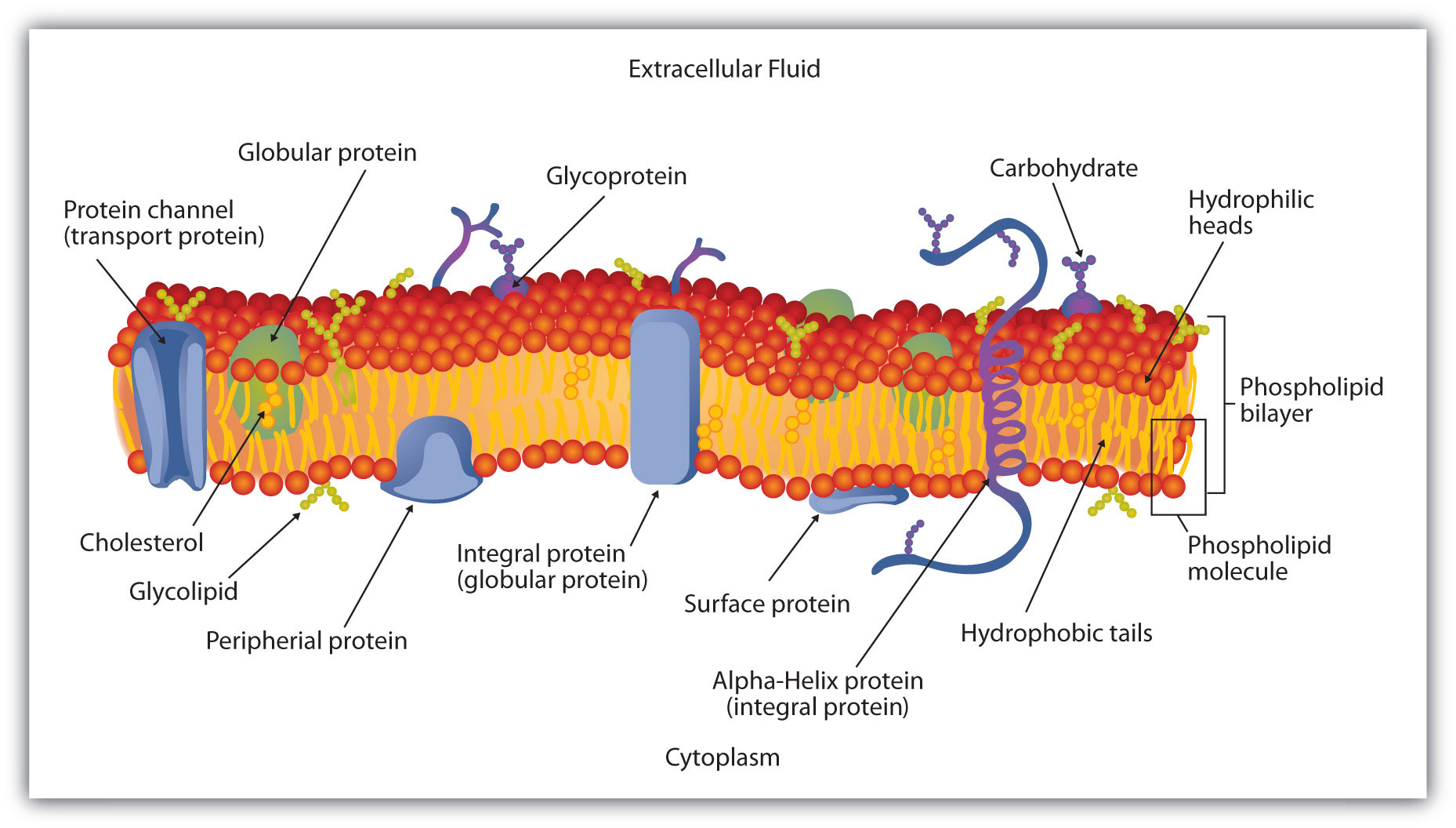
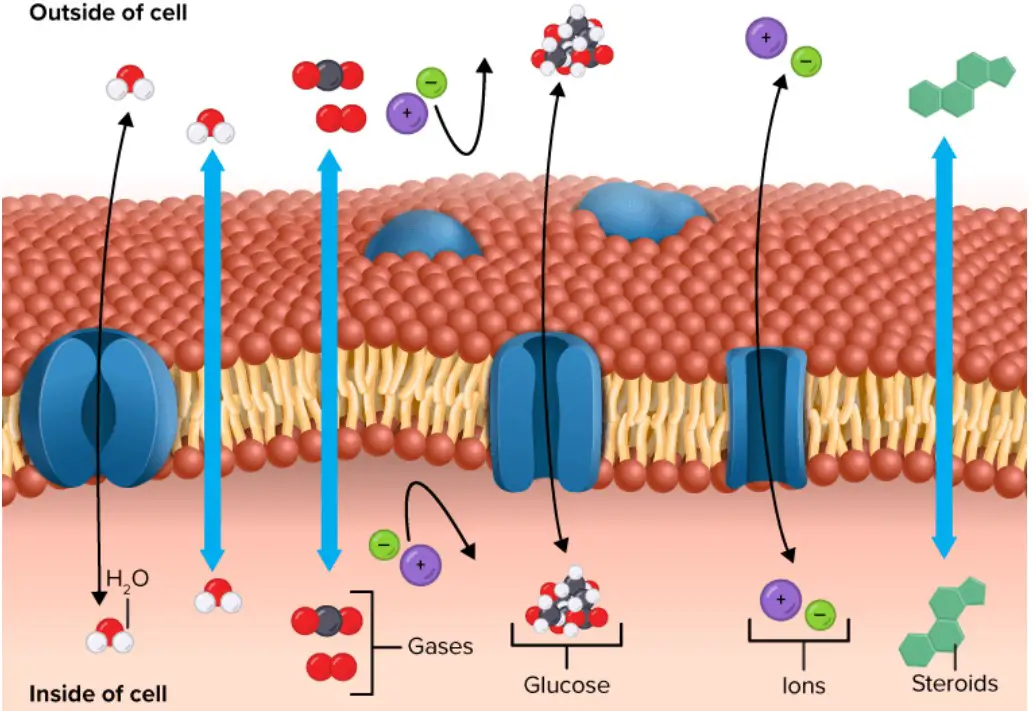
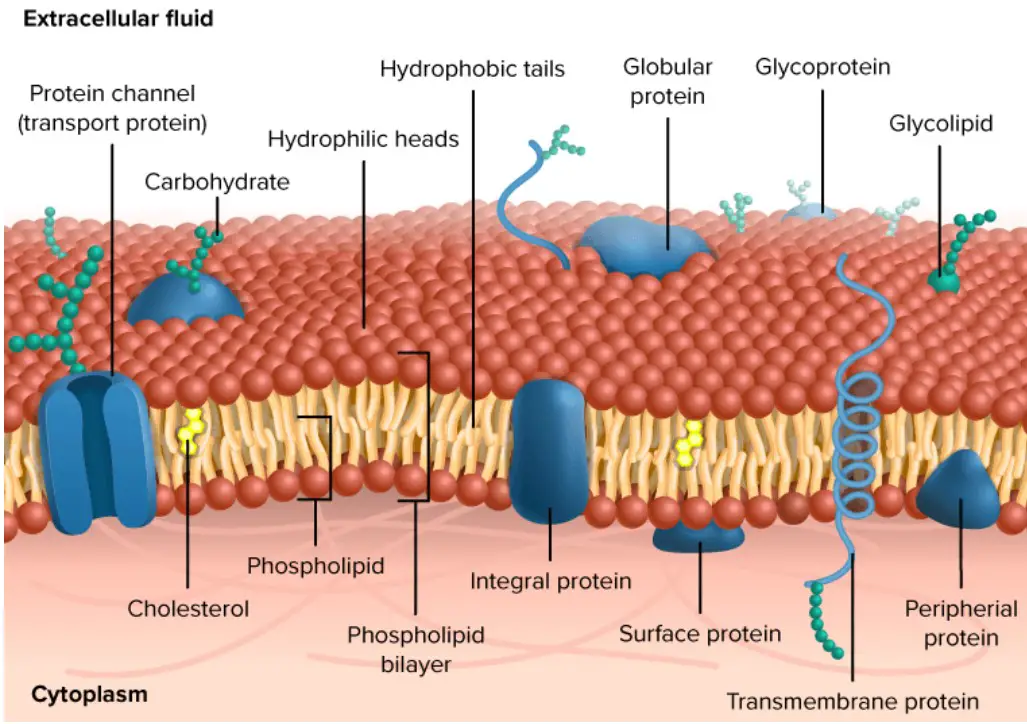
Plasmolysis – Definition, Stages, Functions, Examples,
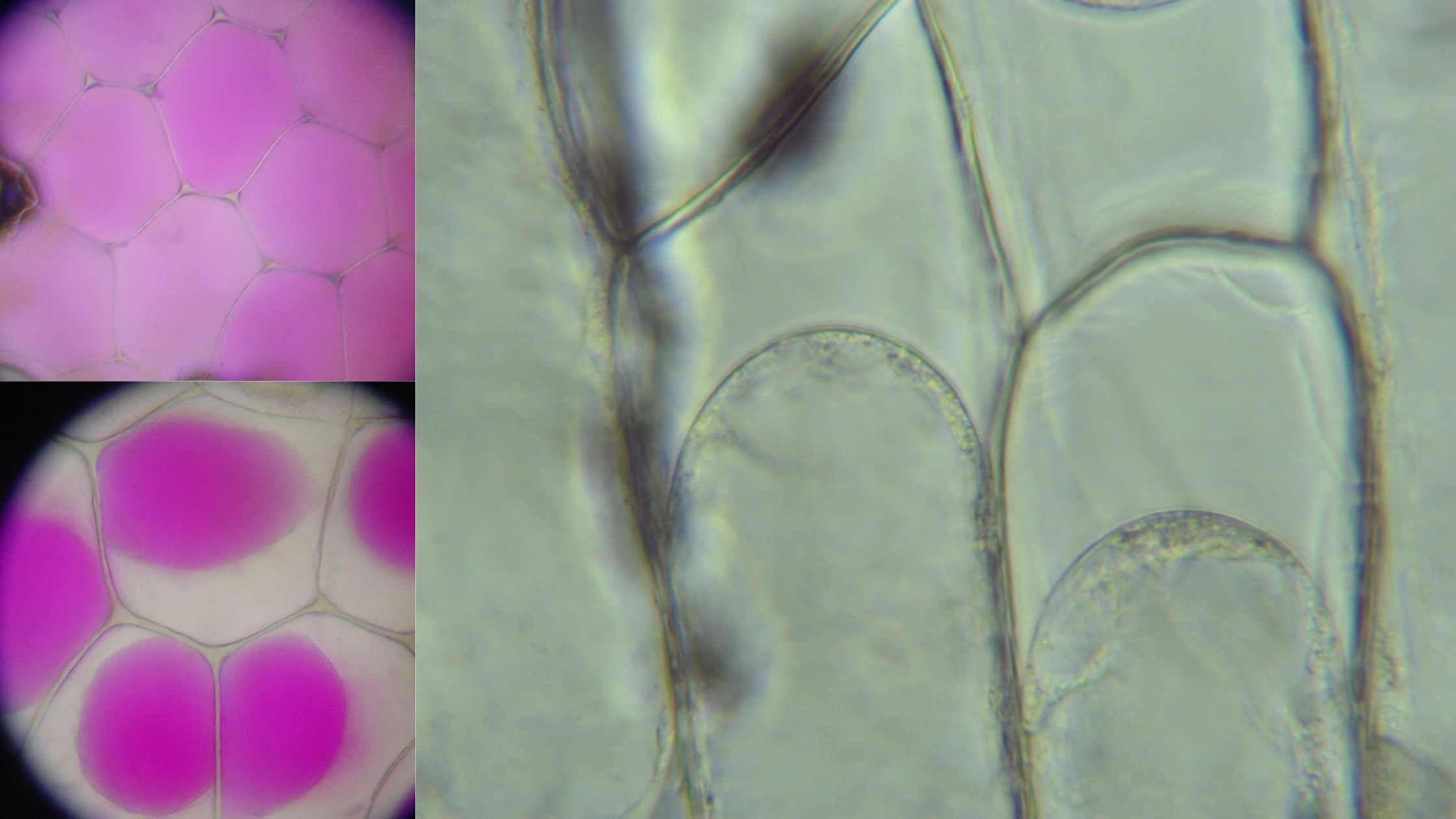
What is Plasmolysis? Definition of Plasmolysis Plasmolysis is the process in which plant cells contract or shrink due to the loss of water when exposed to a hypertonic solution. Stages of Plasmolysis Plasmolysis is a complex process that occurs in plant cells when exposed to hypertonic solutions, leading to water loss and cellular contraction. This … Read more