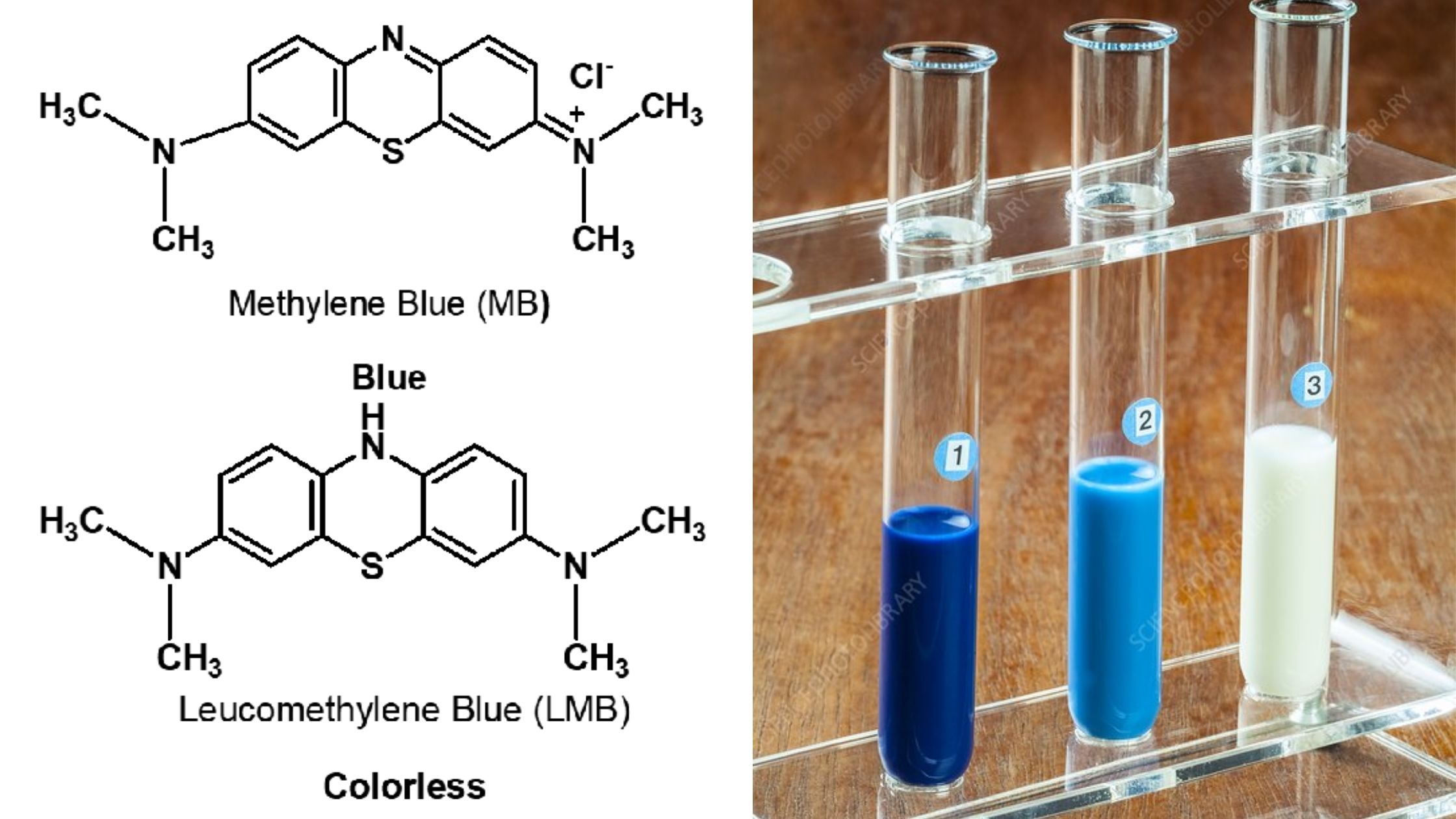
Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT) – Principle, Procedure, Result
It is a rapid and simple test used for the determination of microbiological quality of milk. It is commonly employed in dairy laboratories to estimate the bacterial load present in milk samples. The test is based on the principle that actively growing bacteria utilize dissolved oxygen during their metabolic activities. Due to this oxygen consumption … Read more