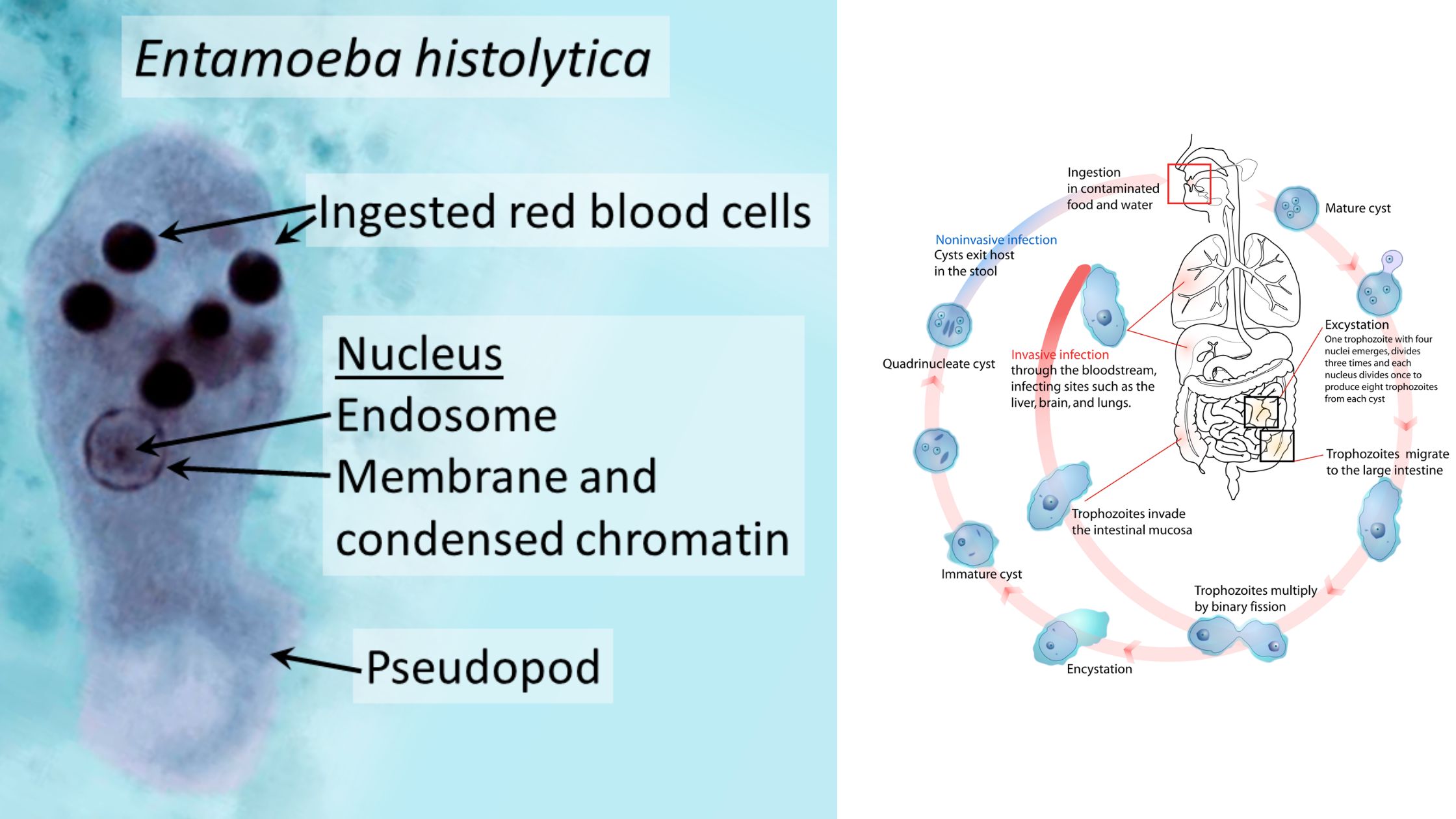
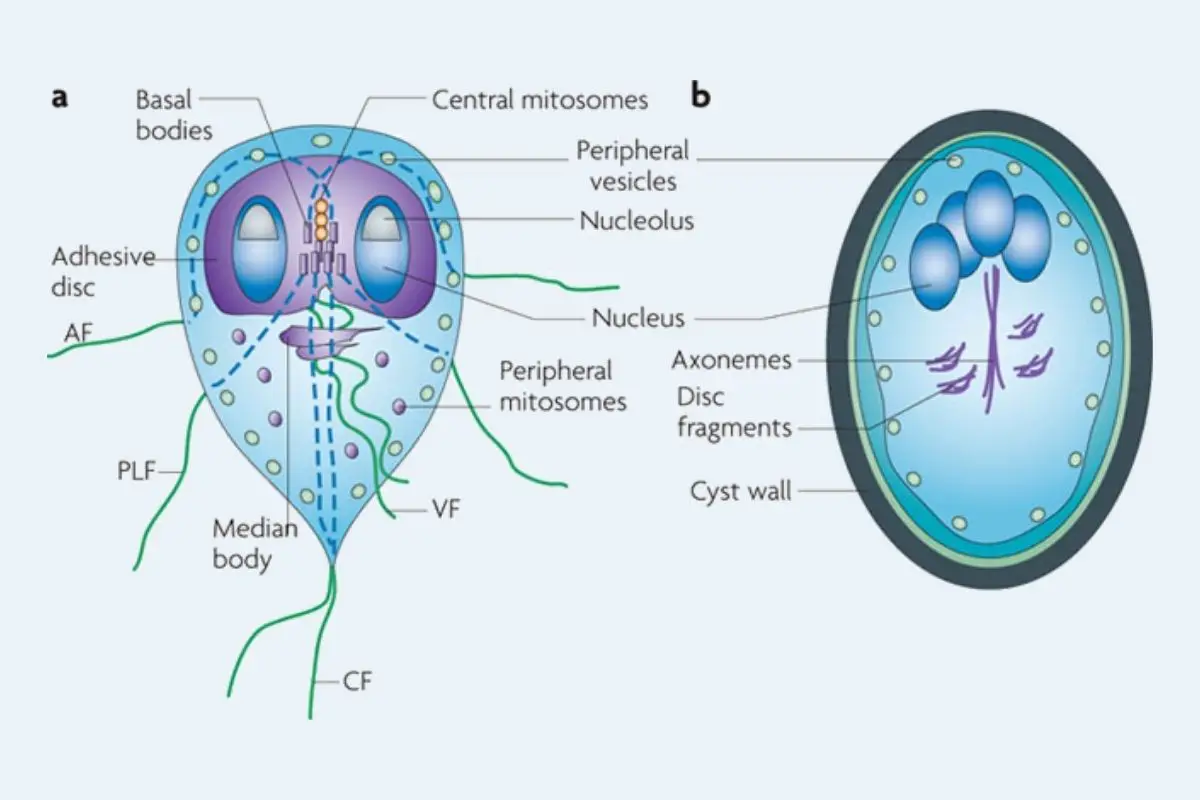
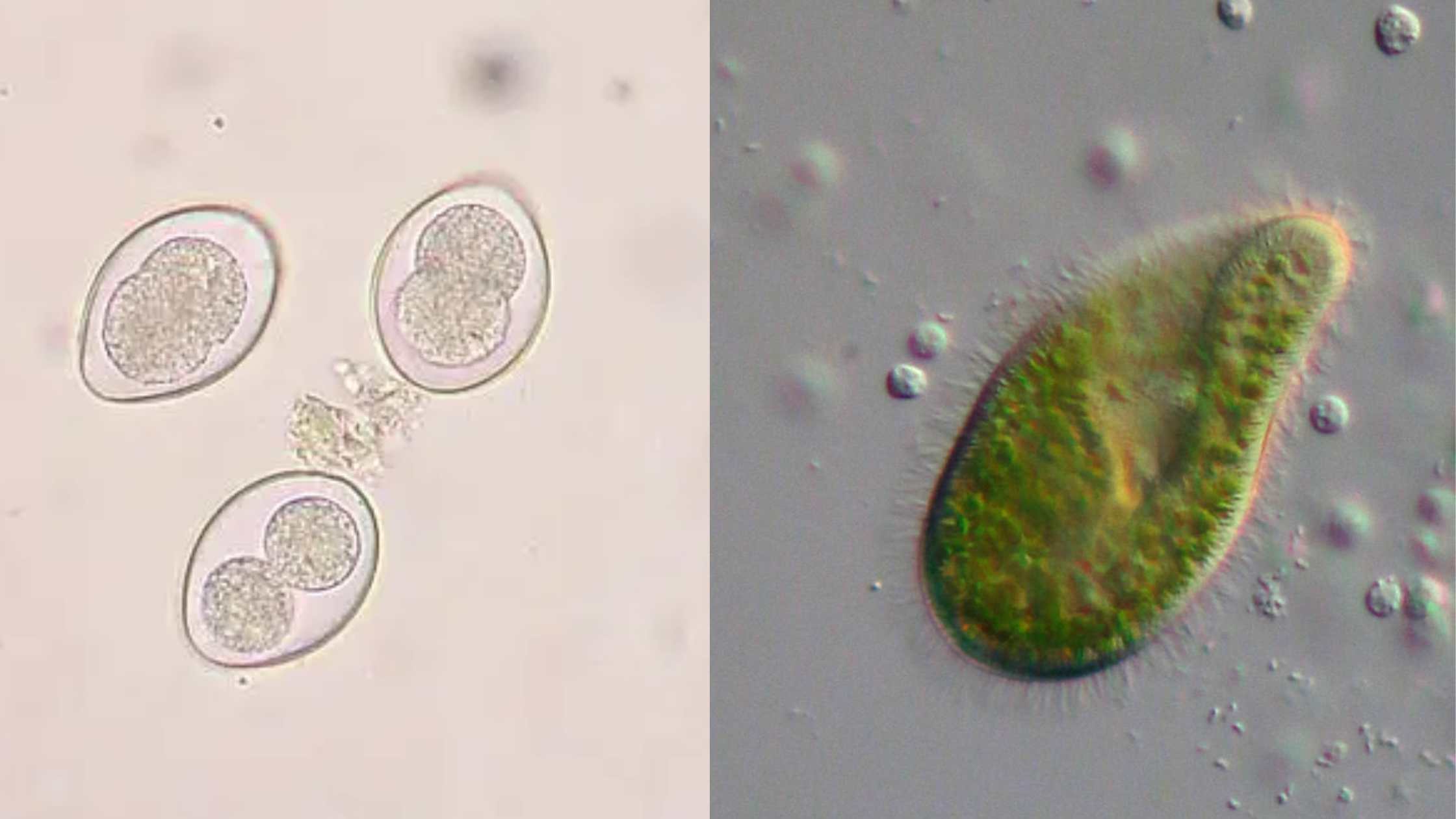
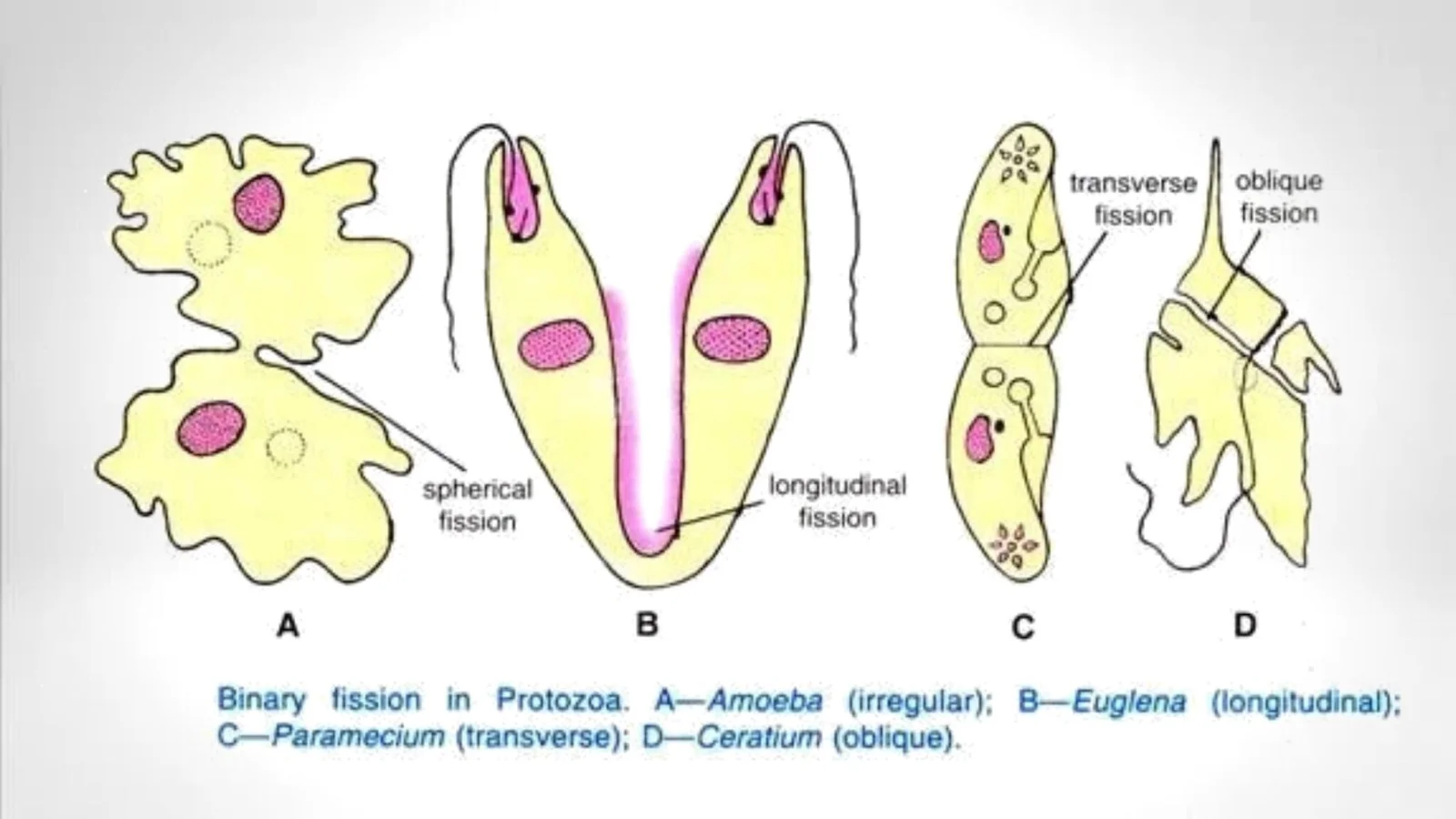
Euglena – Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Reproduction, Importance
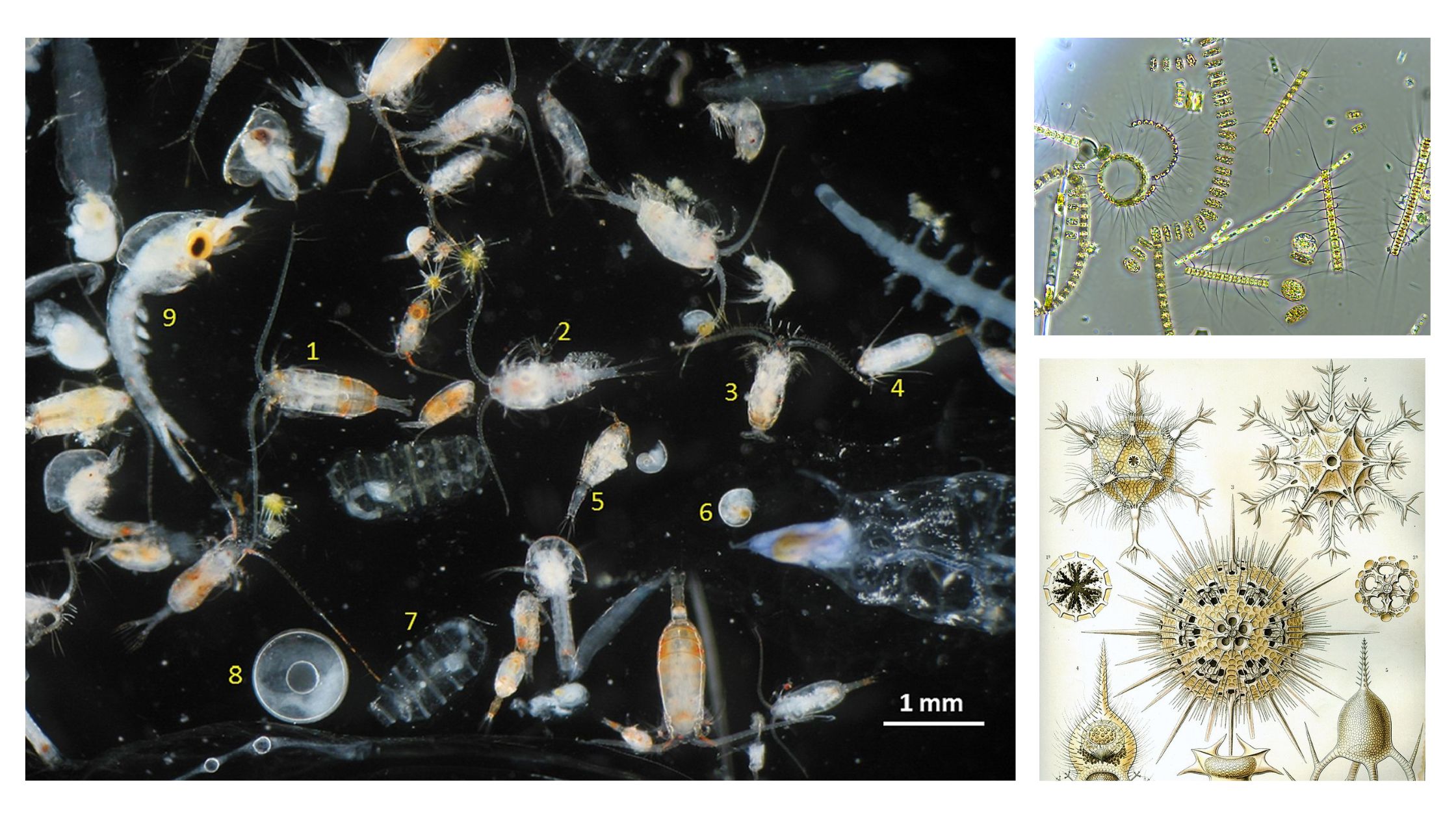
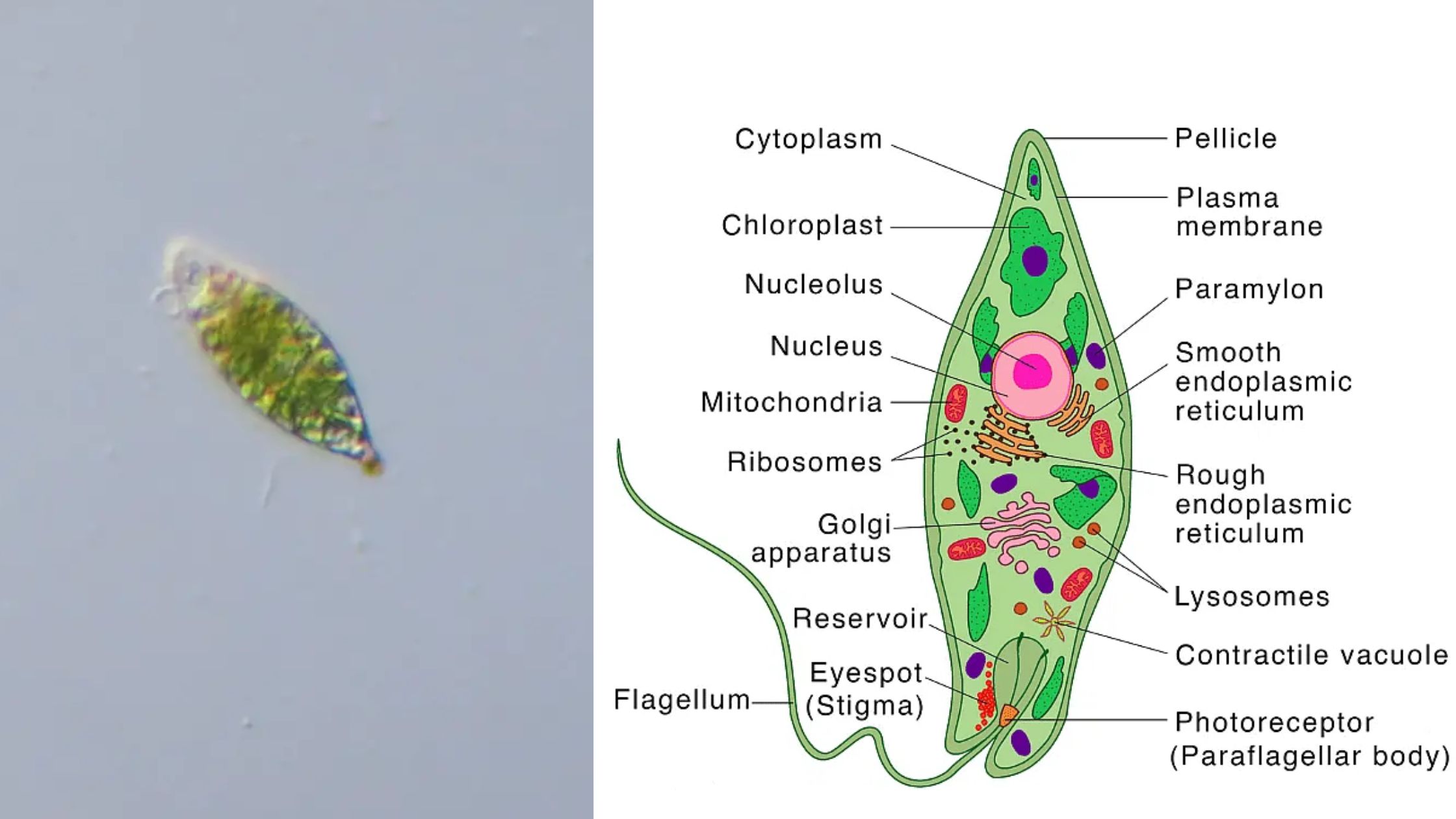
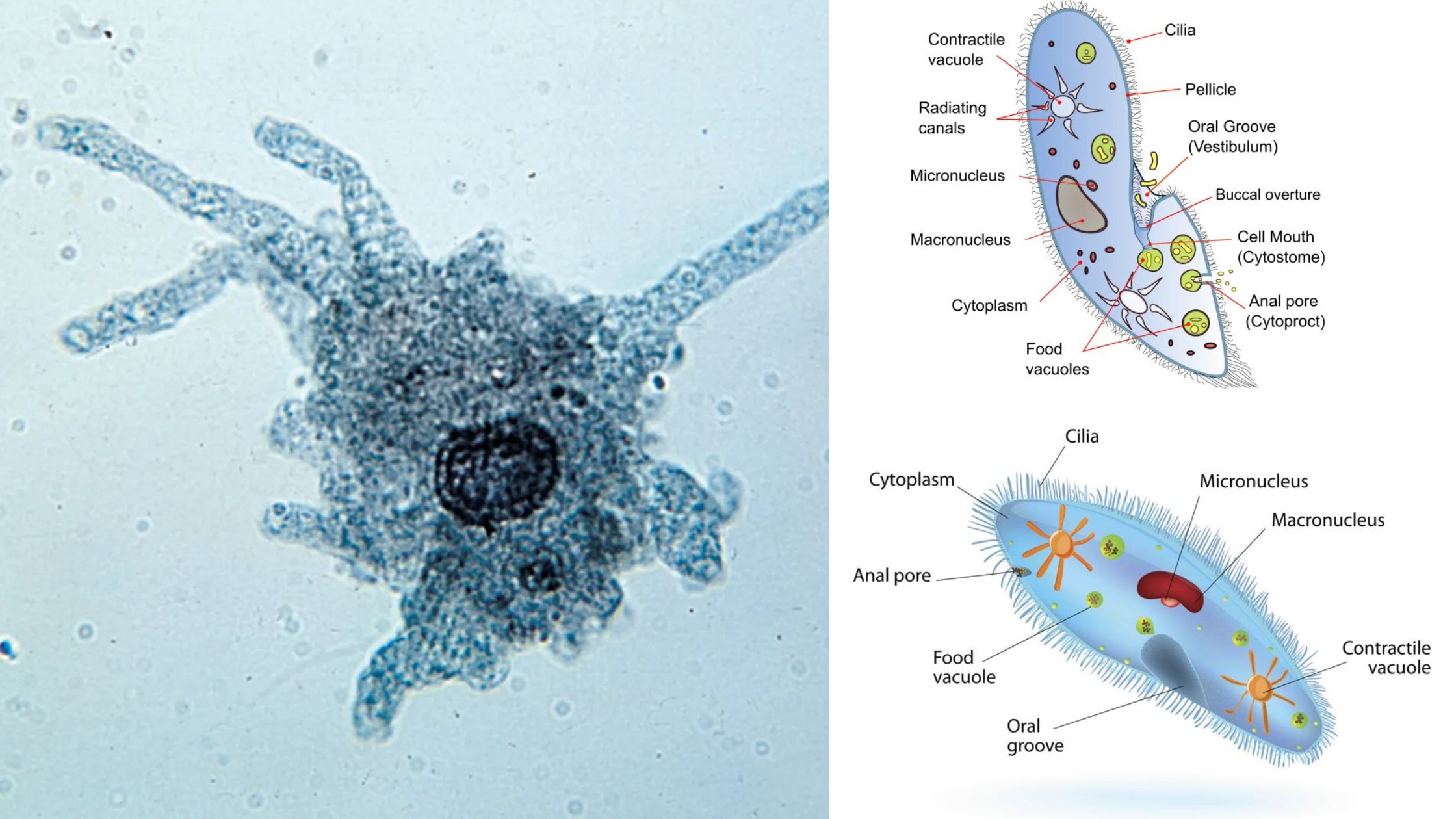
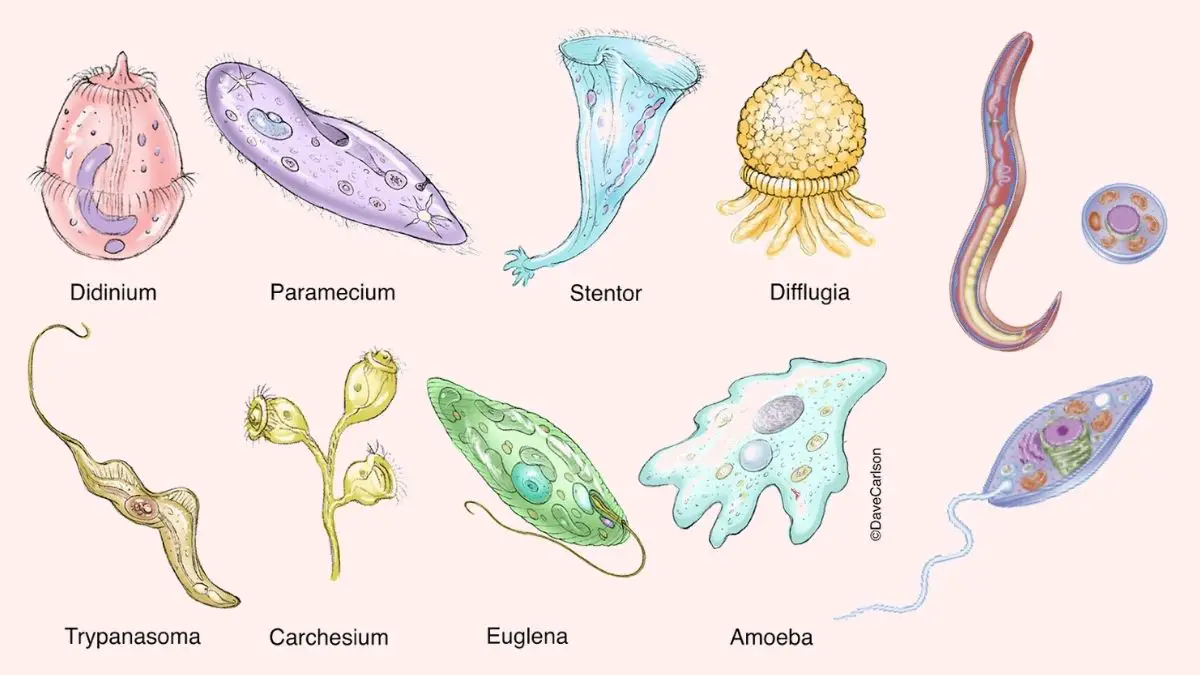
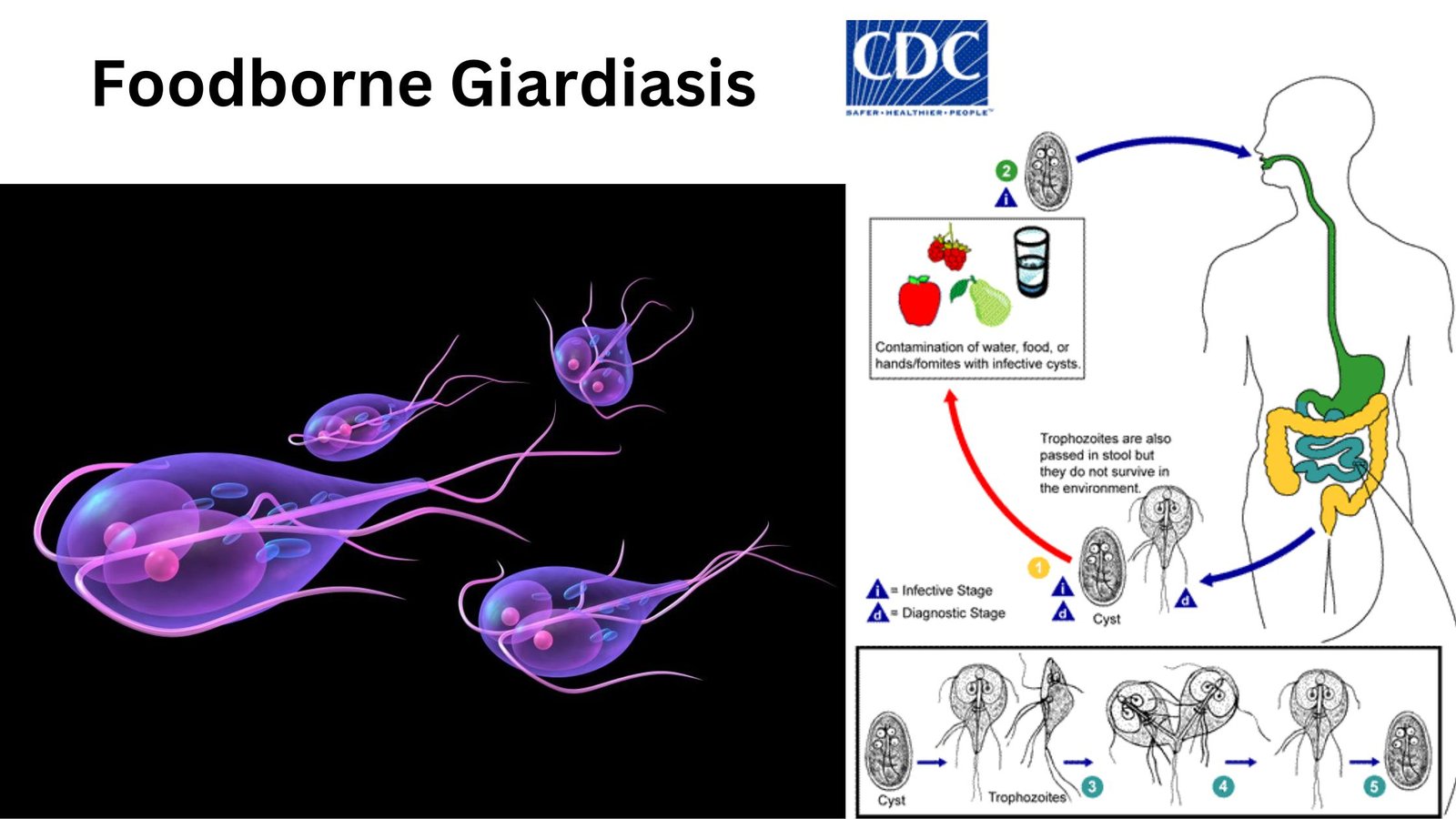
What is Euglena? Euglena is a unicellular microscopic organism which belongs to the group of protists and it shows the characteristics of both plant and animal. It is generally found in fresh water bodies like ponds lakes and marshy places. It is a eukaryotic organism and the cell contains nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. … Read more