Applications of Fluorescence Spectroscopy
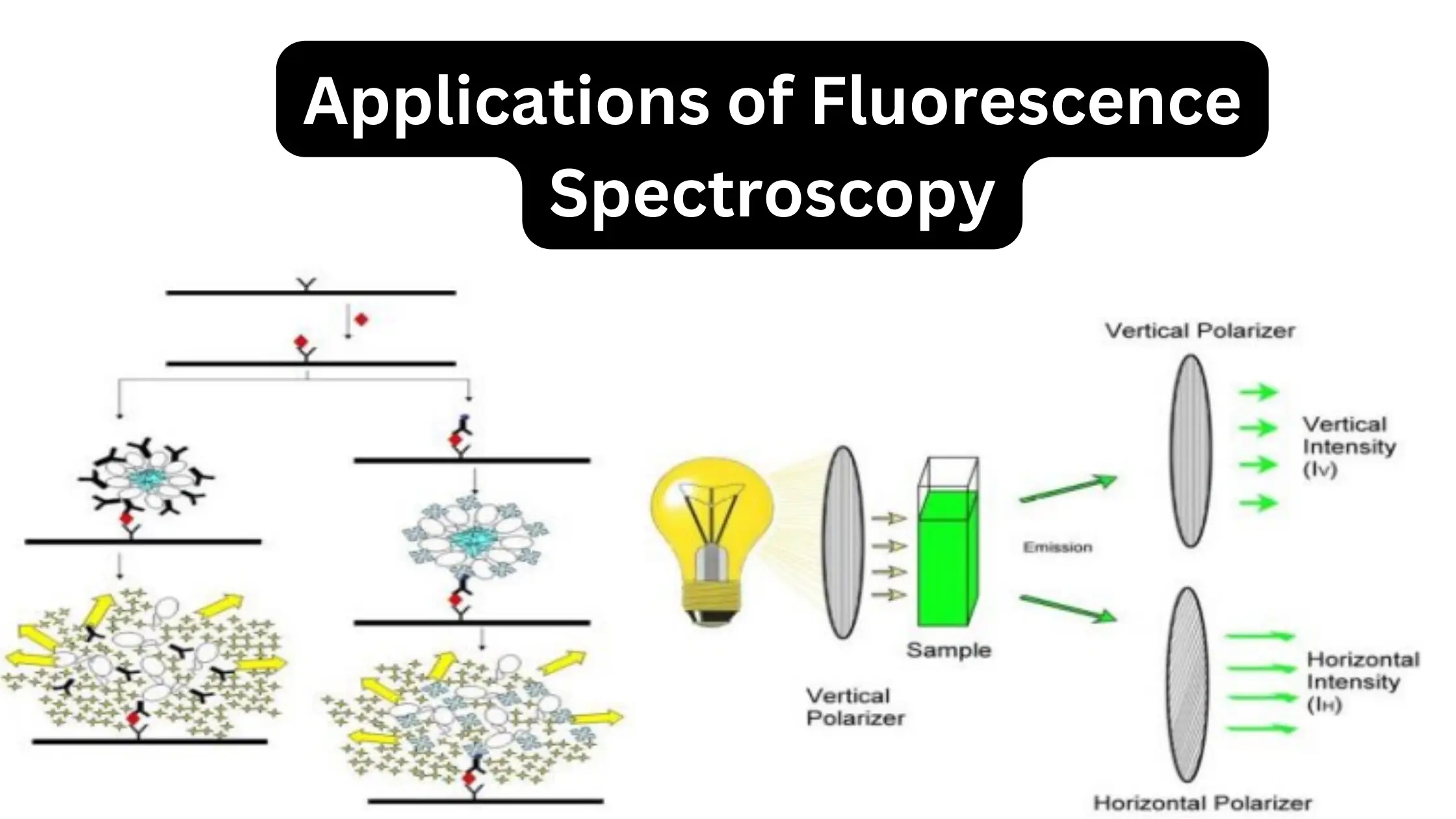
Fluorescence Spectroscopy is an analytical method that studies the fluorescence emitted by a sample when it is excited by light (often UV or visible). Principle of Fluorescence Spectroscopy Applications of Fluorescence Spectroscopy in inorganic chemistry Special fluorimetric applications