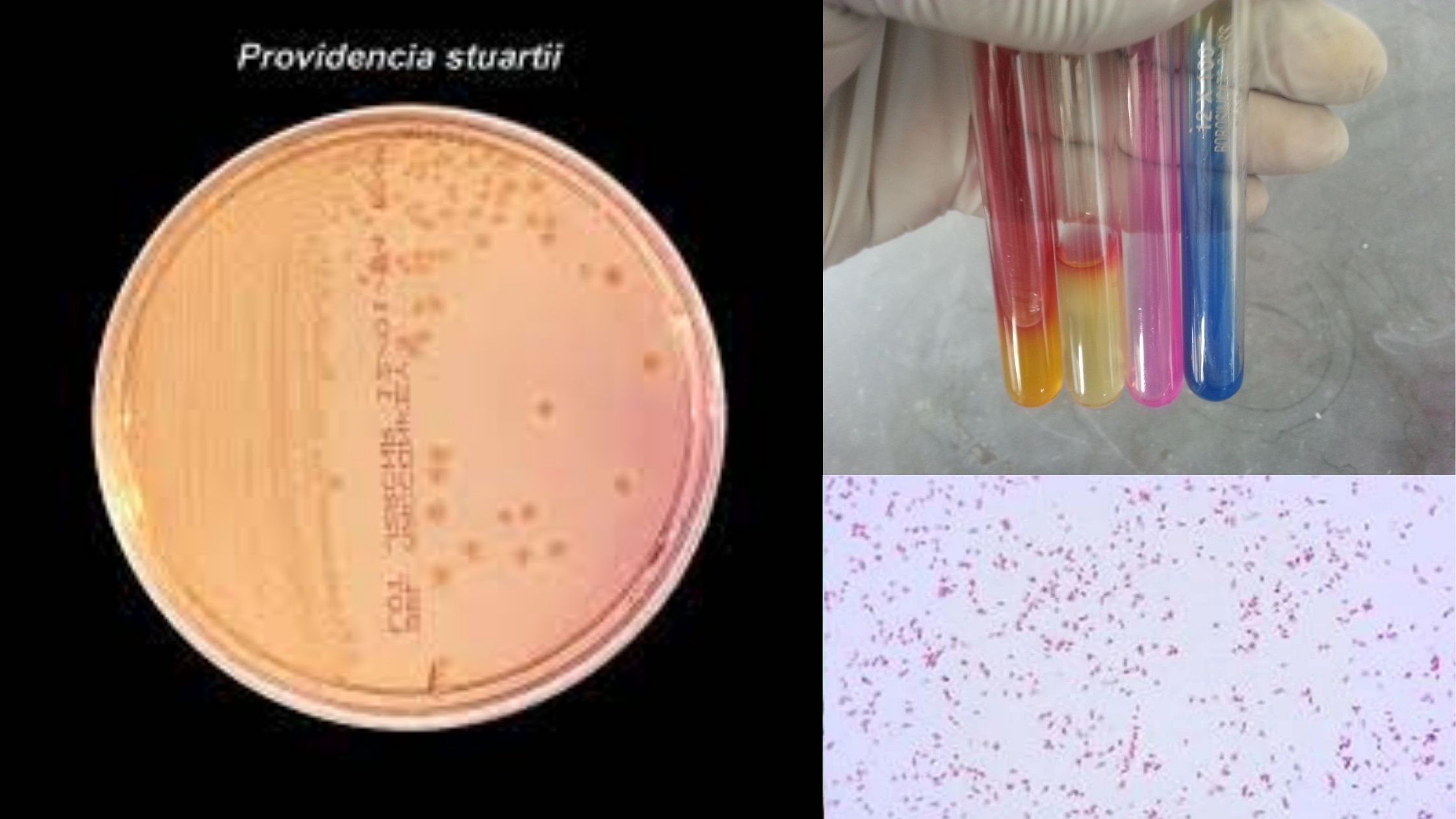
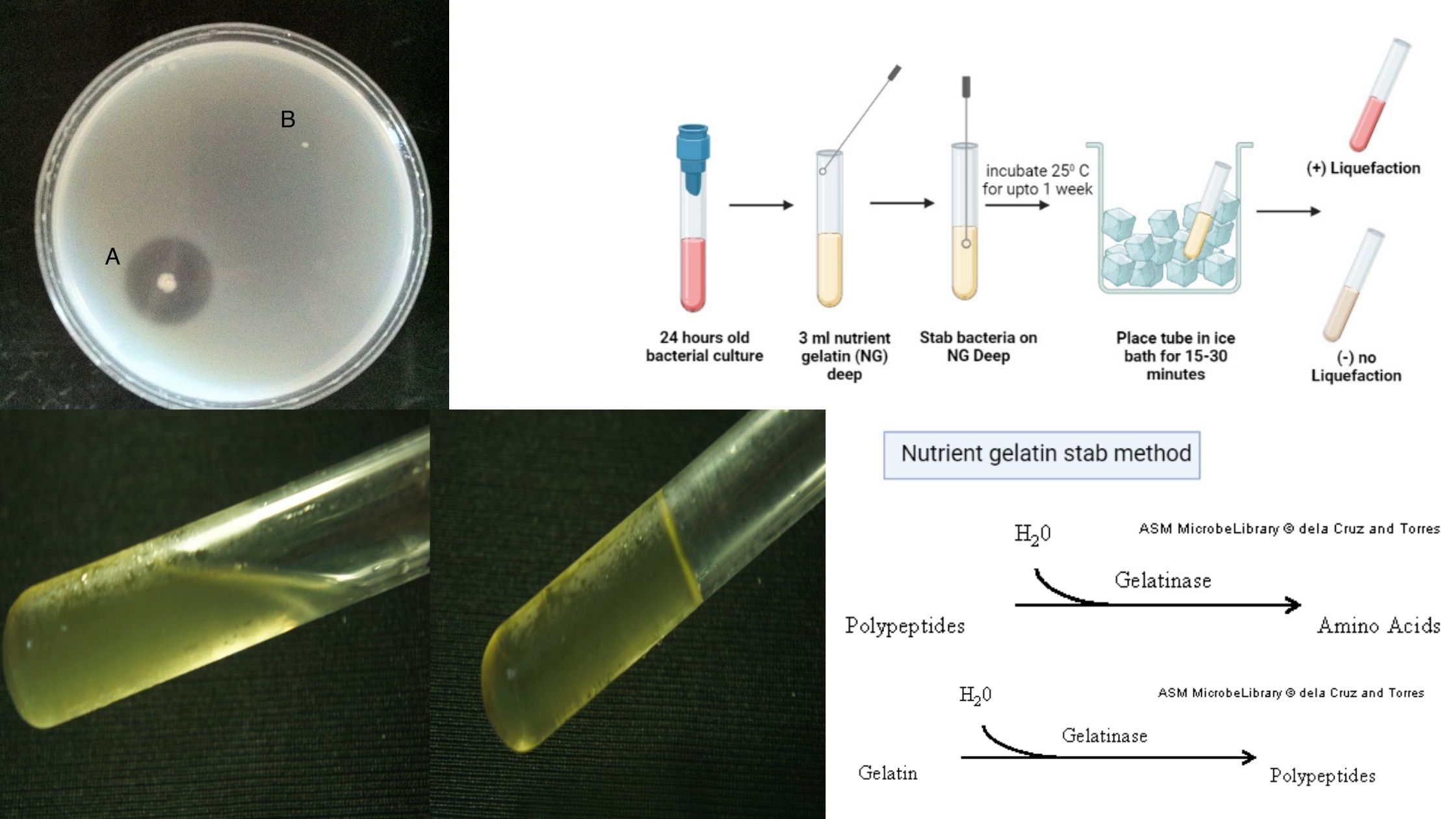
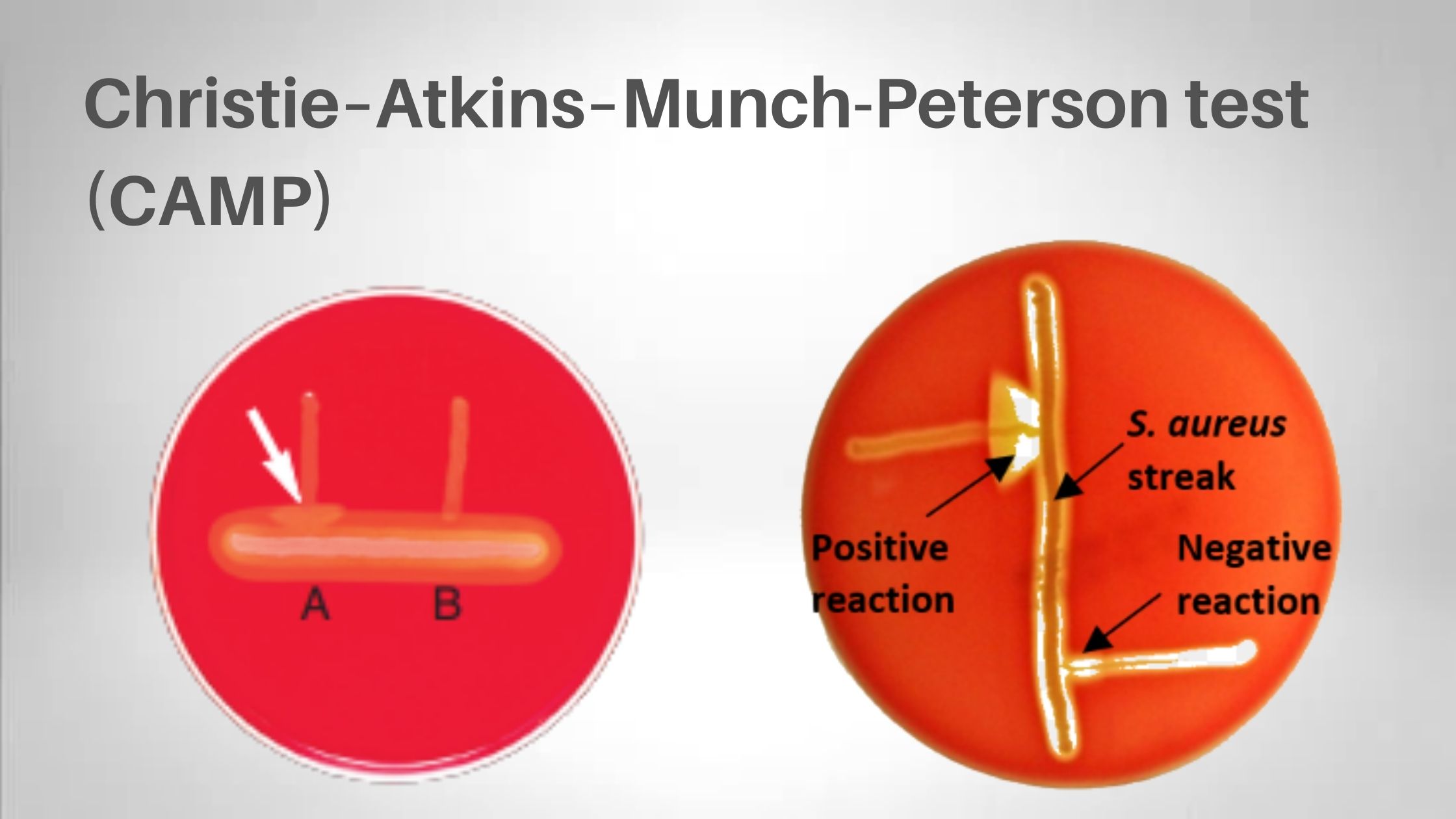
Biochemical Test of Providencia stuartii
The biochemical test of Providencia stuartii refers to the group of laboratory tests that are used to identify this bacterium on the basis of its metabolic and enzymatic activities. It is a Gram-negative rod shaped facultative anaerobic organism belonging to the family Morganellaceae. In clinical microbiology these tests is carried out to differentiate Providencia stuartii … Read more