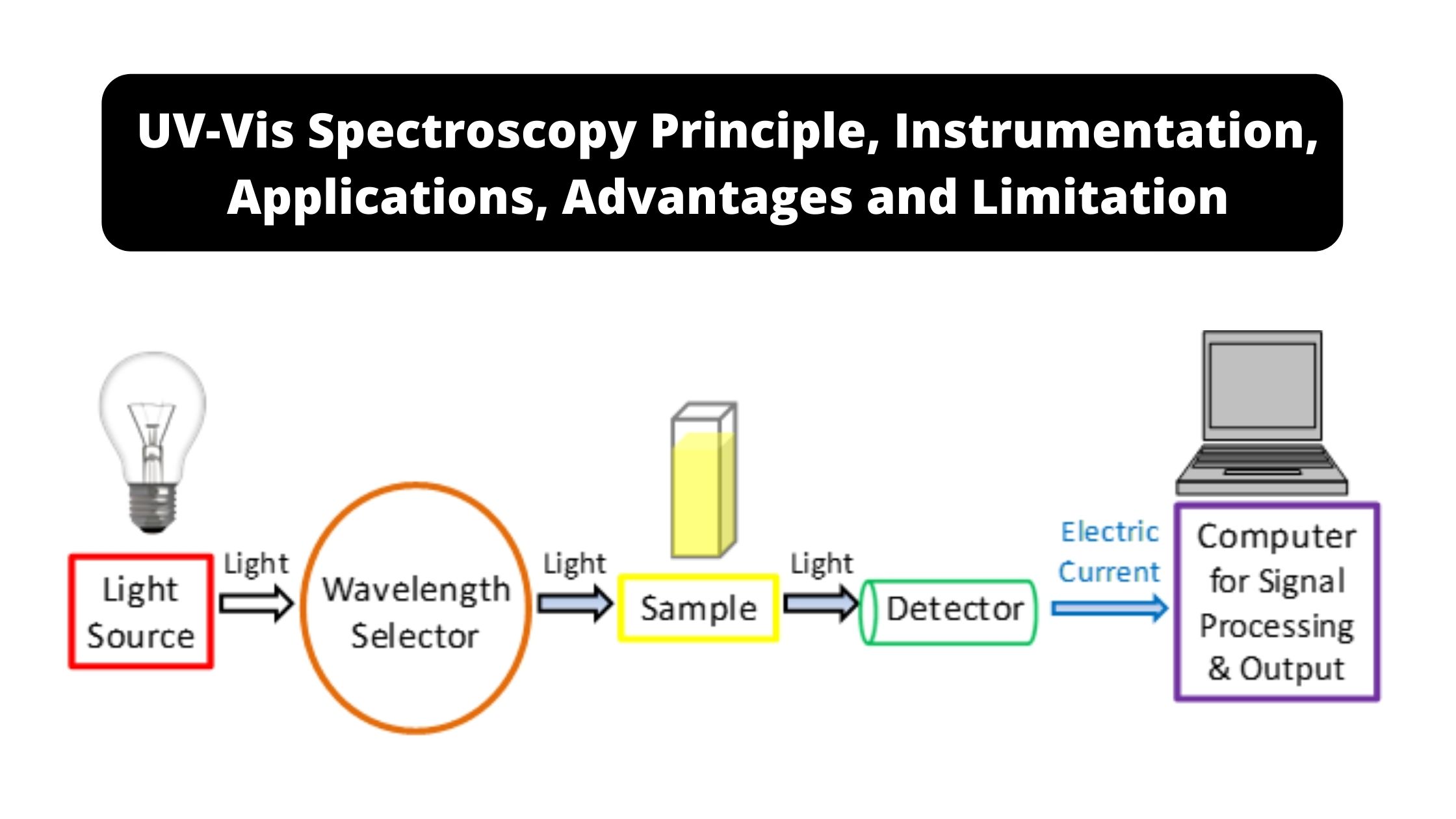
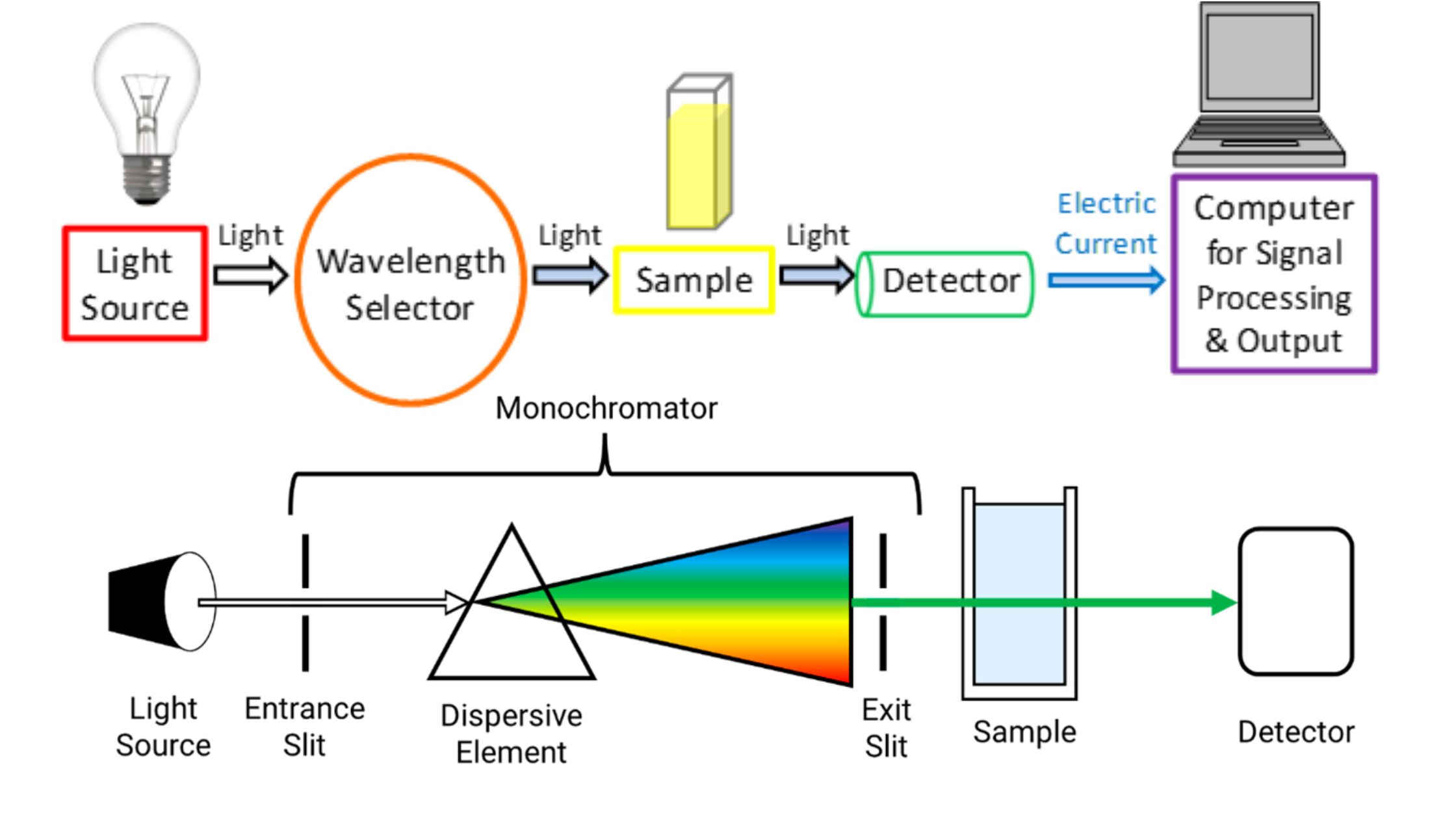
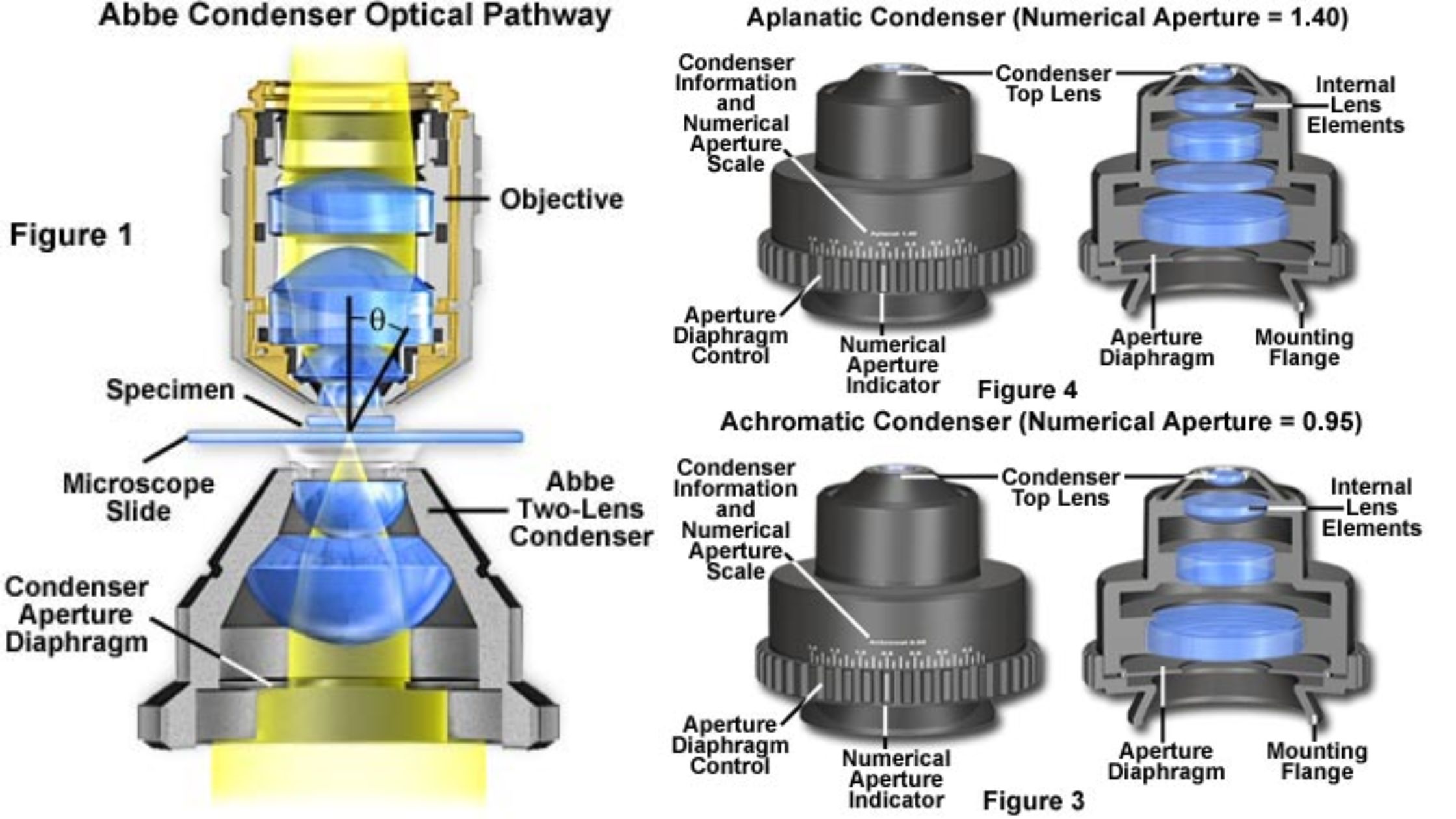
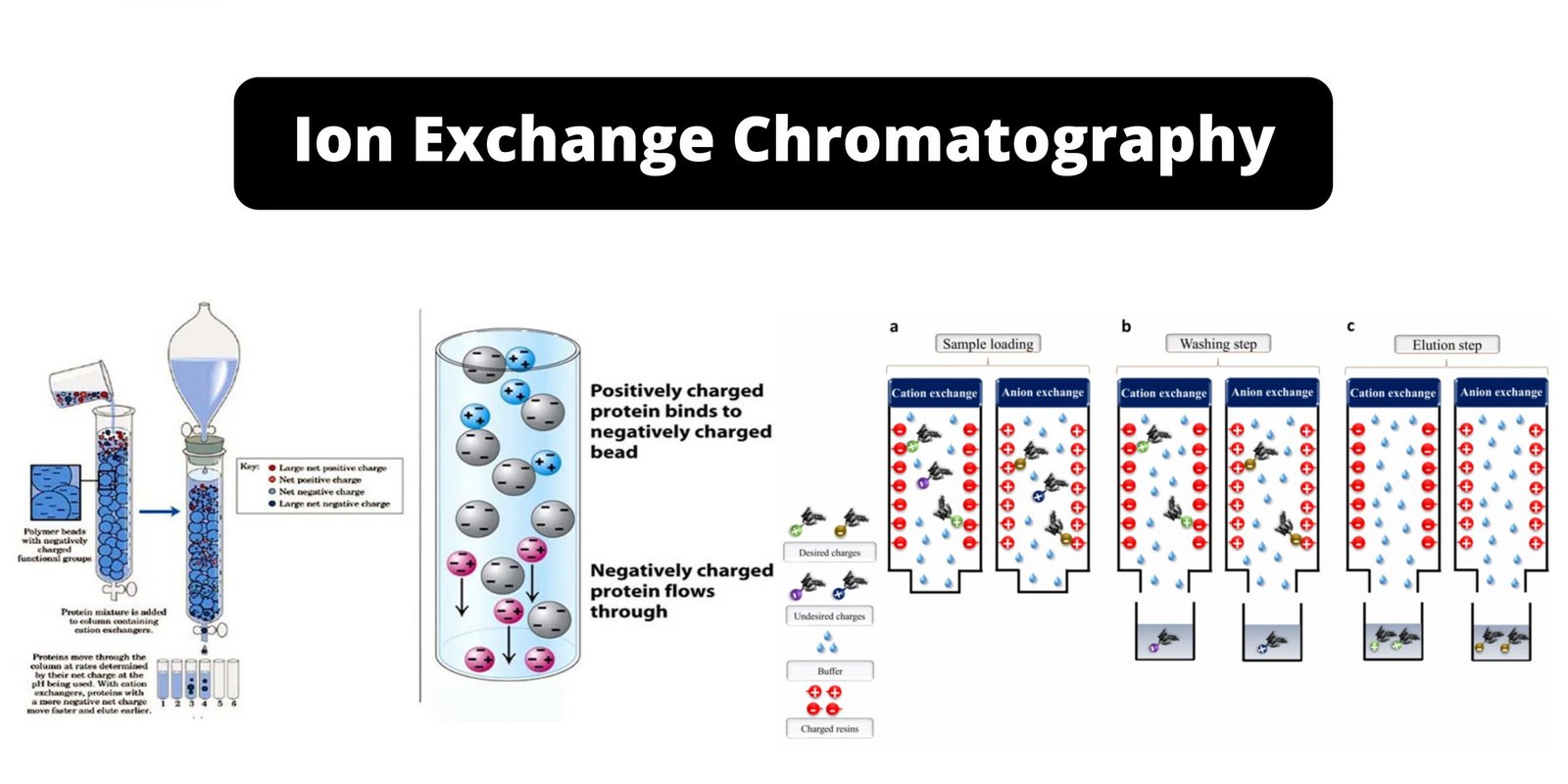
PH Meter – Principle, Parts, Types, Procedure, Calibration, Application, Examples
What is pH Meter? A pH meter is a critical instrument used for measuring the acidity or alkalinity of aqueous solutions, quantified in terms of pH. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, where a value of 7 denotes neutrality, values below 7 indicate acidity, and values above 7 denote alkalinity. This scale reflects … Read more