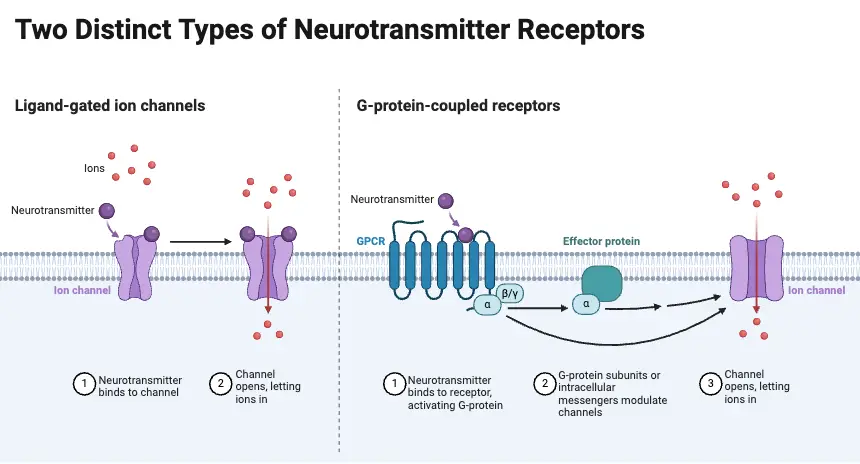
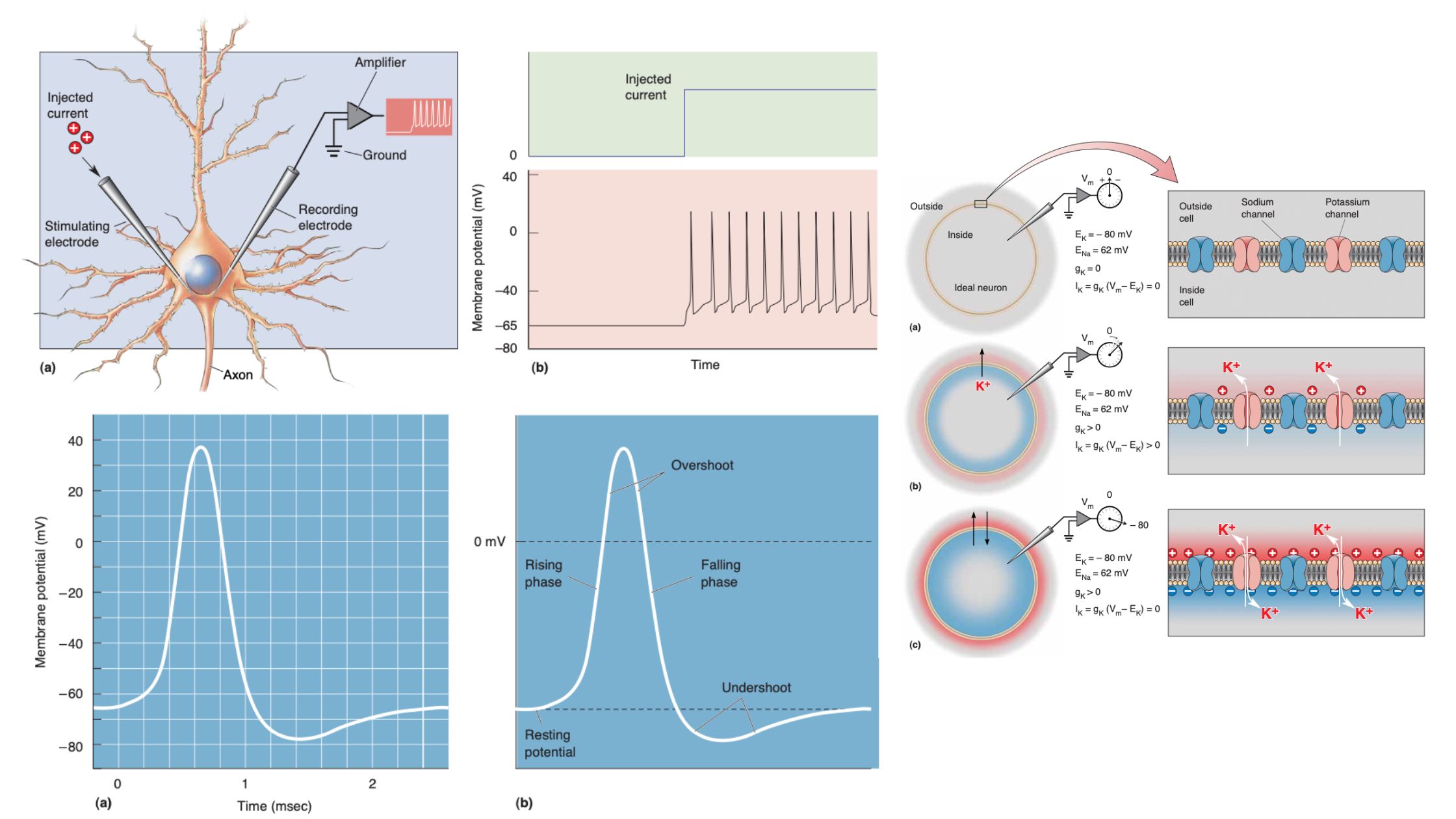
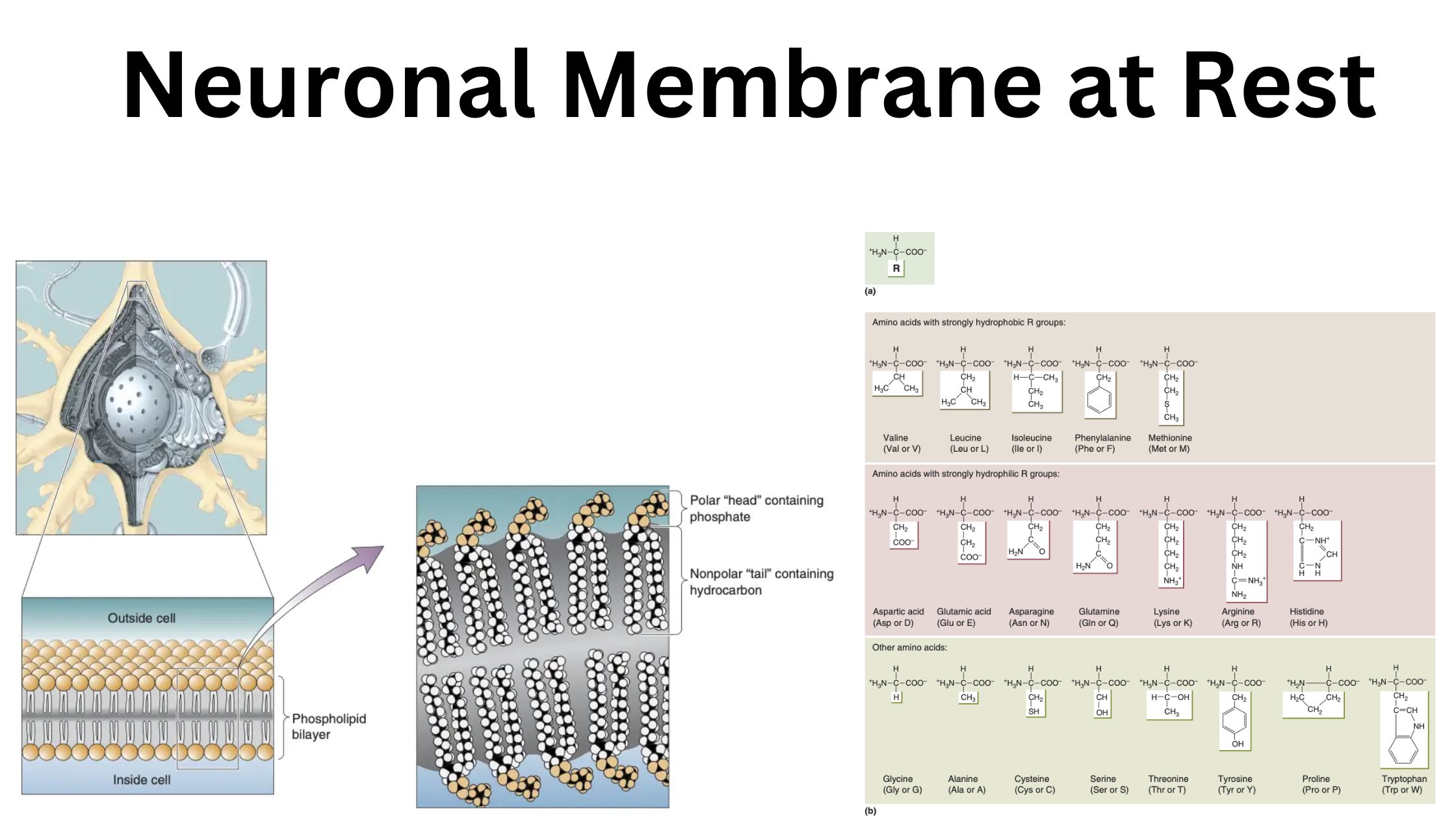
9 Best Books for Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the nervous system, encompassing a variety of fields such as biology, psychology, medicine, and engineering. It aims to understand the structure and function of the brain and nervous system, including how neurons communicate, how neural circuits influence behavior and cognition, and how various factors can affect brain health … Read more