Homogenizer – Principle, Parts, Types, Procedure, Uses
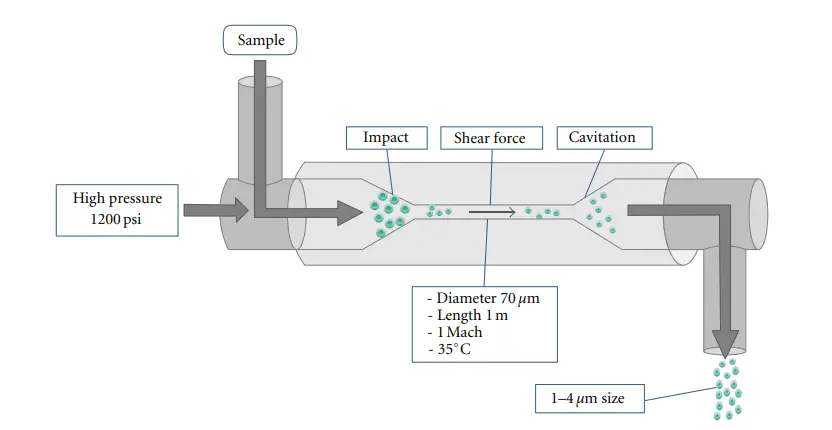
Homogenizer Definition A homogenizer is a device used to mix, emulsify, and evenly distribute particles in liquids, creating a uniform and homogeneous mixture. Principle of Homogenizer Parts of Homogenizer 1. Homogenizing Valve – It is the main part where actual homogenization occur, the liquid is forced by a very small gap creating high velocity & … Read more