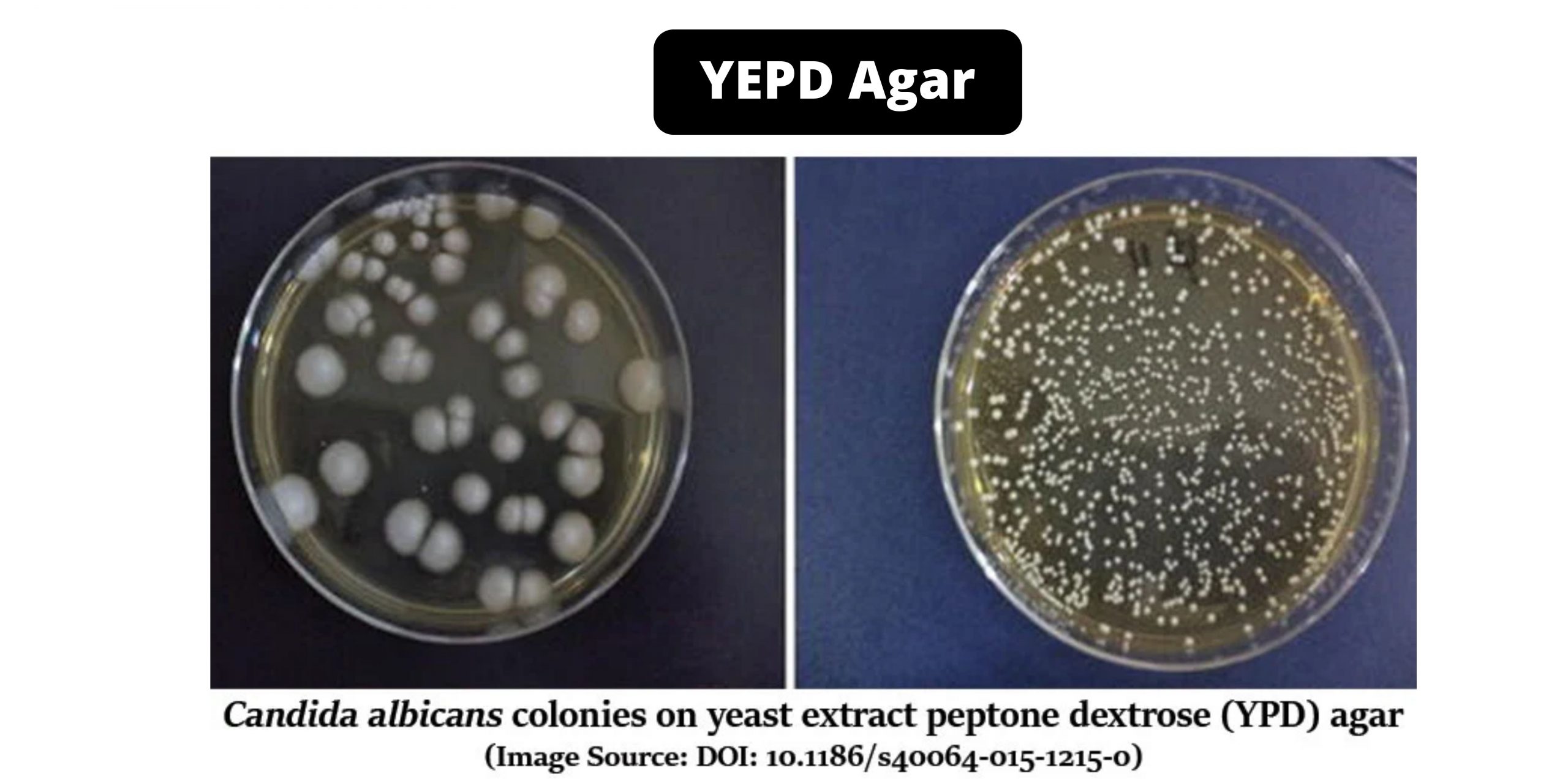
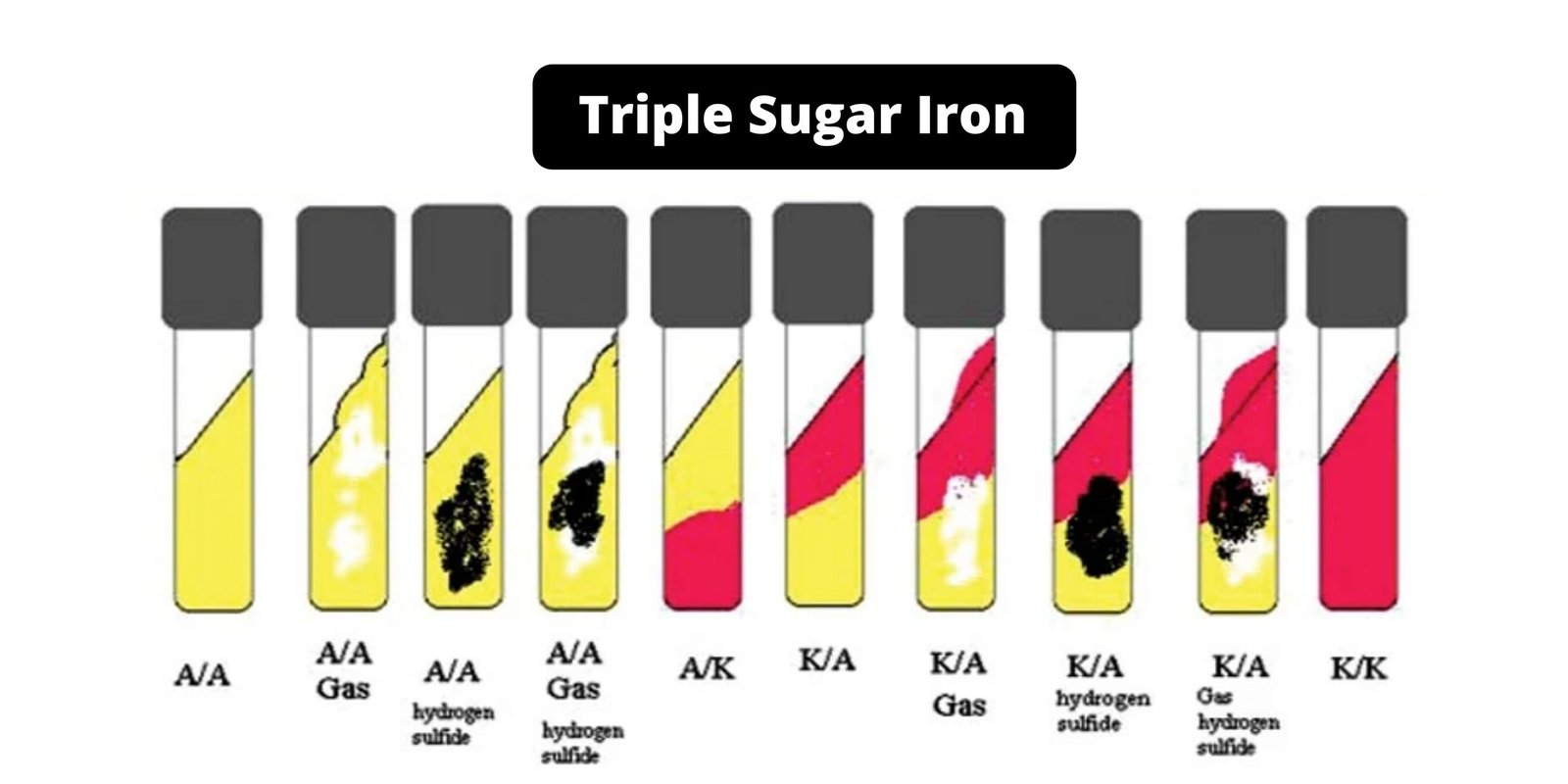
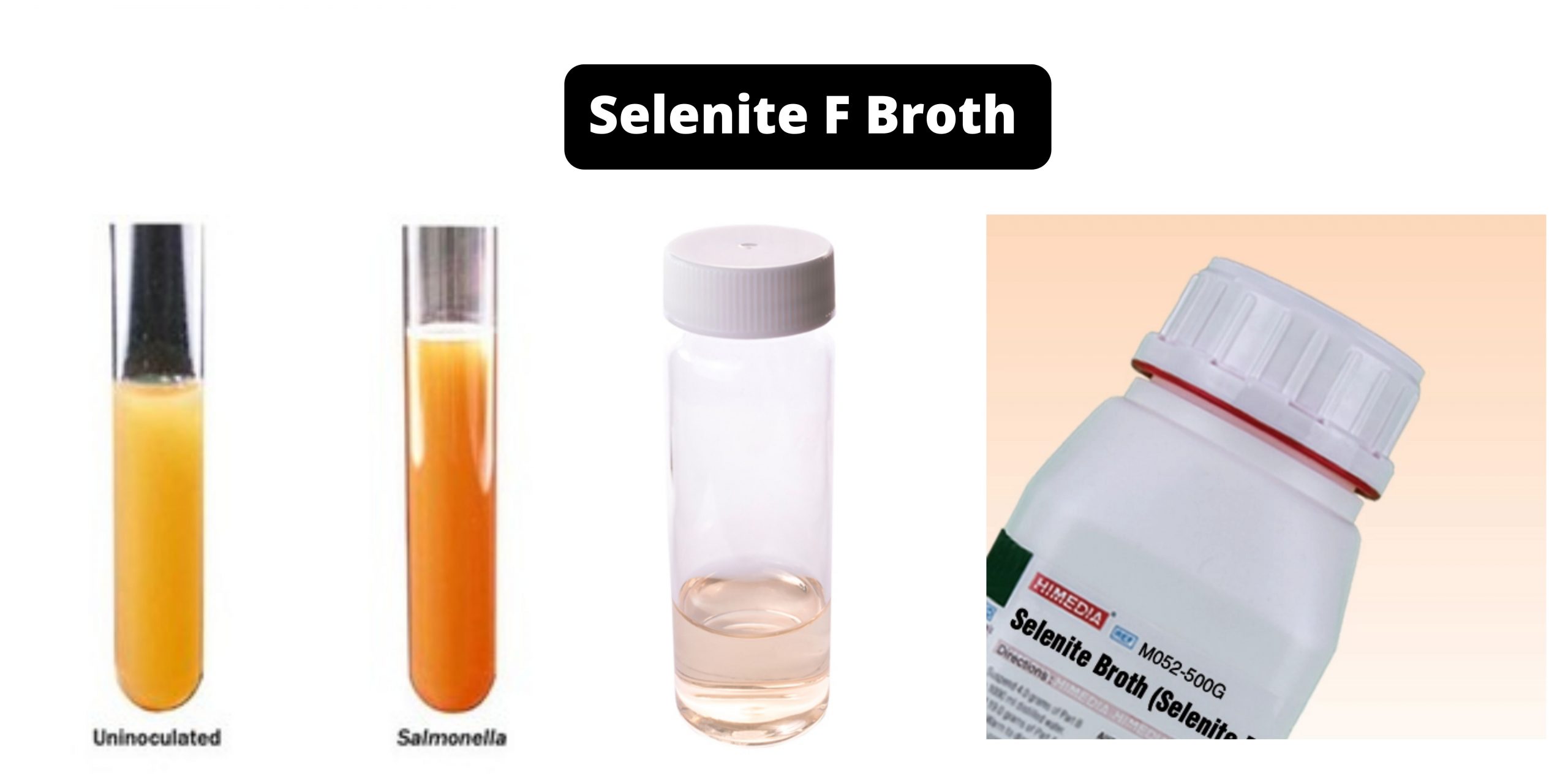
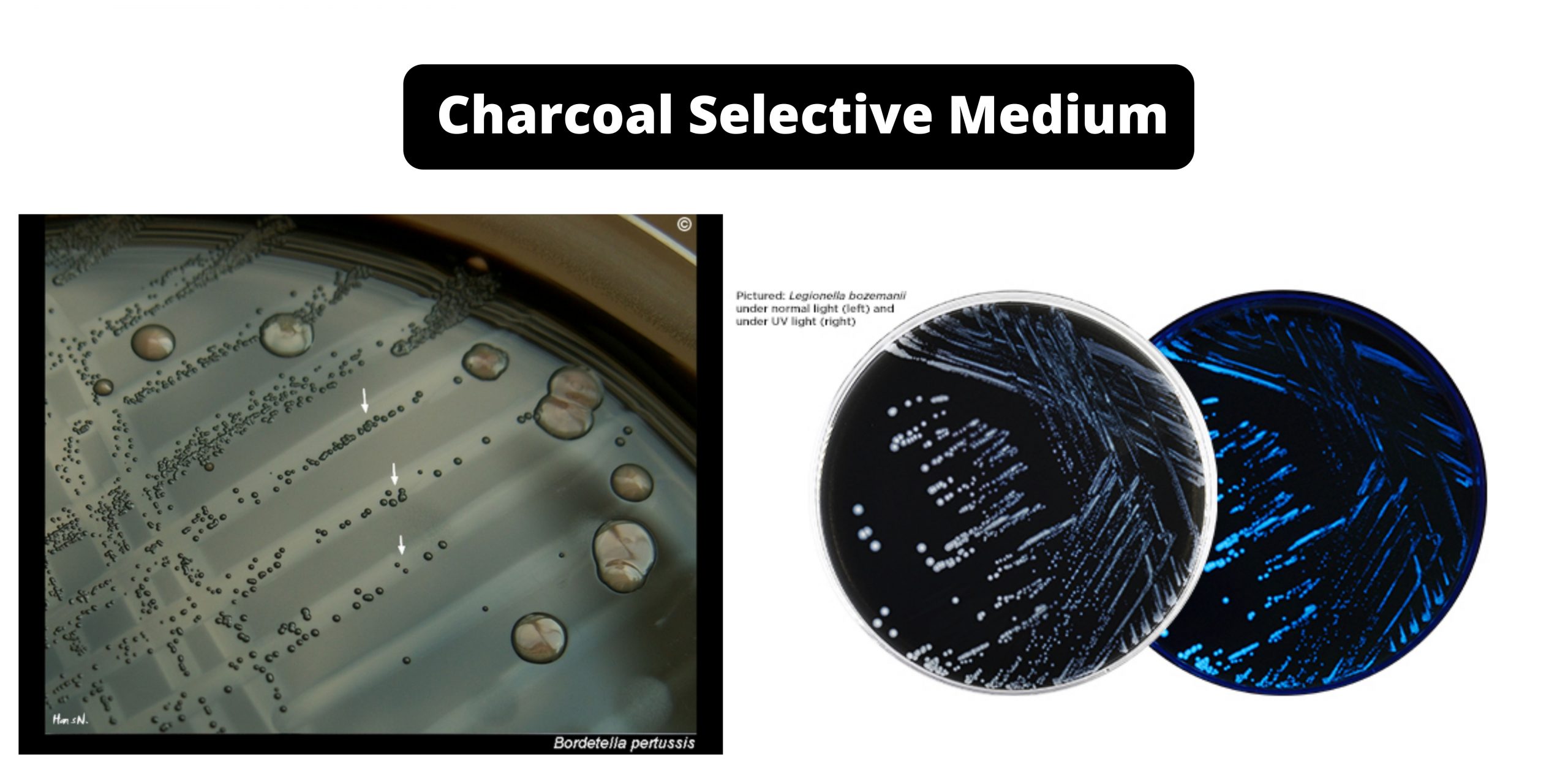
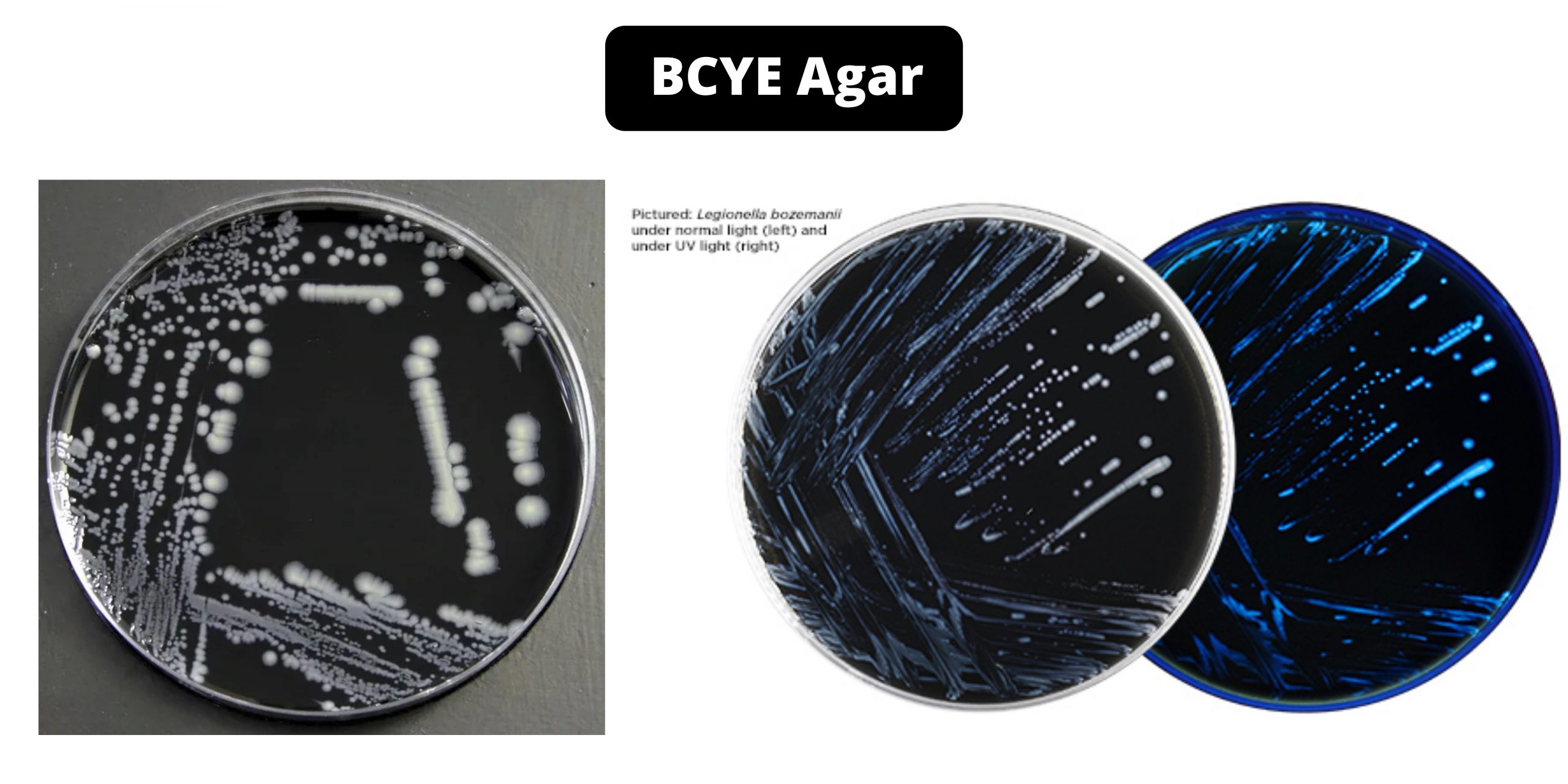
YEPD Agar – Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
Yeasts, unicellular eukaryotes, are a well-studied model organism in molecular genomics. They are chemoorganotrophs because they use organic compounds for energy. Yeast extract peptone, or YEPD), Growth Agar is used to maintain and propagate yeasts. YPD is a complete medium that allows for yeast growth.