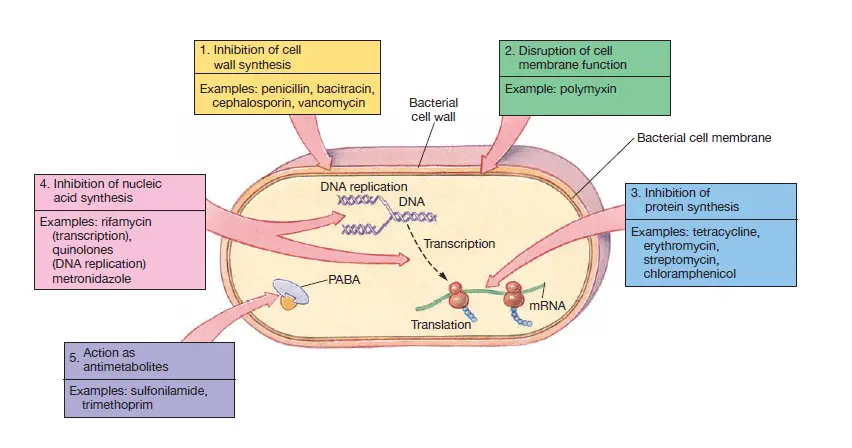
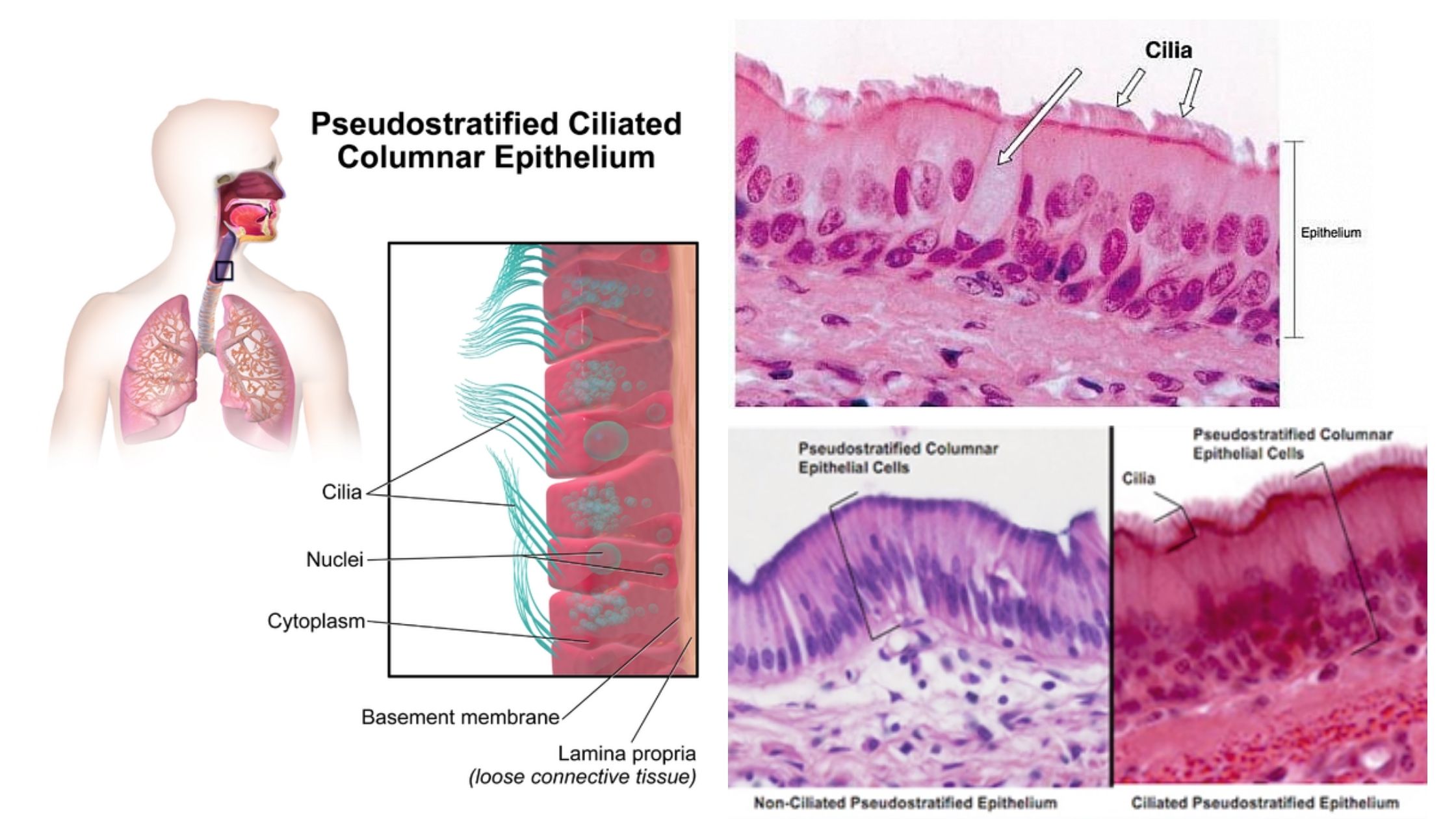
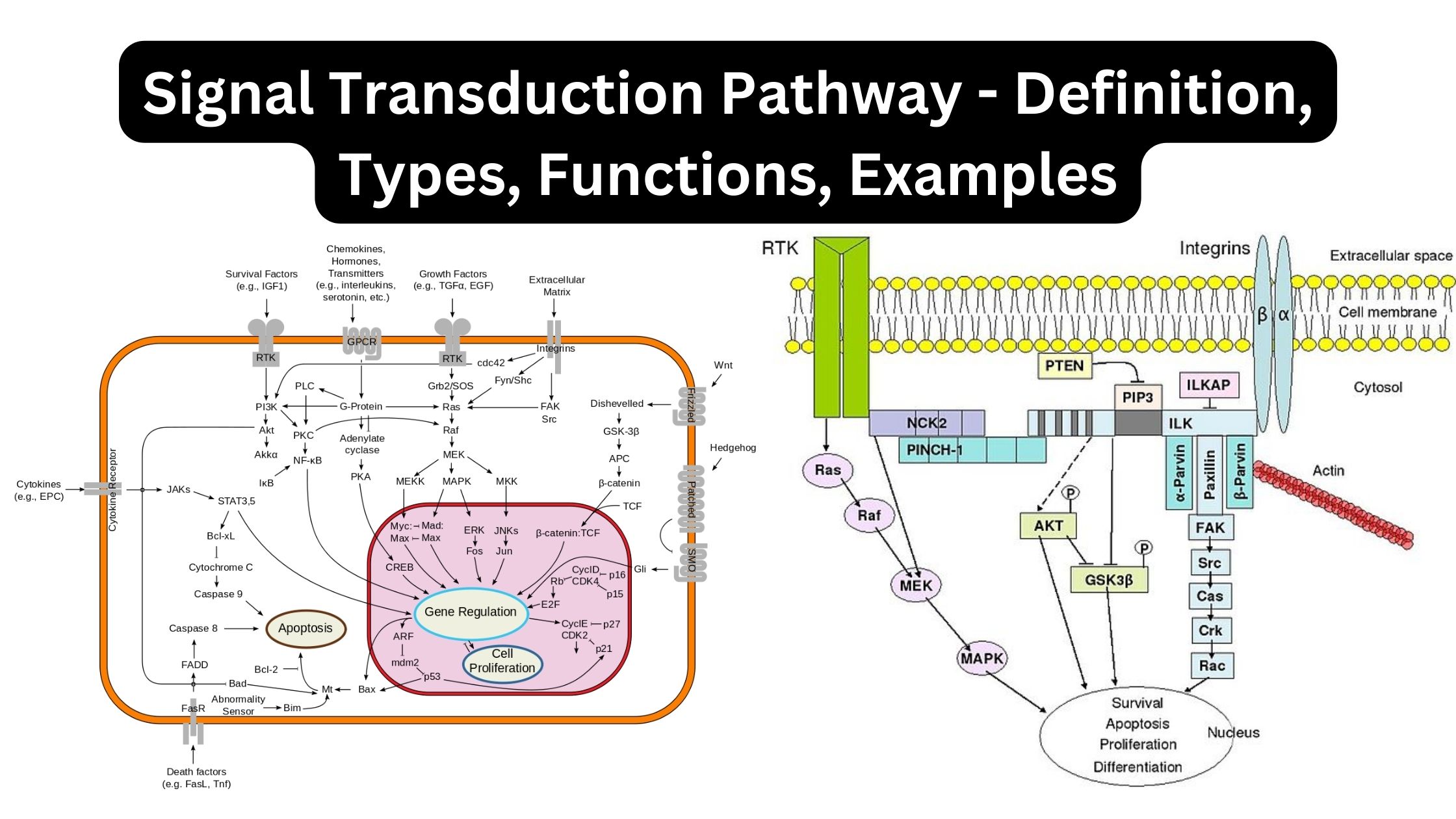
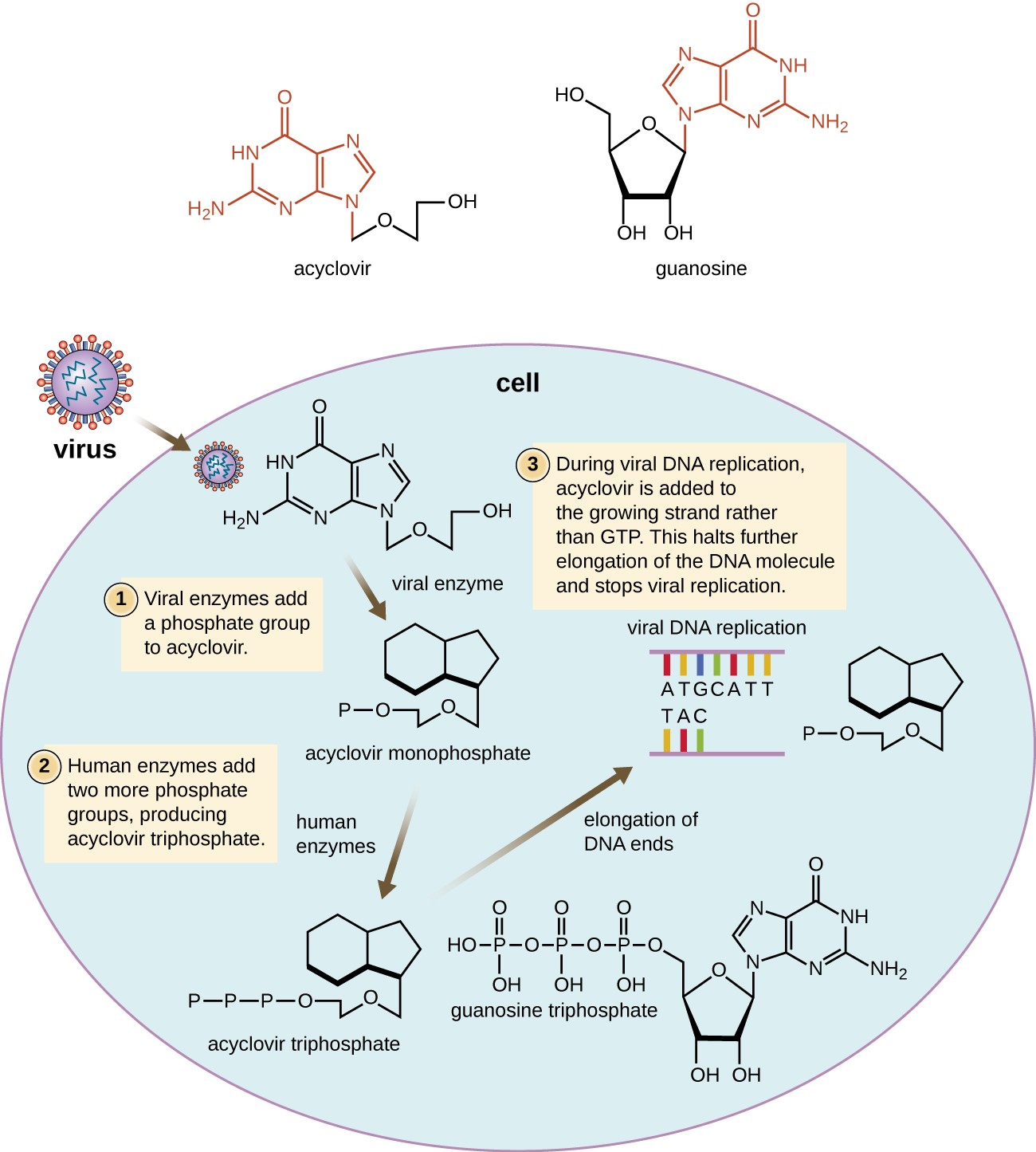
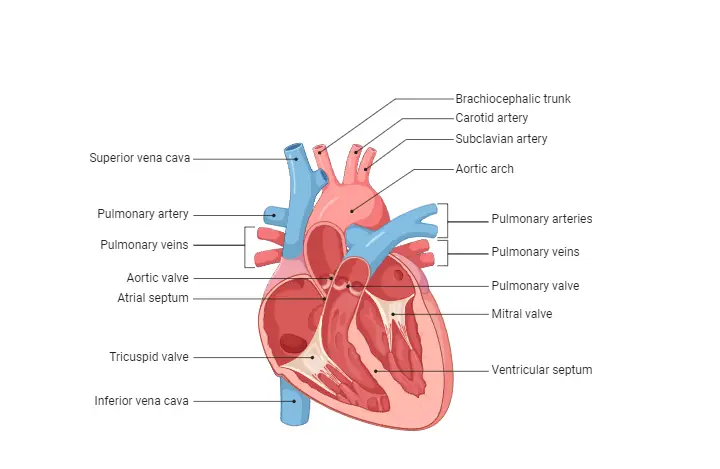
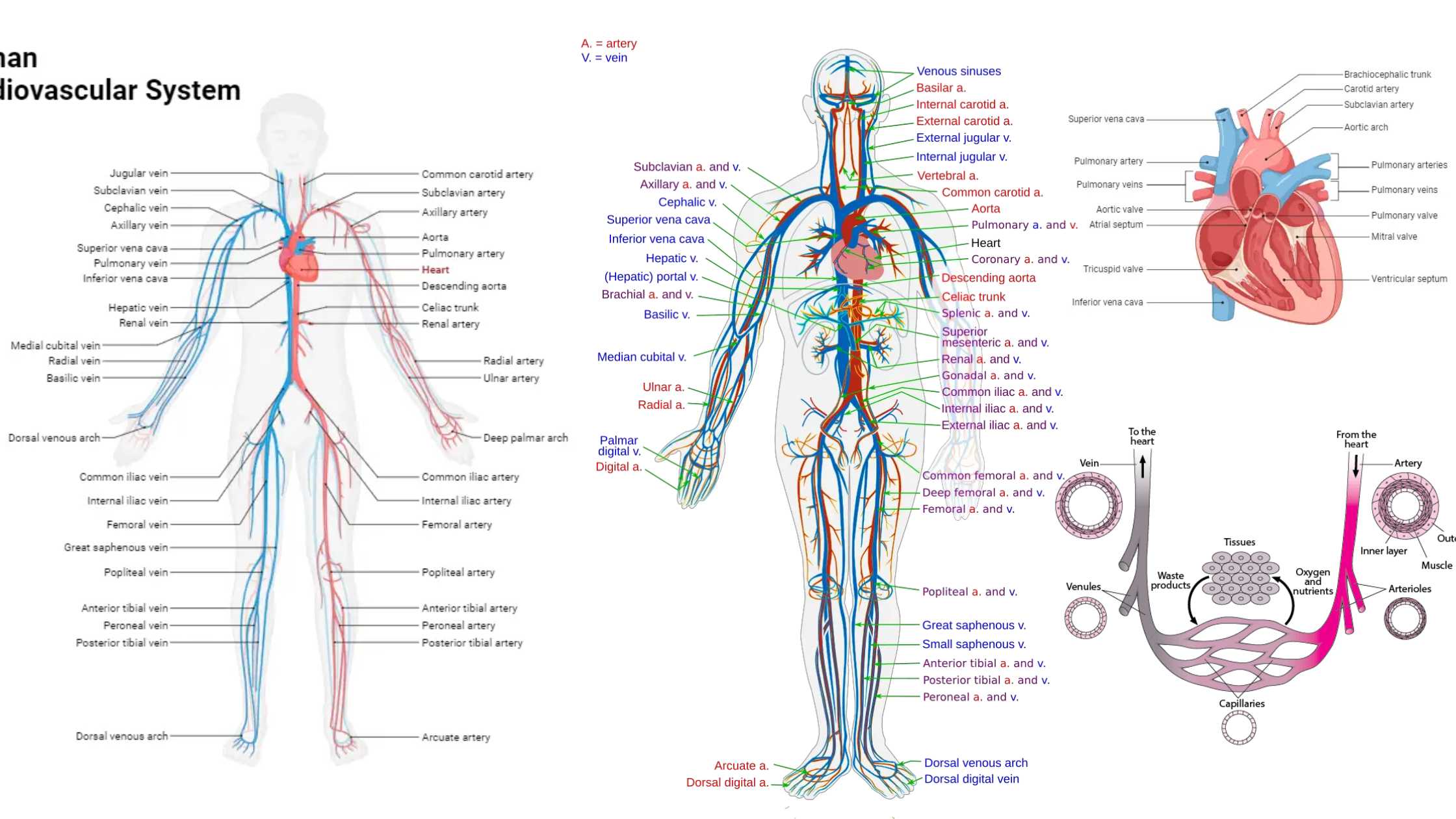
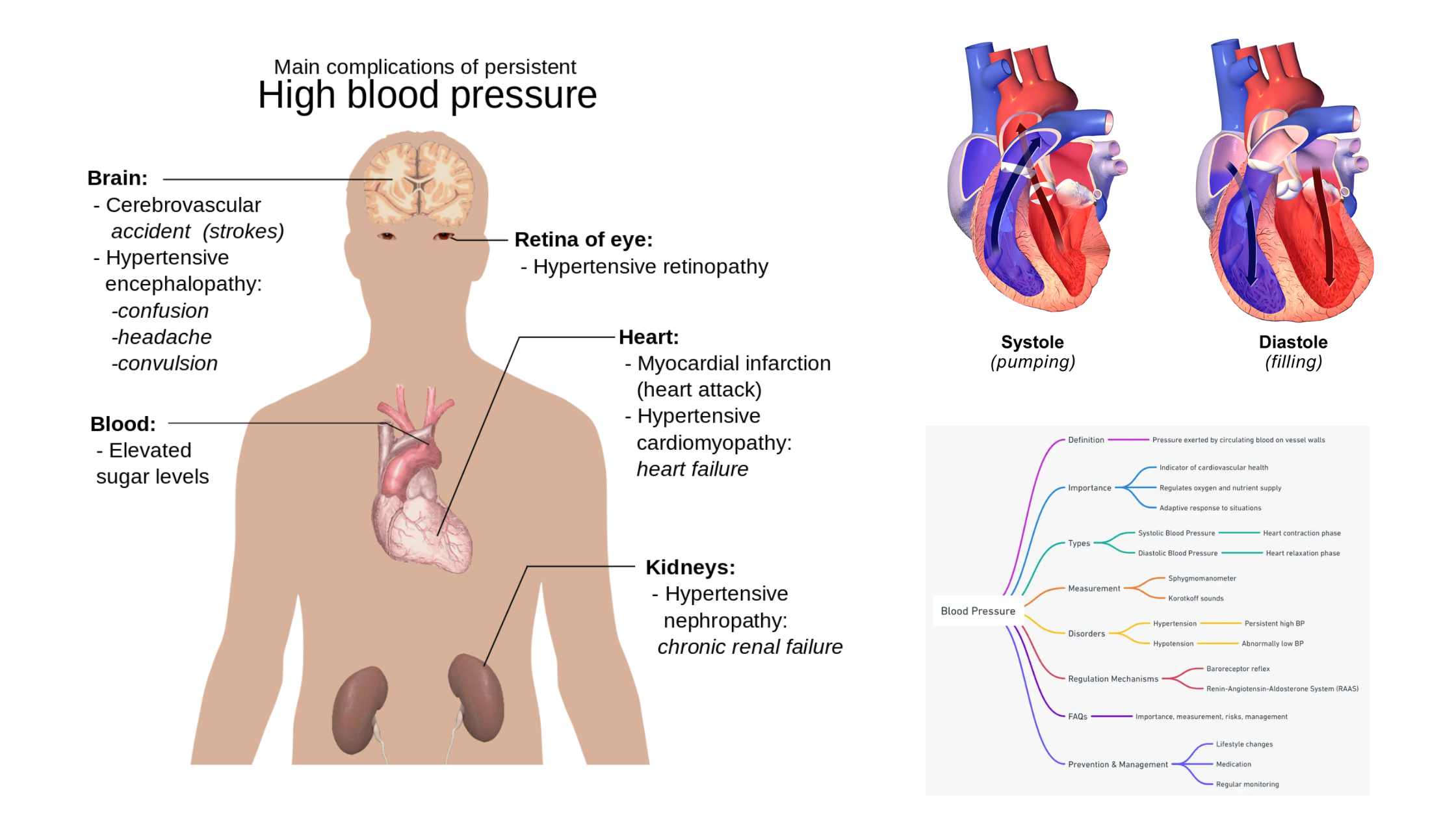
Transmission of Diseases
Maintain an infectious disease in a human population the pathogens must need to be transmitted from one host or source to another. In Biology the term transmission is refers to the passing of a pathogen from one individual to another individual which can cause a serious disease or infection. The transmission of disease is occurred … Read more