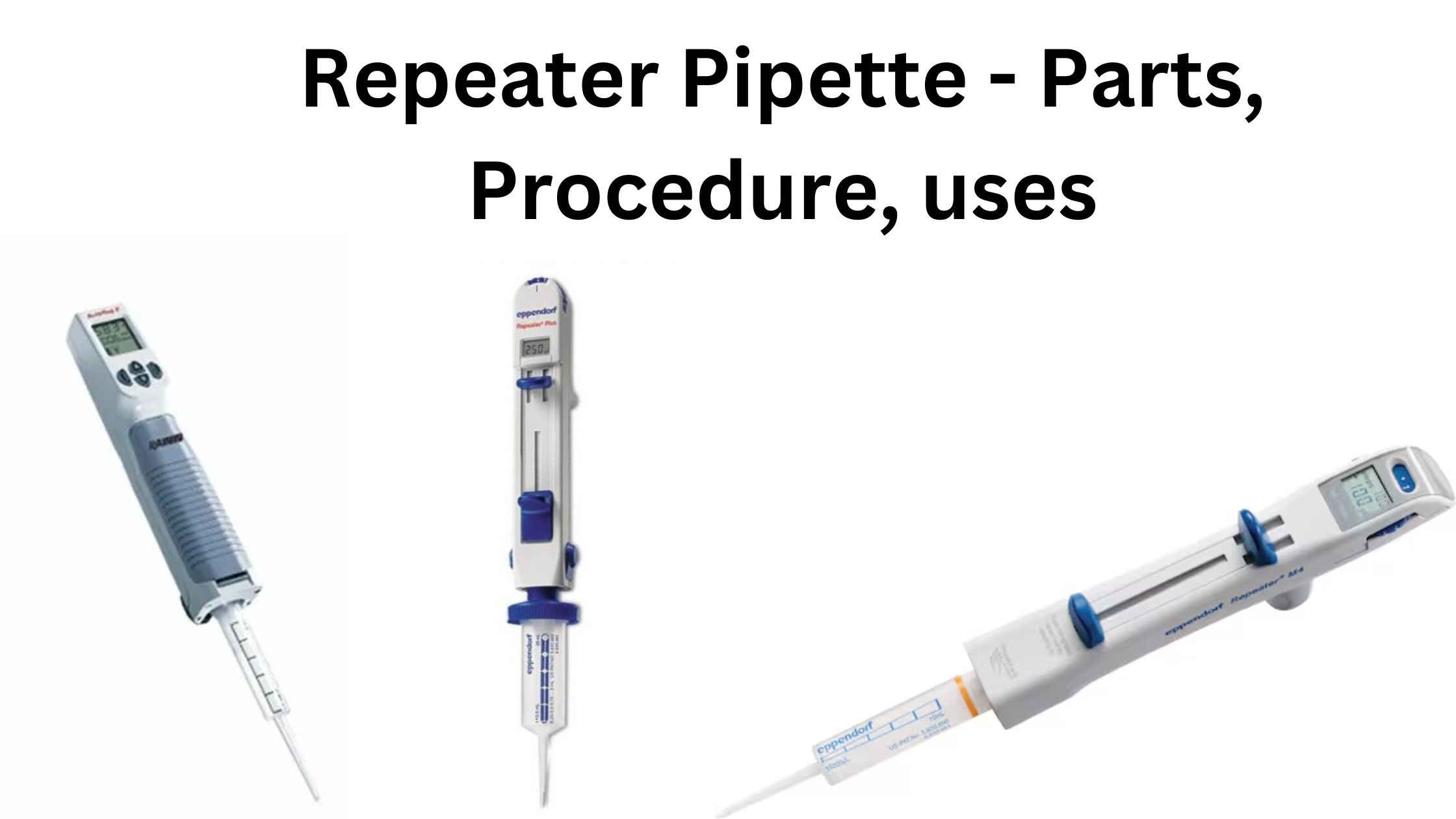
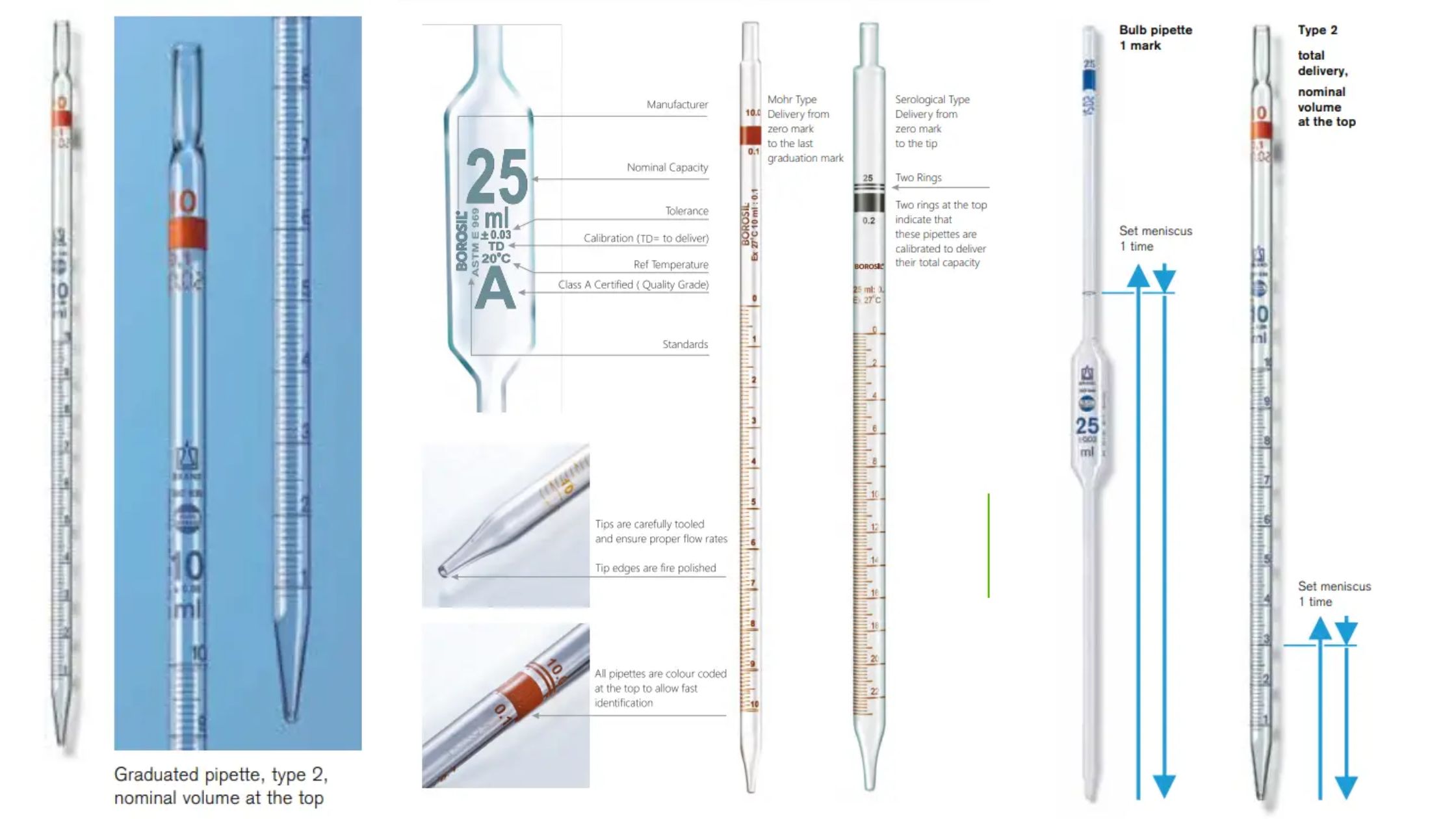
Repeater Pipette – Parts, Procedure, uses
What is Repeater Pipette? How Repeater Pipettes Work Repeater pipettes enable the precise and repetitive dispensing of liquid in equal volumes. They improve efficiency by eliminating the need for repeated aspiration. Here’s a breakdown of their operation: Mechanism of Action Parts of Repeater Pipettes Repeater pipettes are designed for precise and efficient liquid dispensing. They … Read more