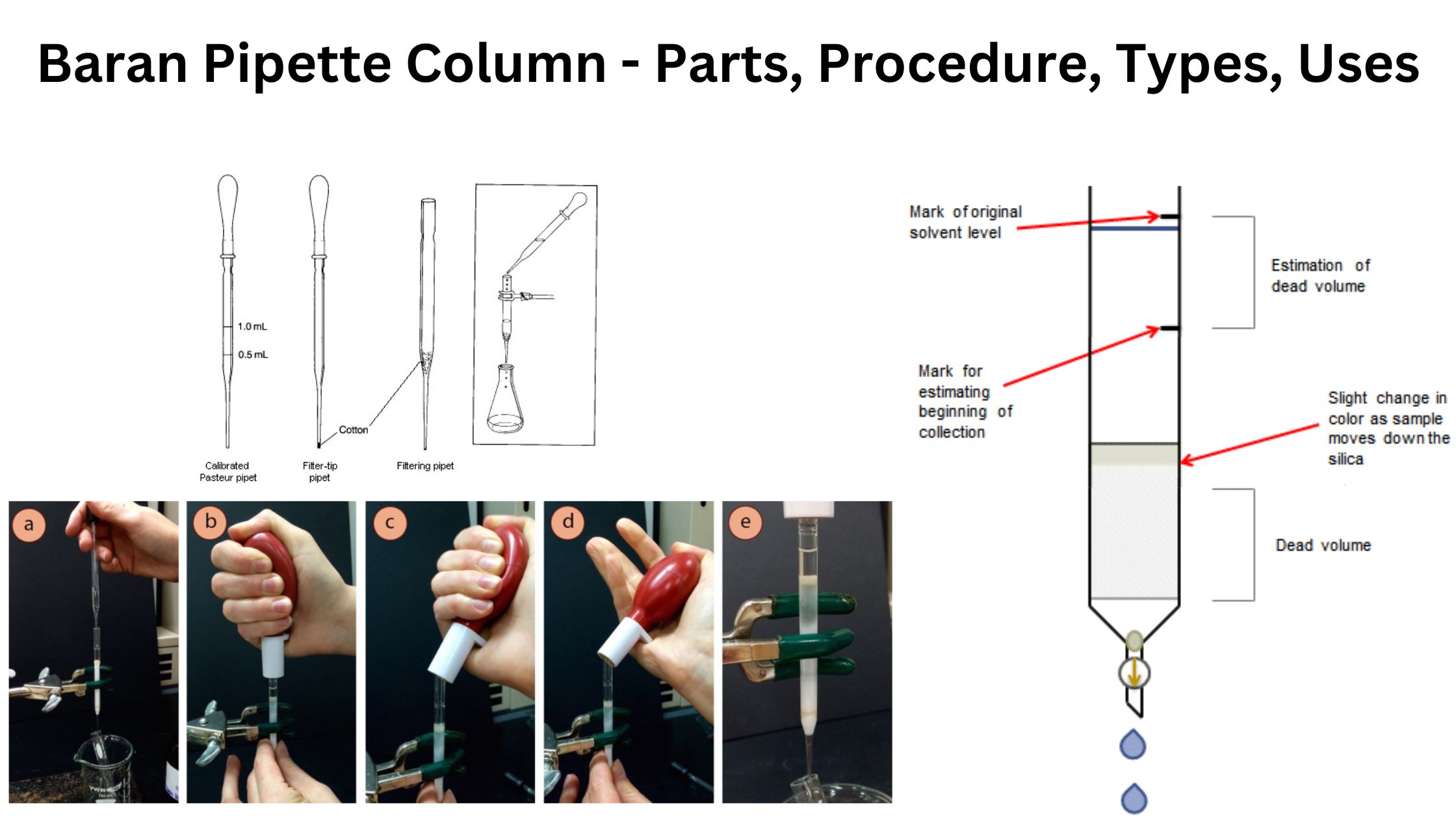
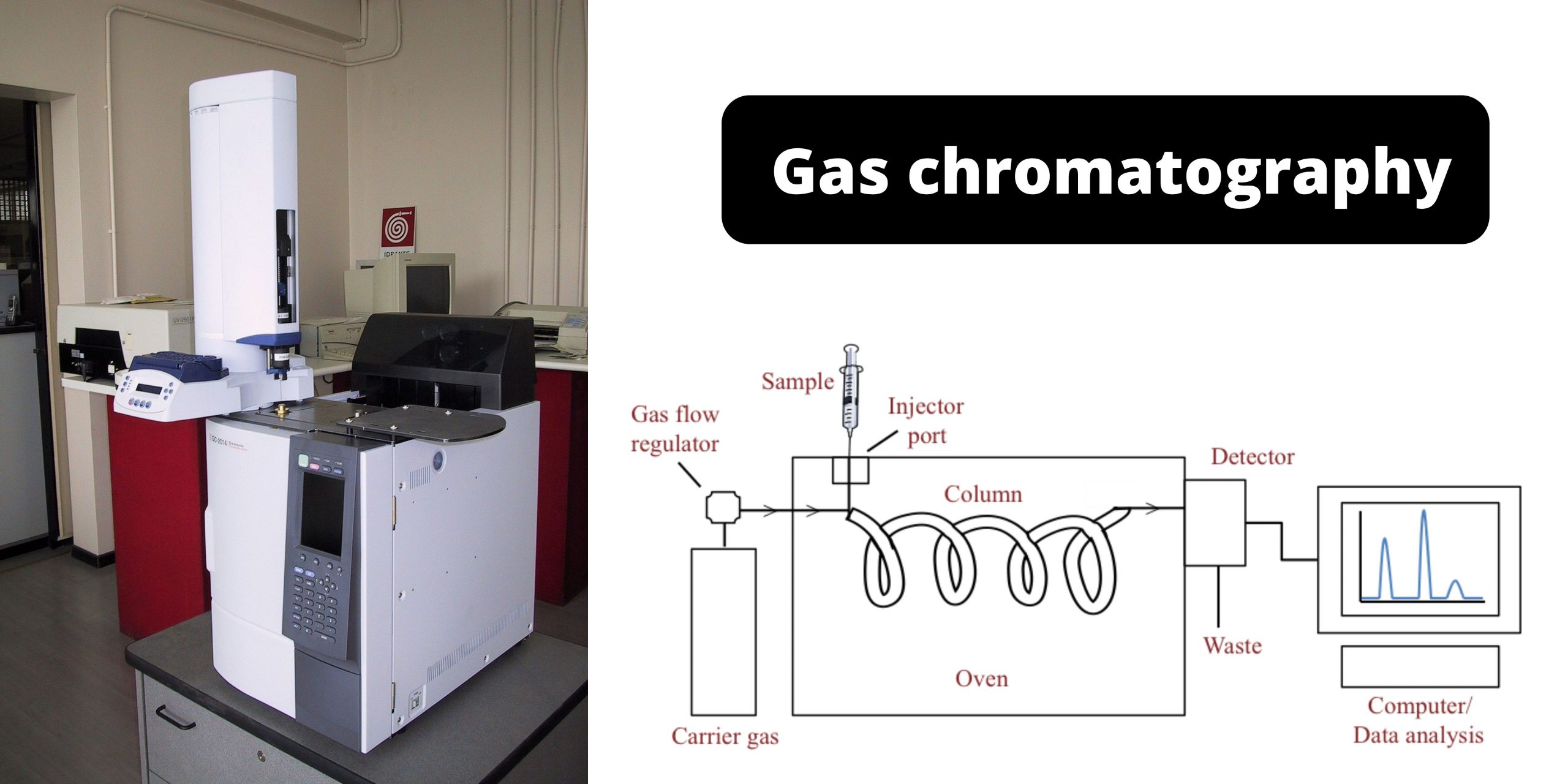
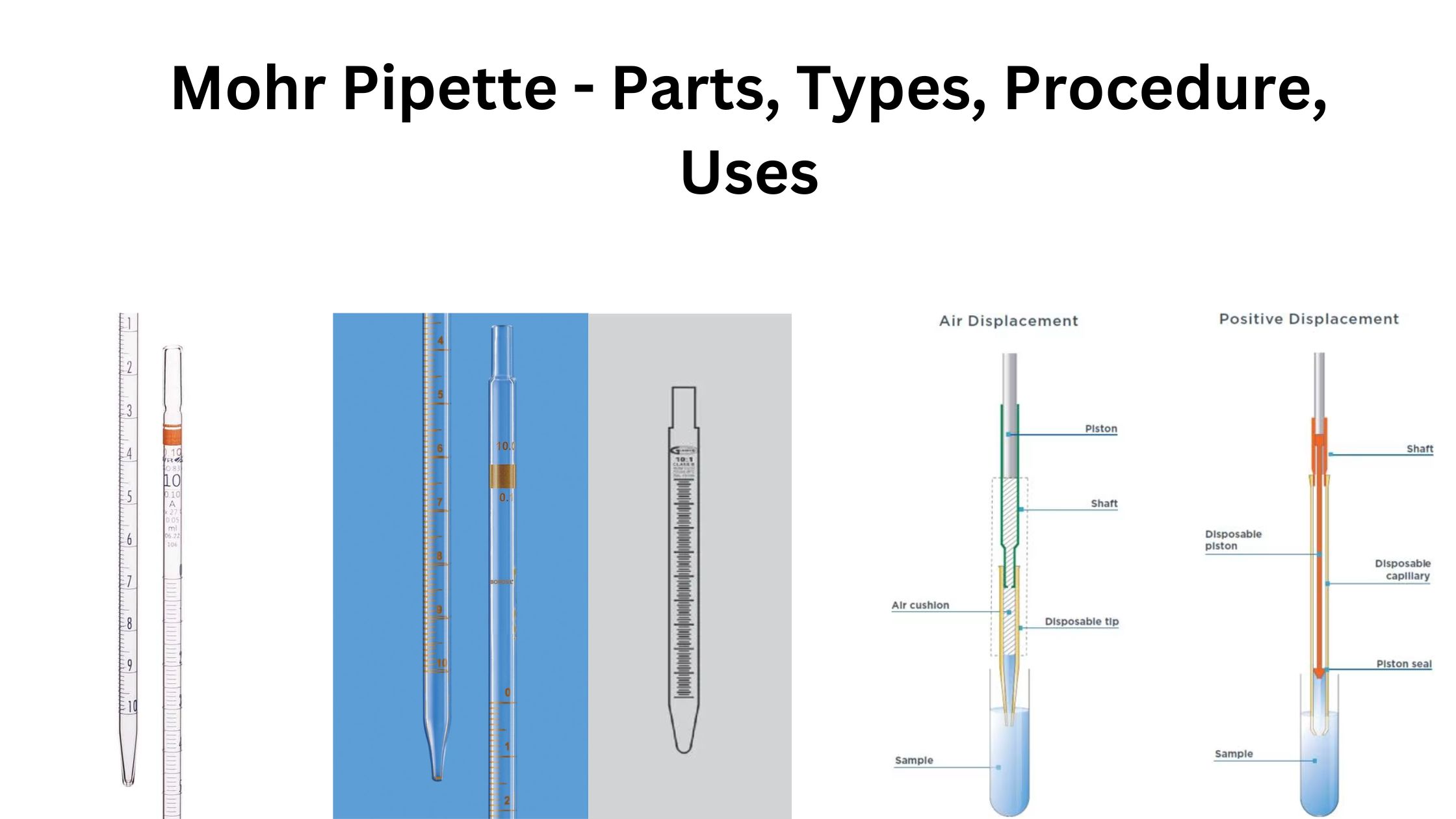
Scanning Electron Microscope – Principle, Parts, Uses
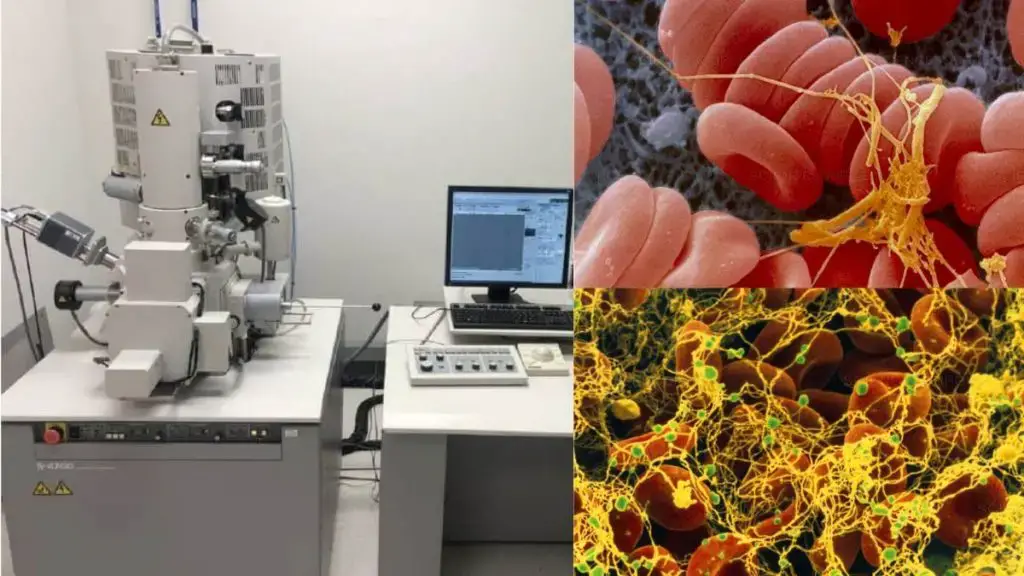
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) produces high-resolution images from an electron beam that scans a focused beam over the surface of a specimen. The benefit of using electrons as opposed to an optical light microscope is that, due to electronegativity, the resultant interactions with the orbitals surrounding the atom create signals that indicate surface morphology … Read more