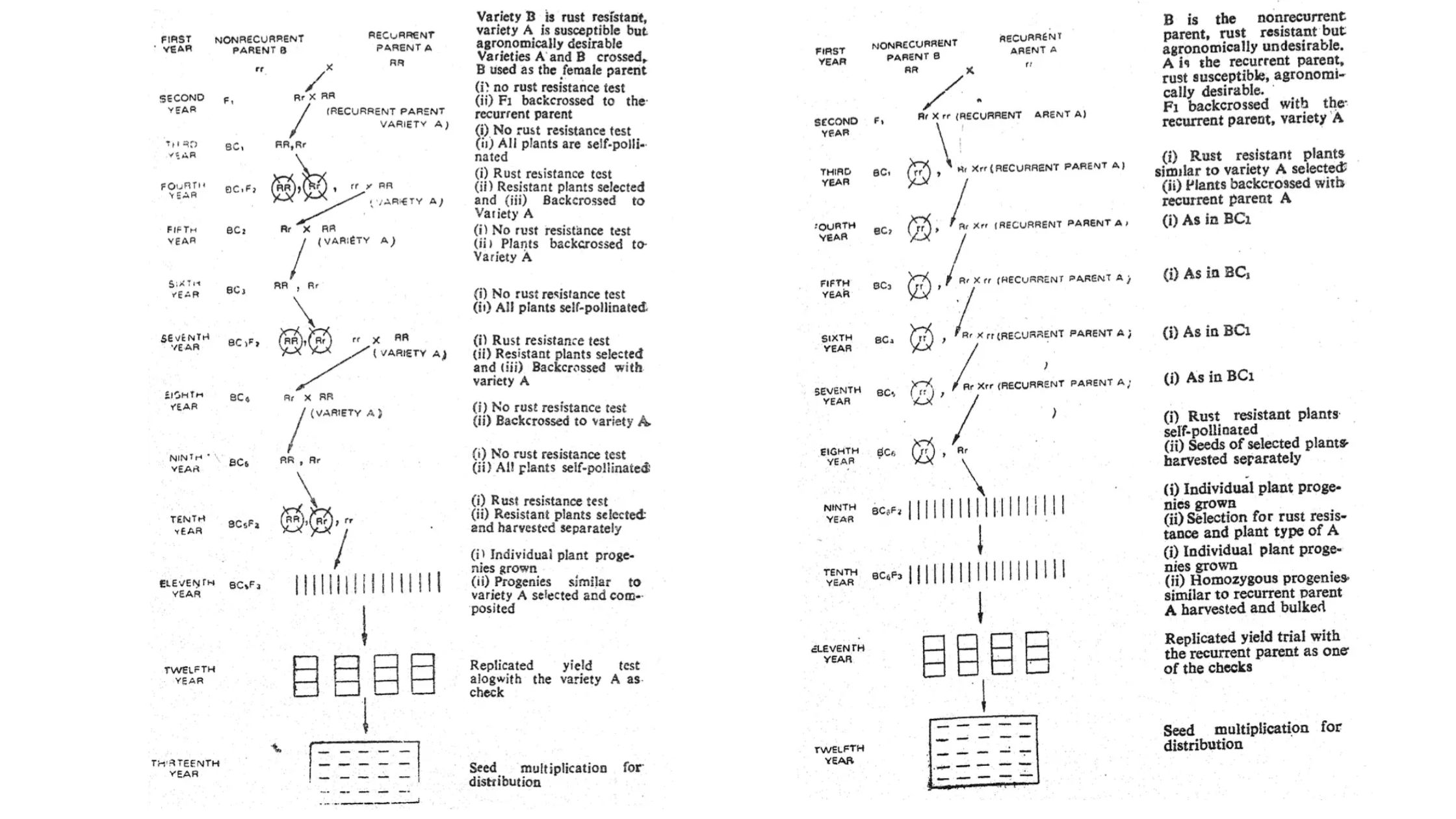
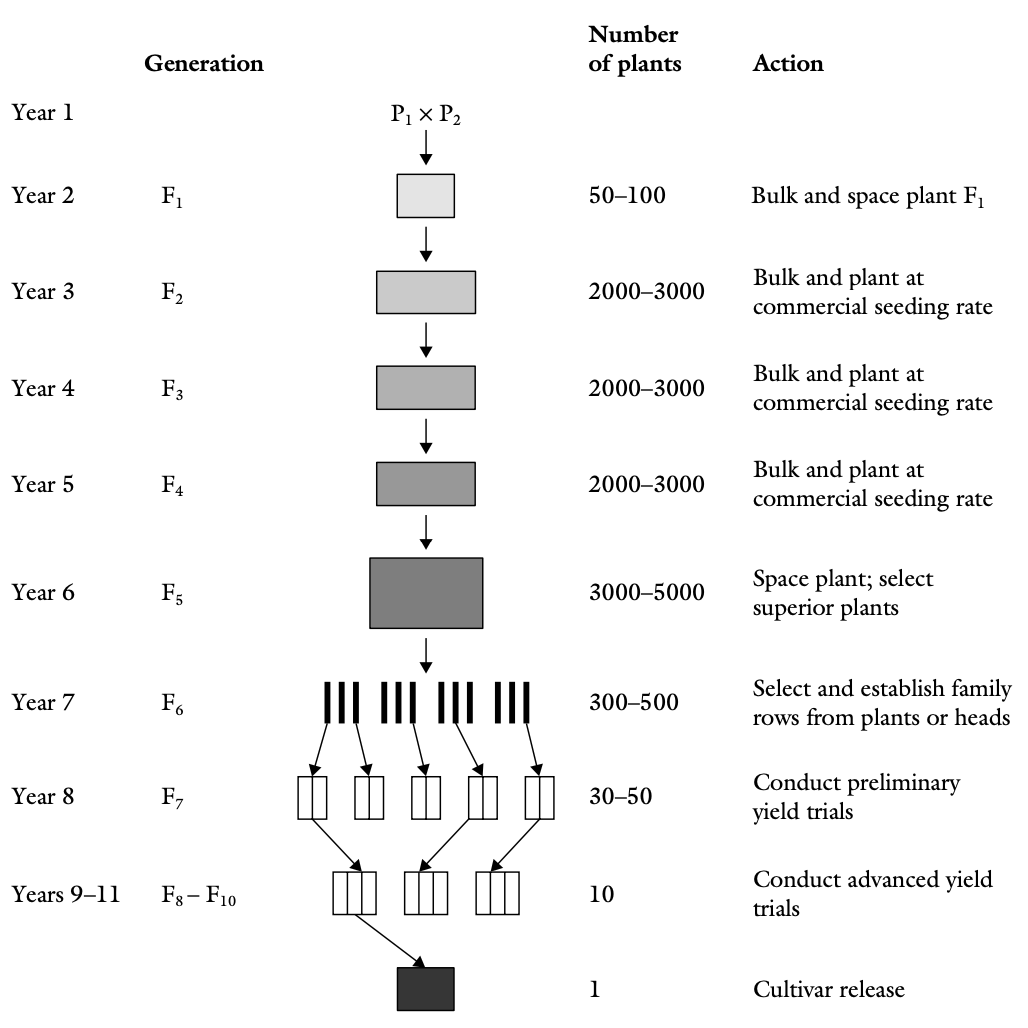
Polyploidy in Plant Breeding
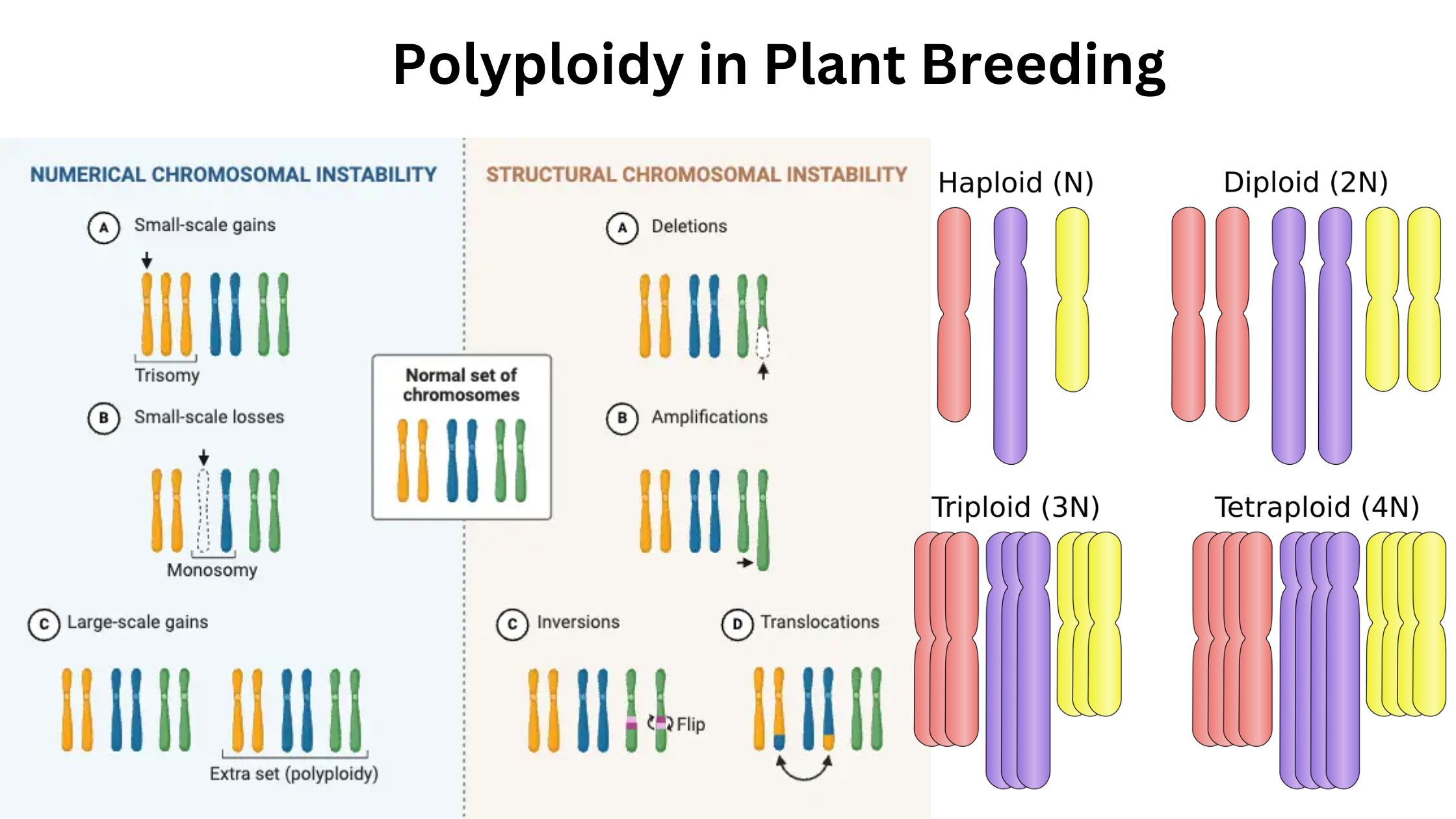
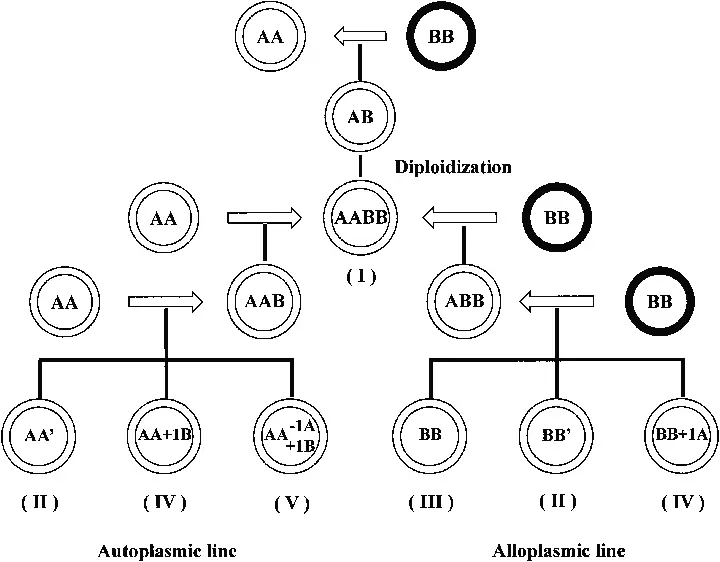
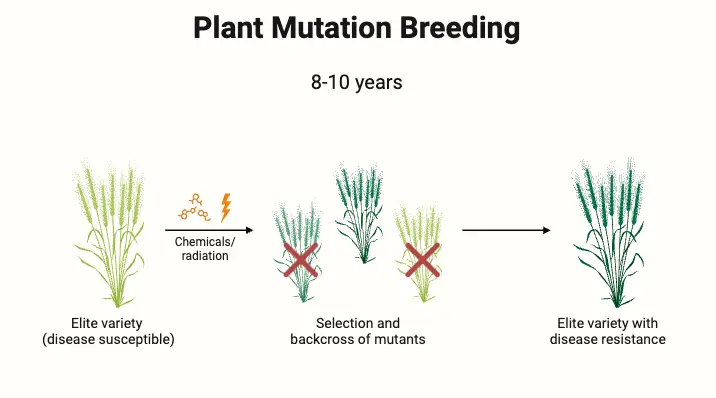
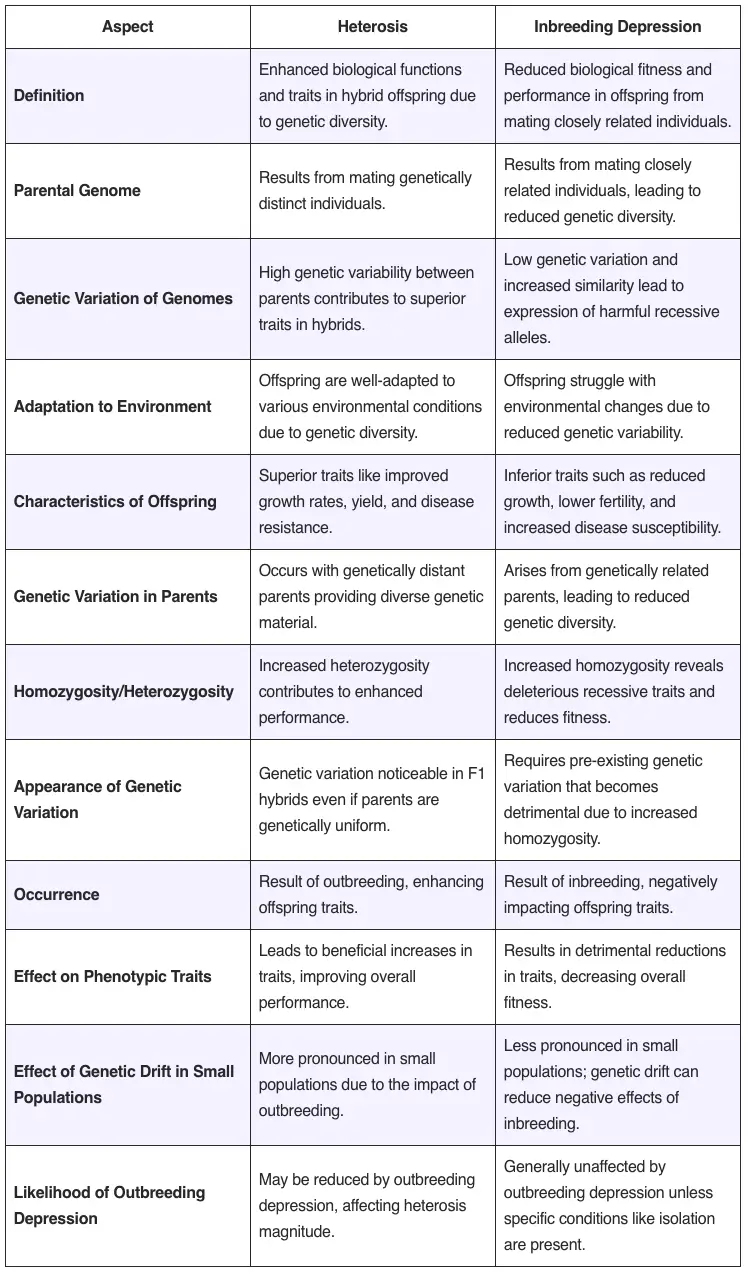
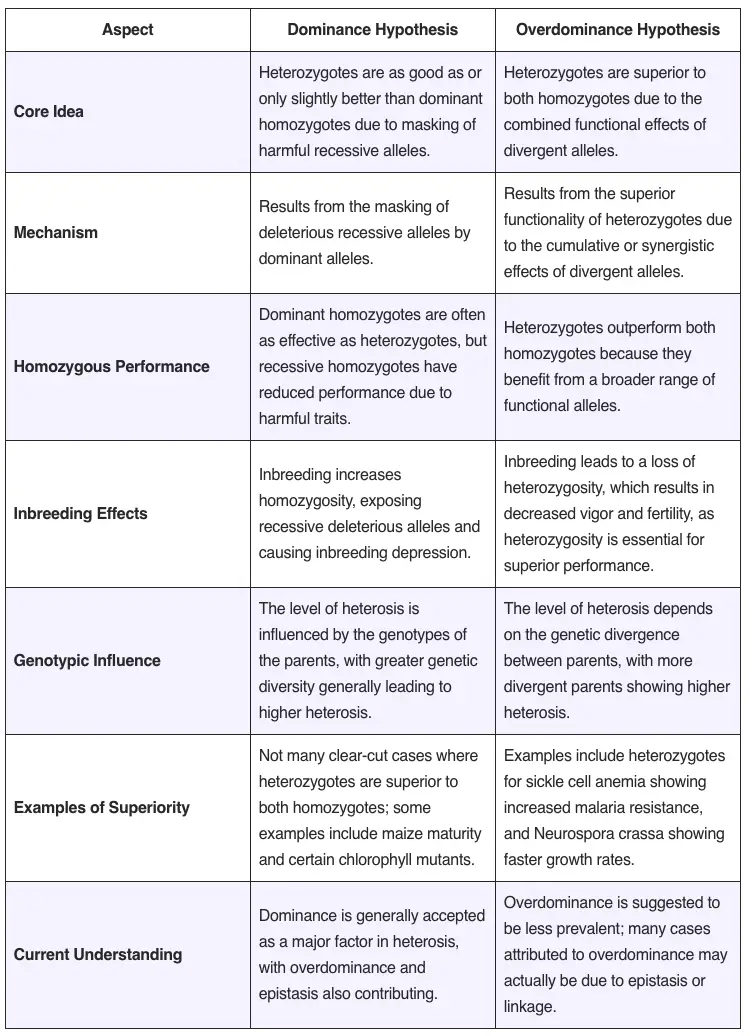
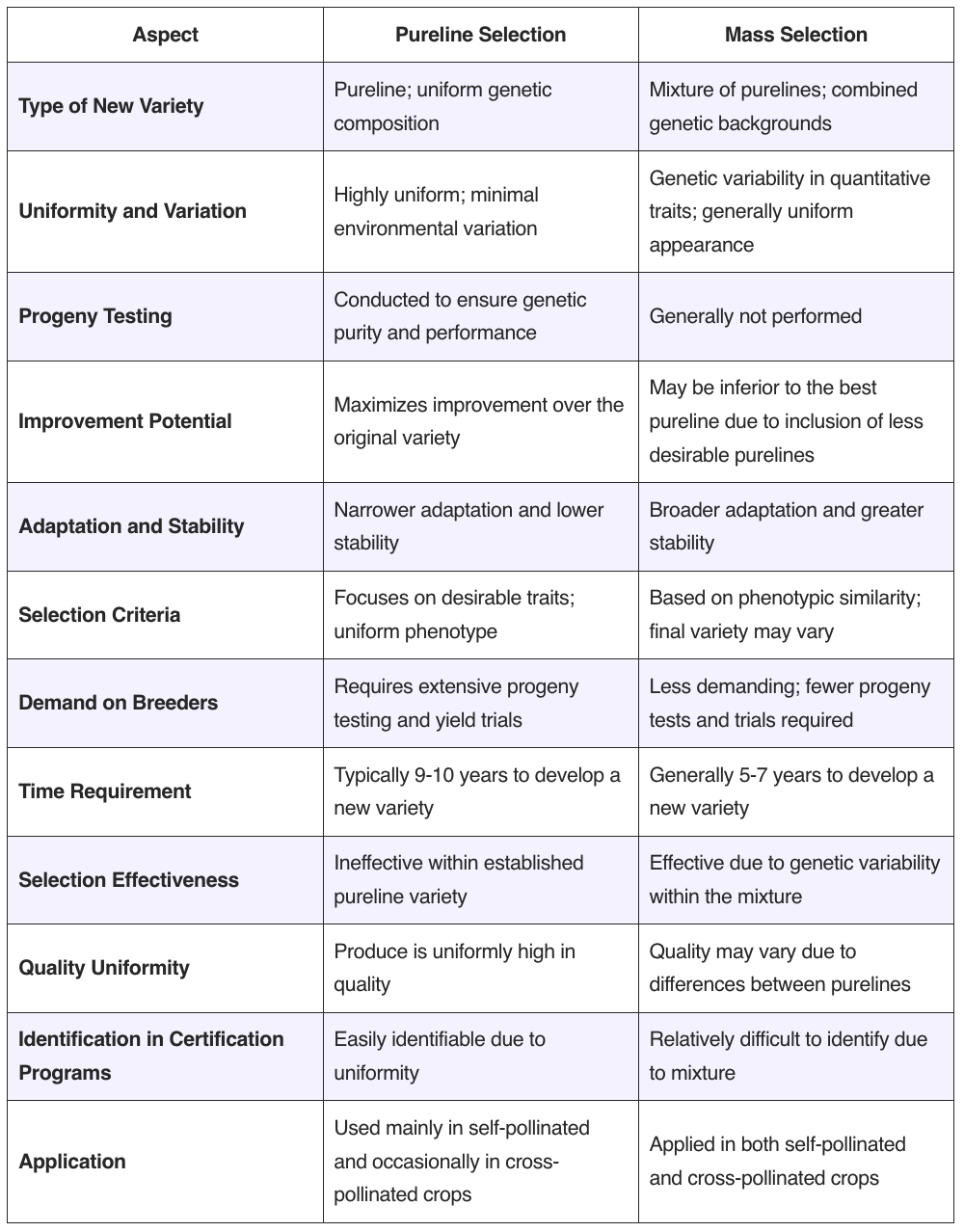
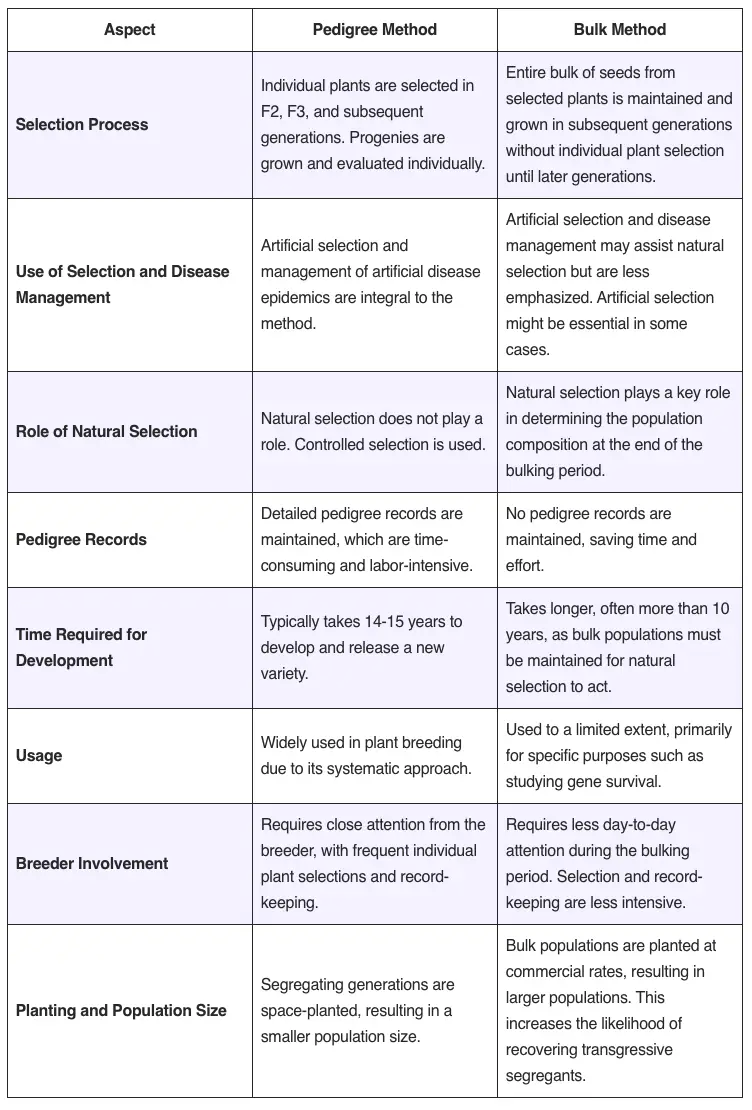
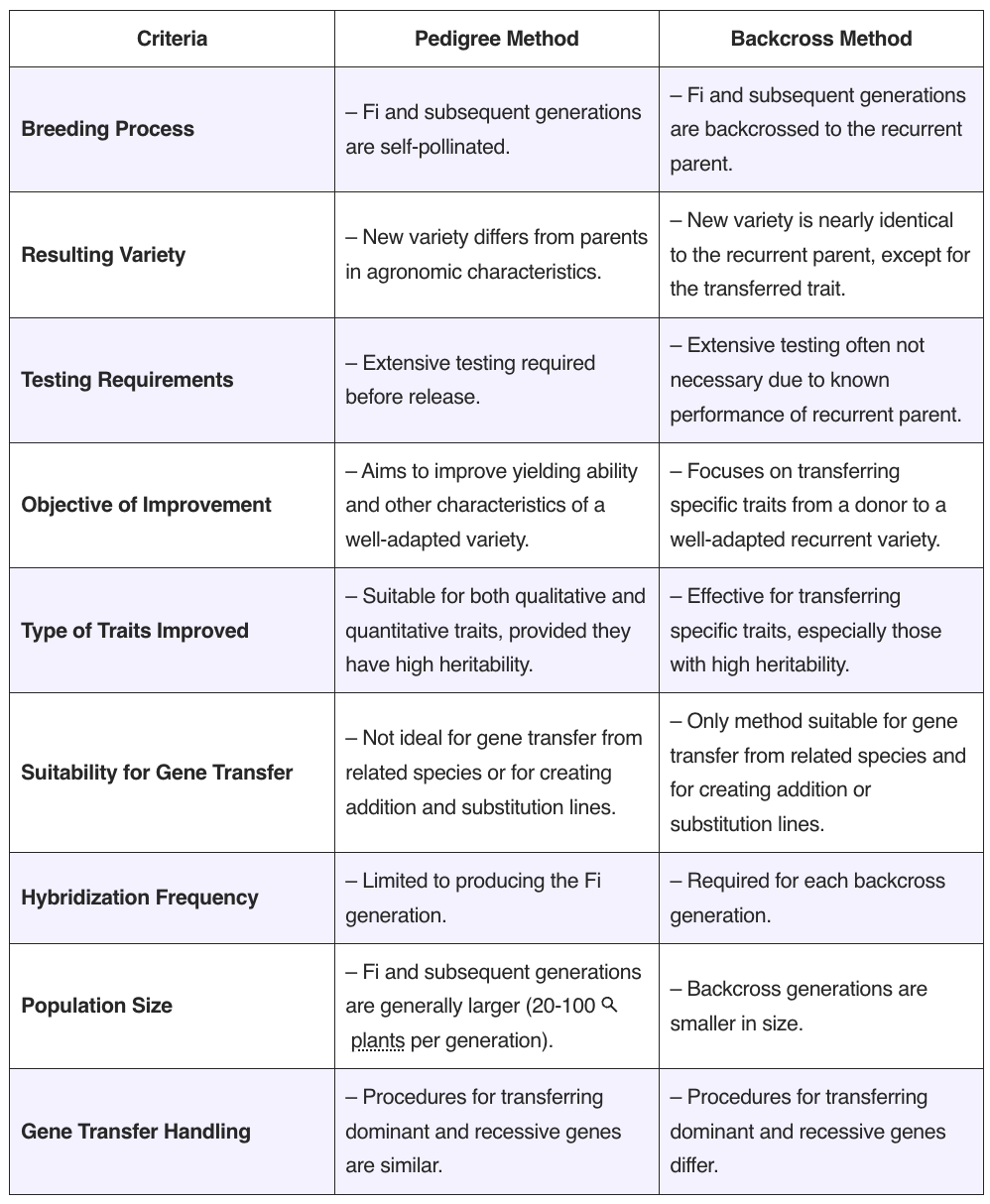
Polyploidy plays a pivotal role in plant breeding, especially in enhancing the genetic diversity and adaptability of crops. Polyploidy refers to the condition in which a plant has more than two complete sets of chromosomes, a state that naturally occurs due to irregularities in mitotic or meiotic divisions. These irregularities can lead to an increase … Read more