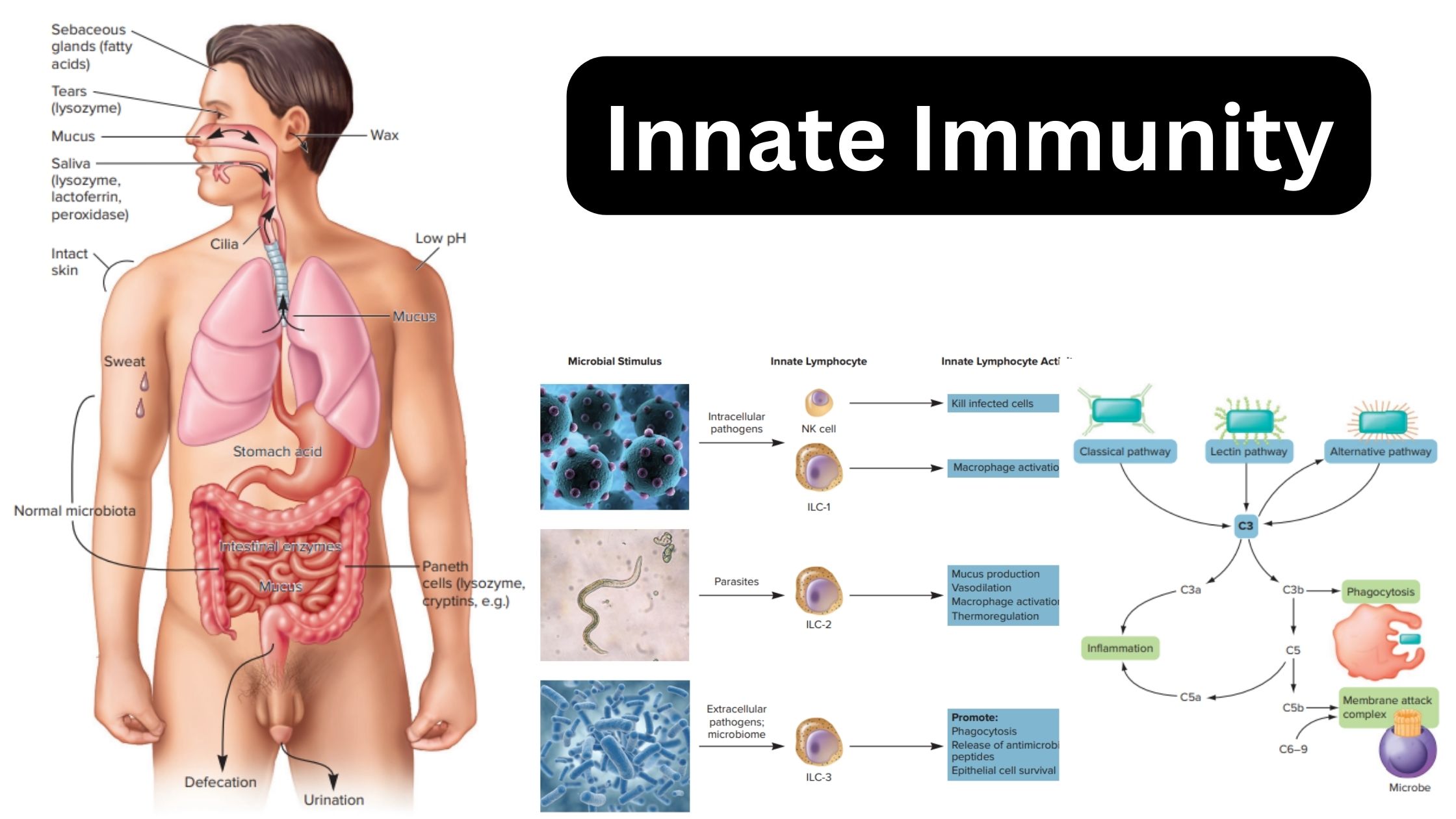
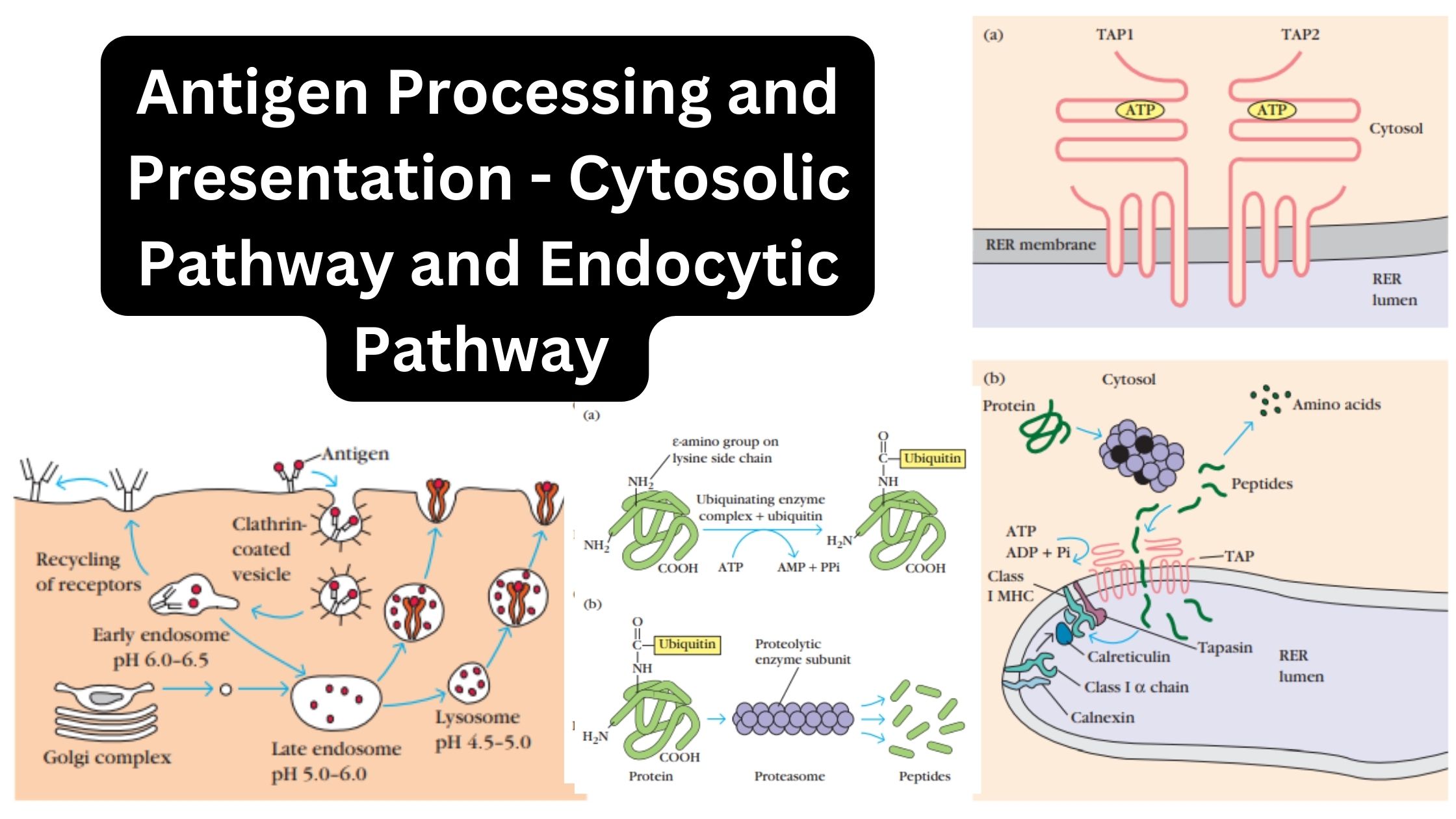
Mast cell – Definition, Structure, Functions
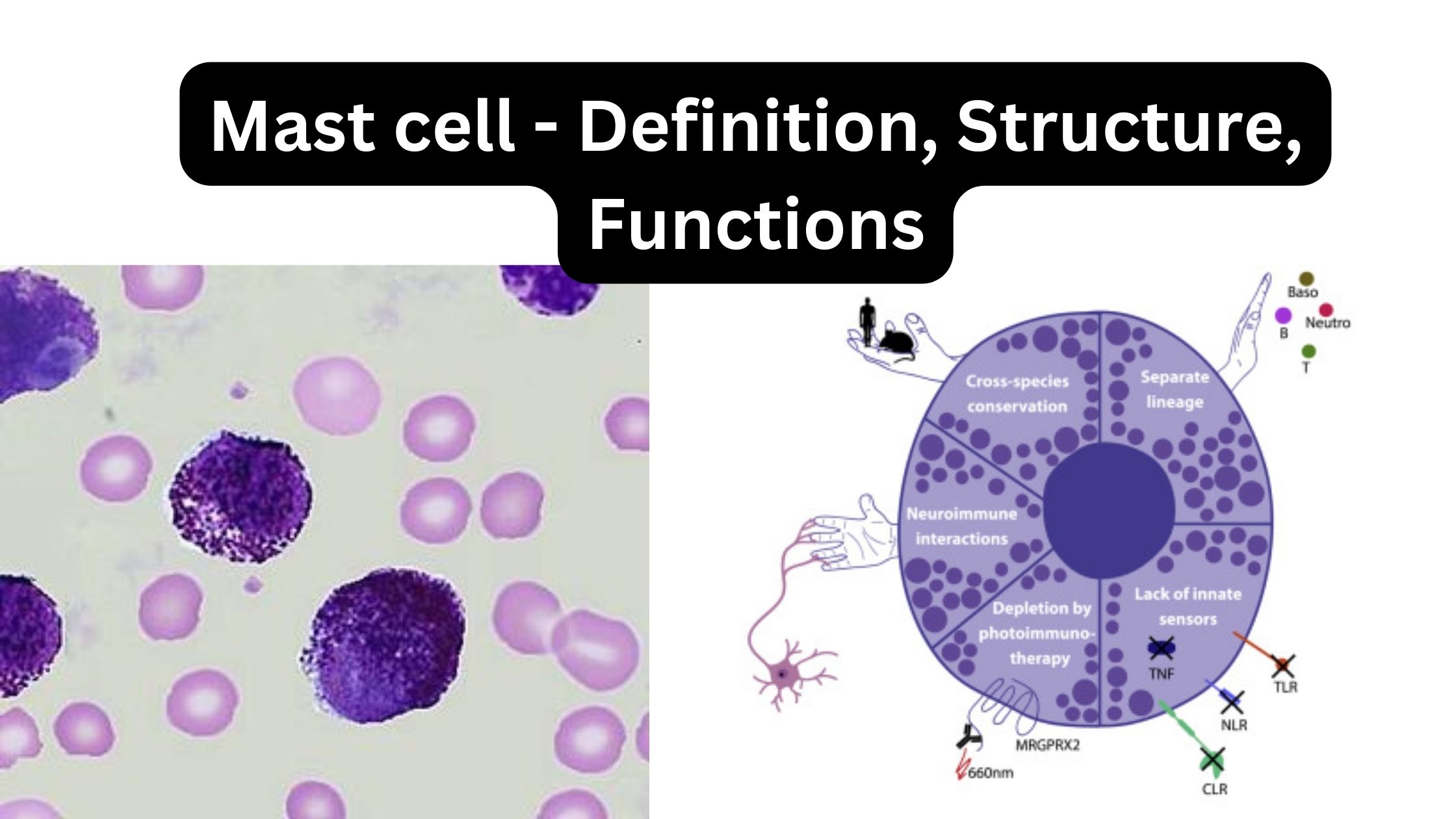
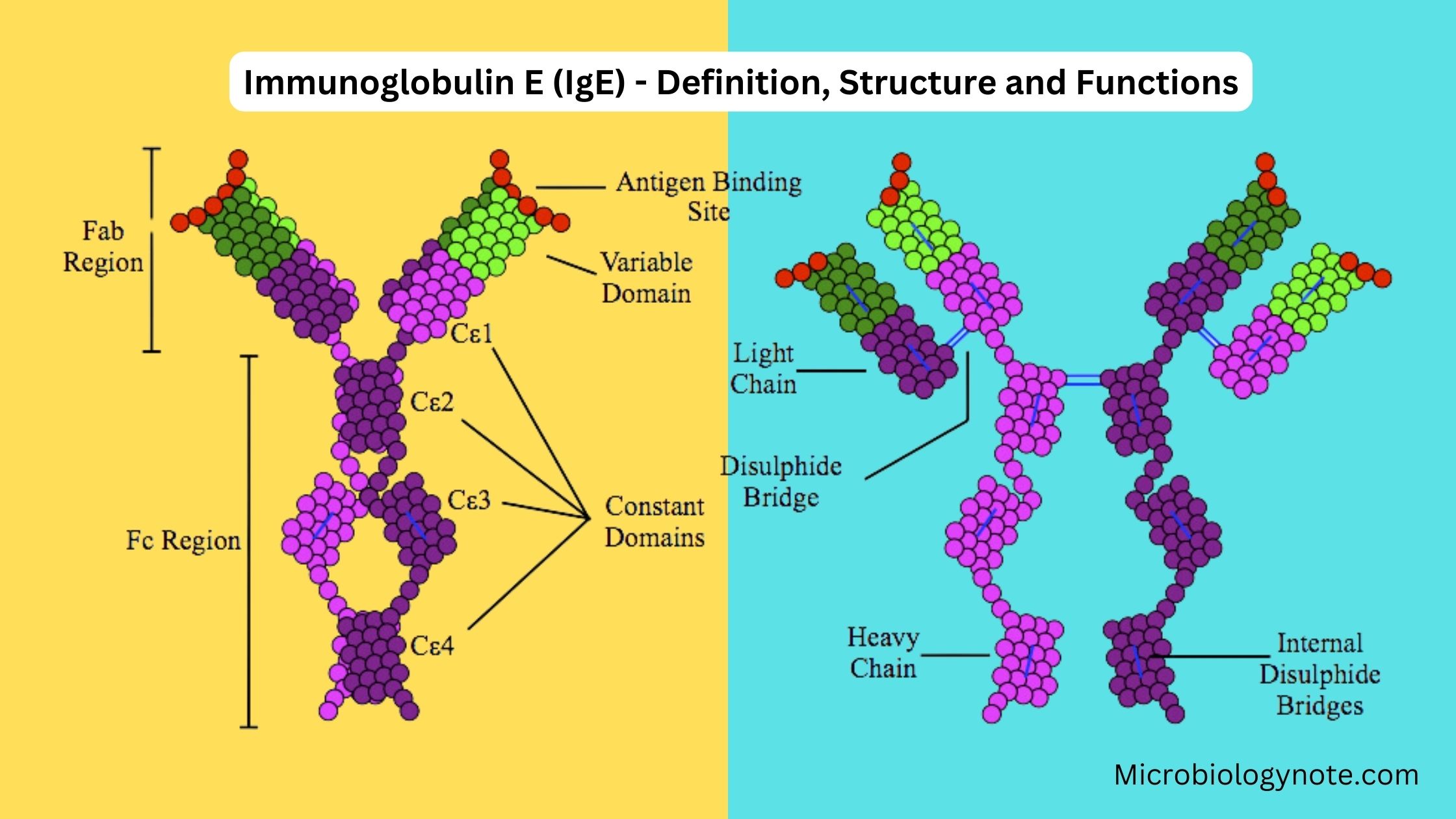
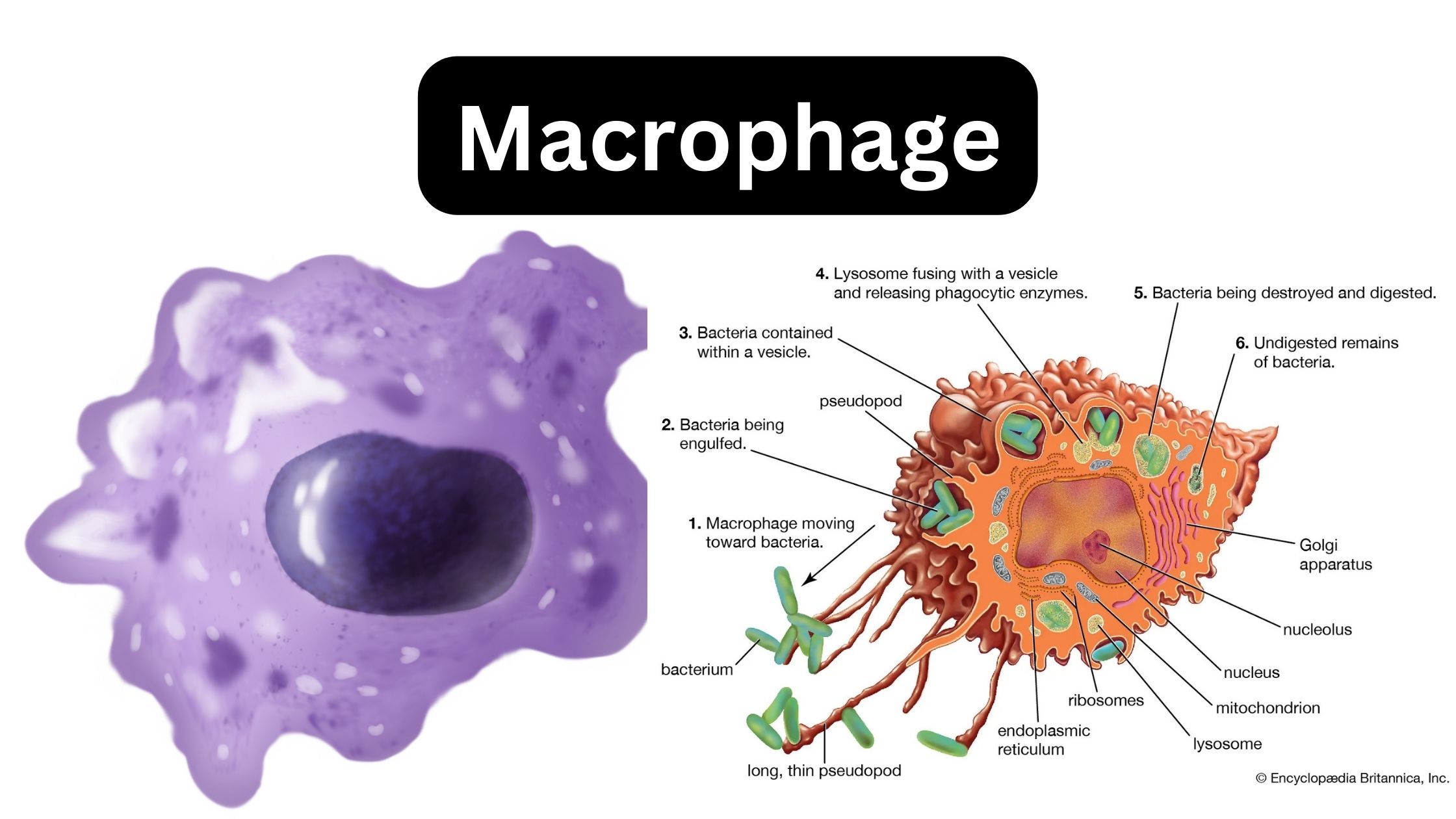
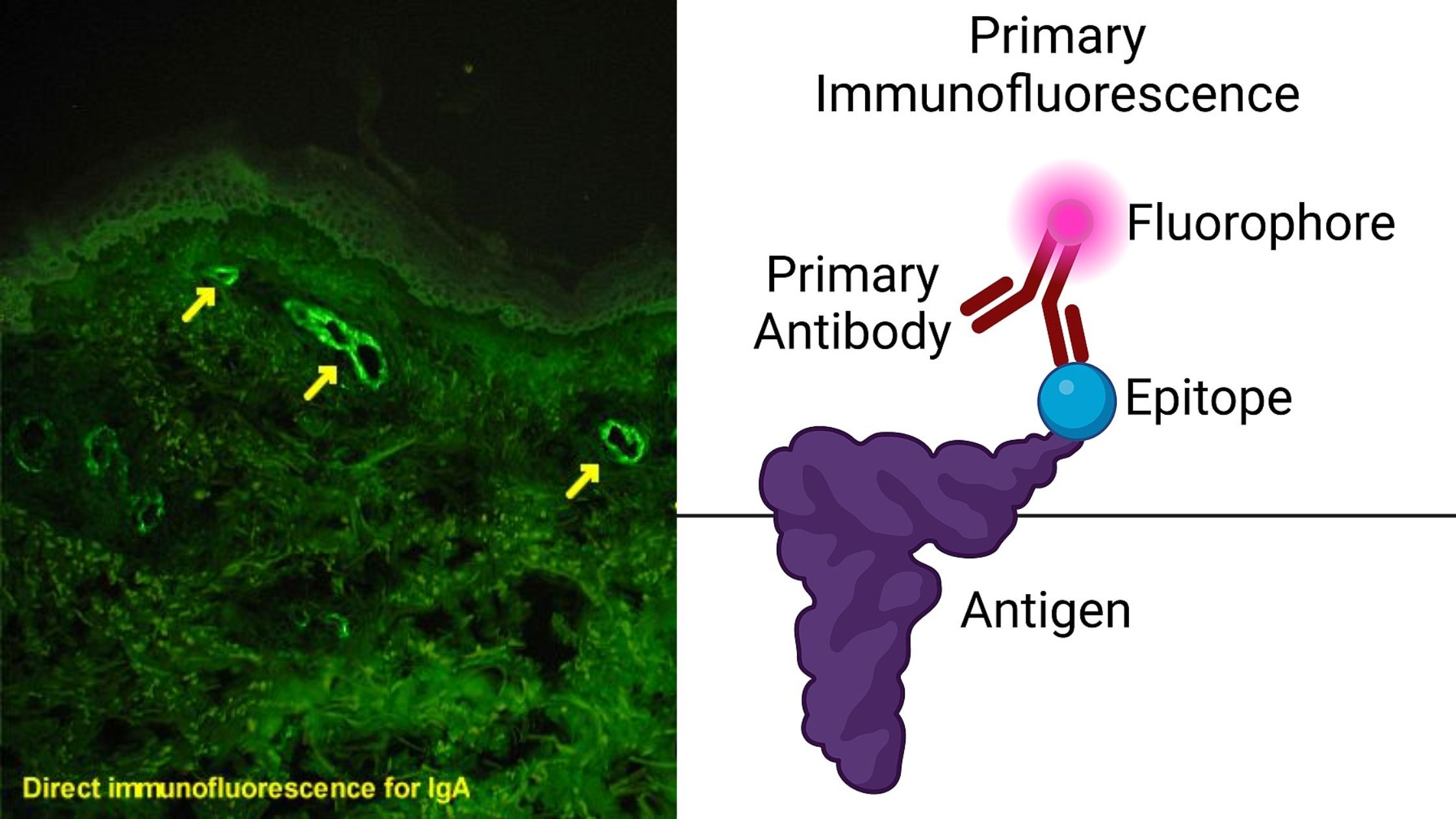
What are mast cells? Definition of mast cells Mast cells are a type of immune cell found in connective tissue that are involved in allergic reactions, immune responses, inflammation, and wound healing. They contain granules rich in histamine and play a crucial role in the body’s defense against pathogens. Structure of Mast cell Types of … Read more