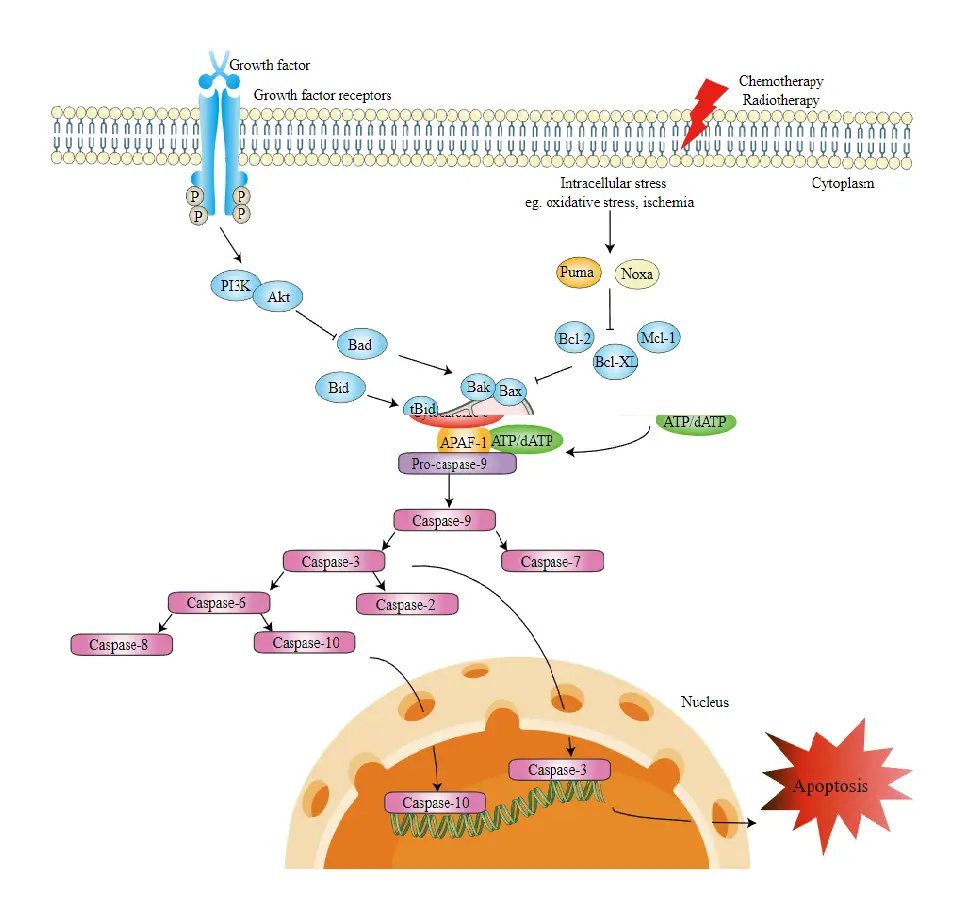
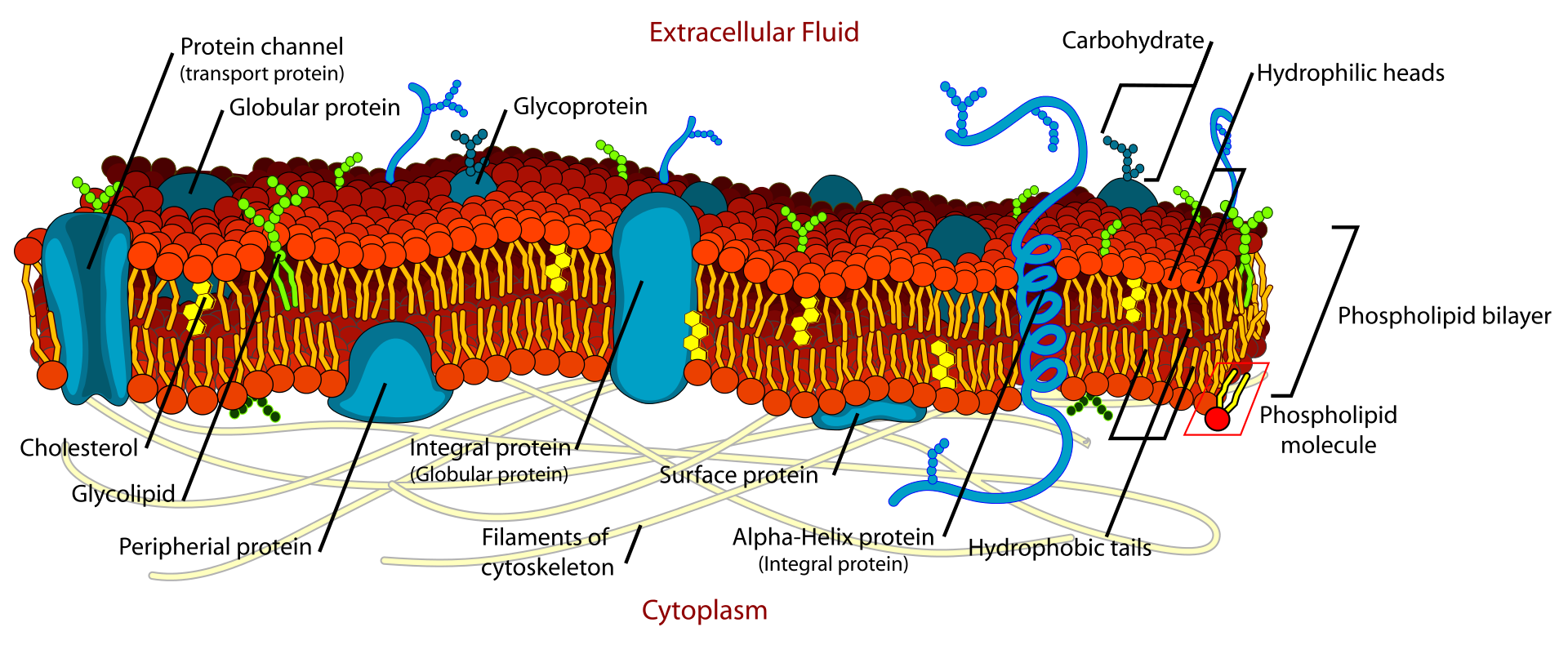
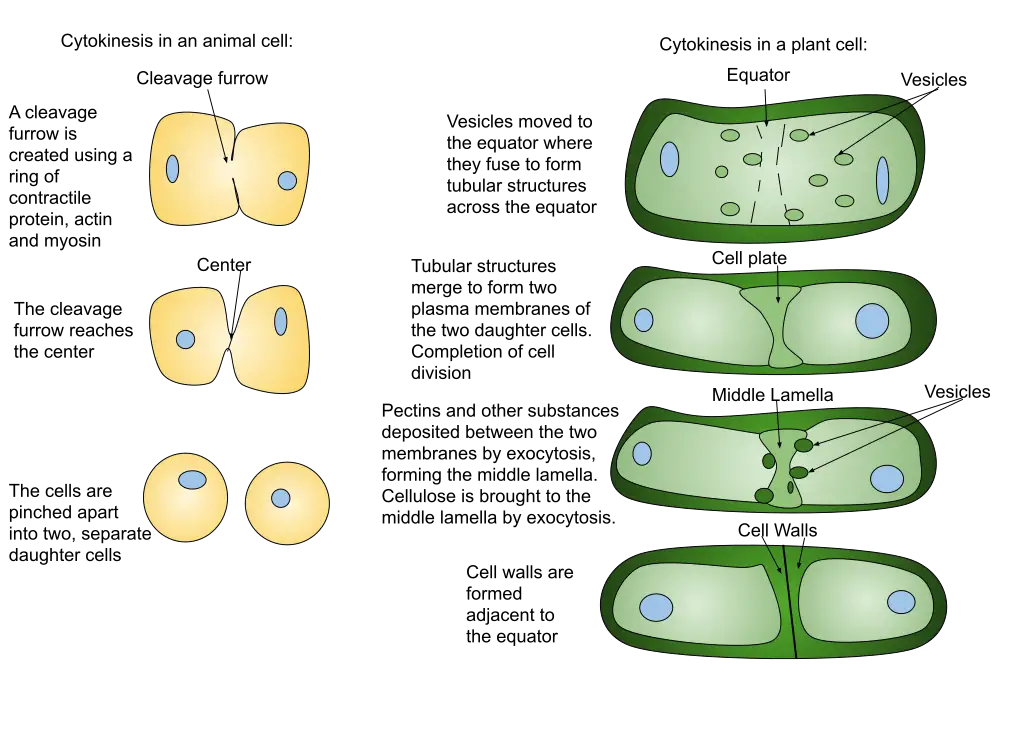
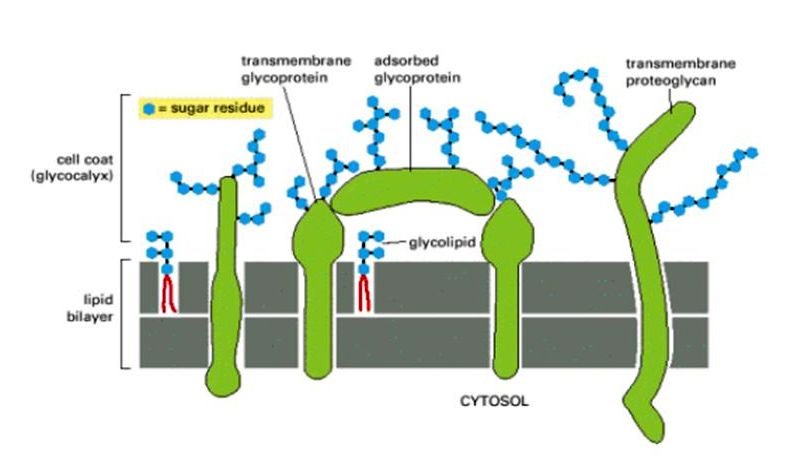
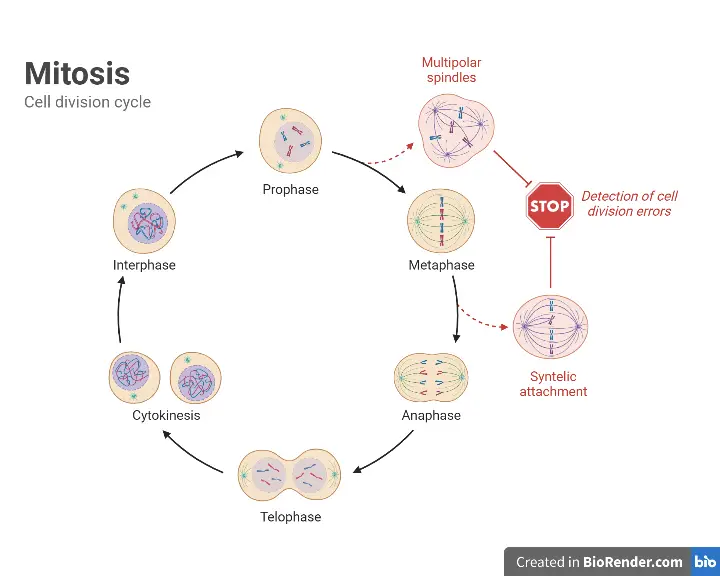
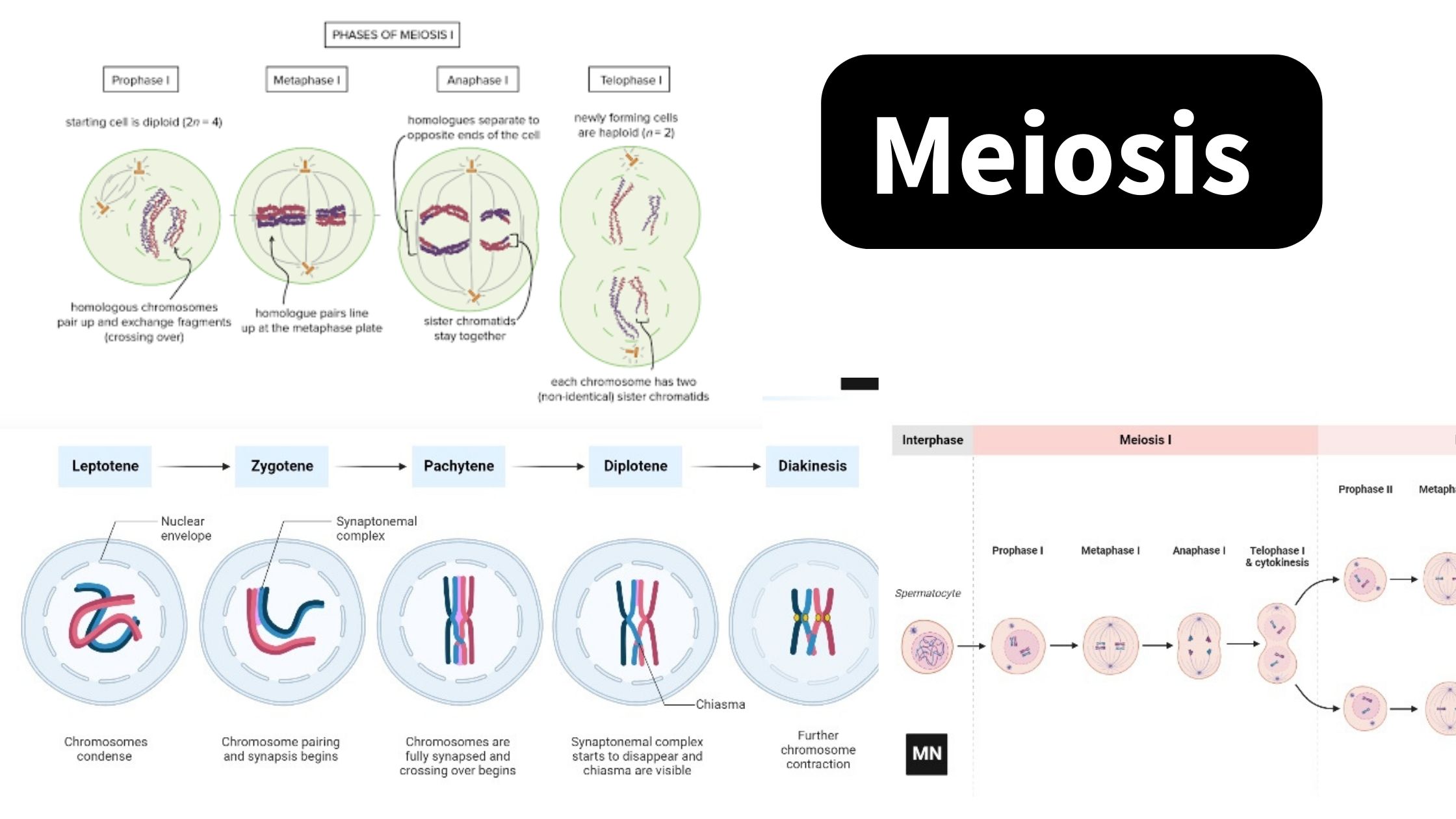
Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis – Definition, Process
Intracellular stimuli, such as DNA damage, predominantly trigger apoptosis via the intrinsic route. The intrinsic apoptosis pathway, which is comprised of conserved signalling proteins, is physically connected with mitochondria and sensitive to mitochondrial oxidative stress in vertebrates. Members of the Bcl family linked to the mitochondrial membrane have an effect on the process, including the … Read more