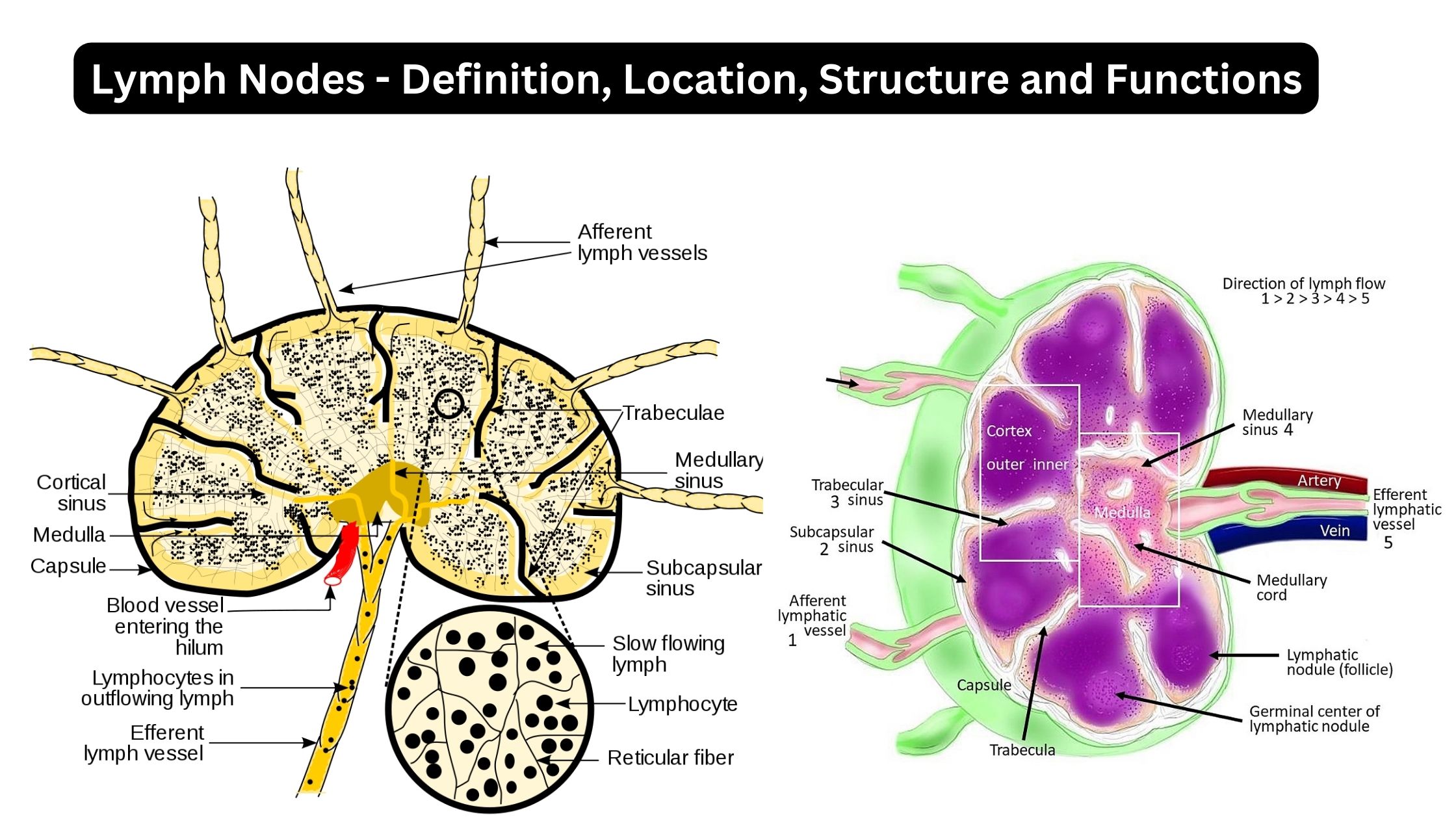
Rh Blood Group System – Definition, Antigens, Antibody
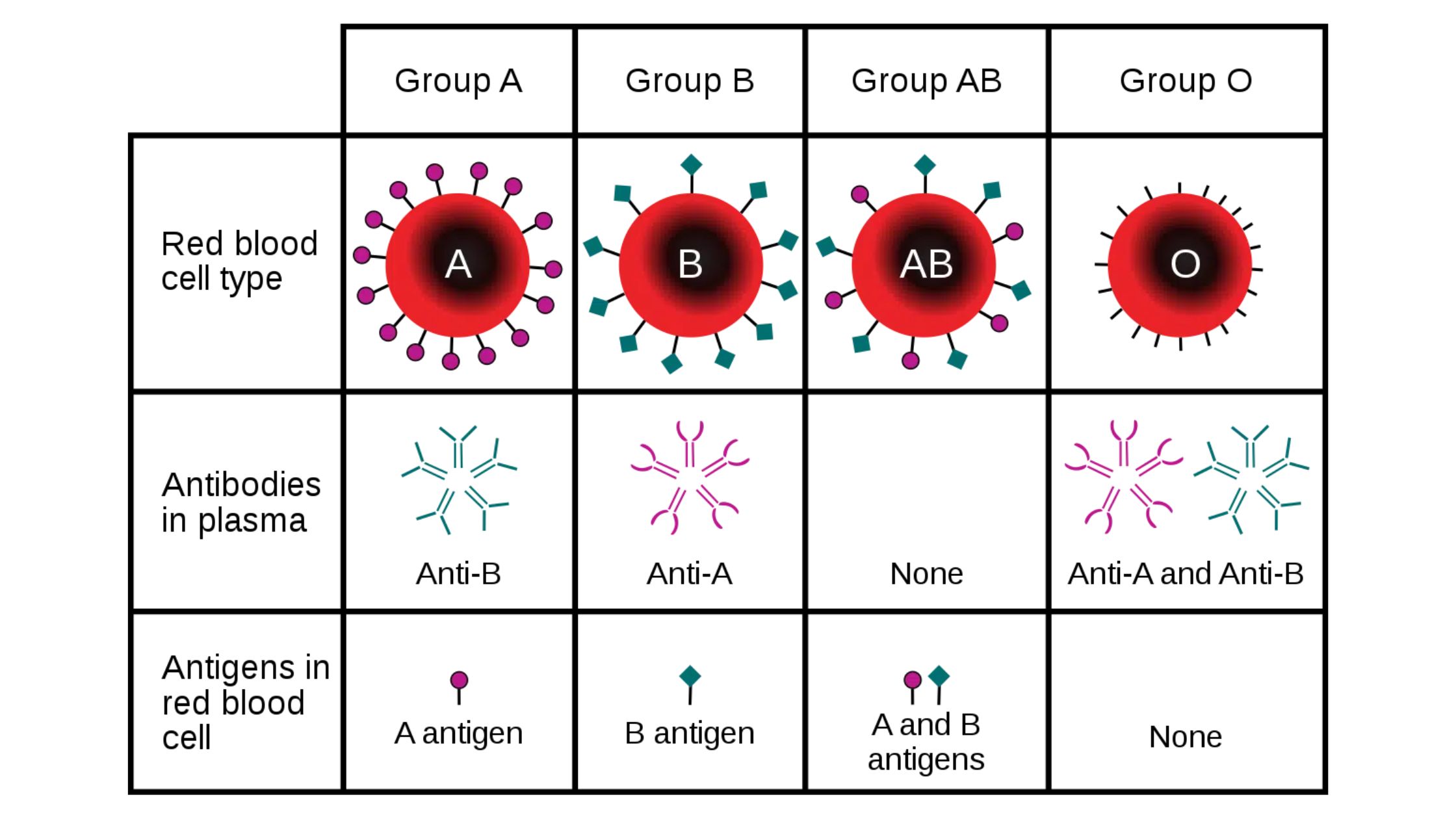
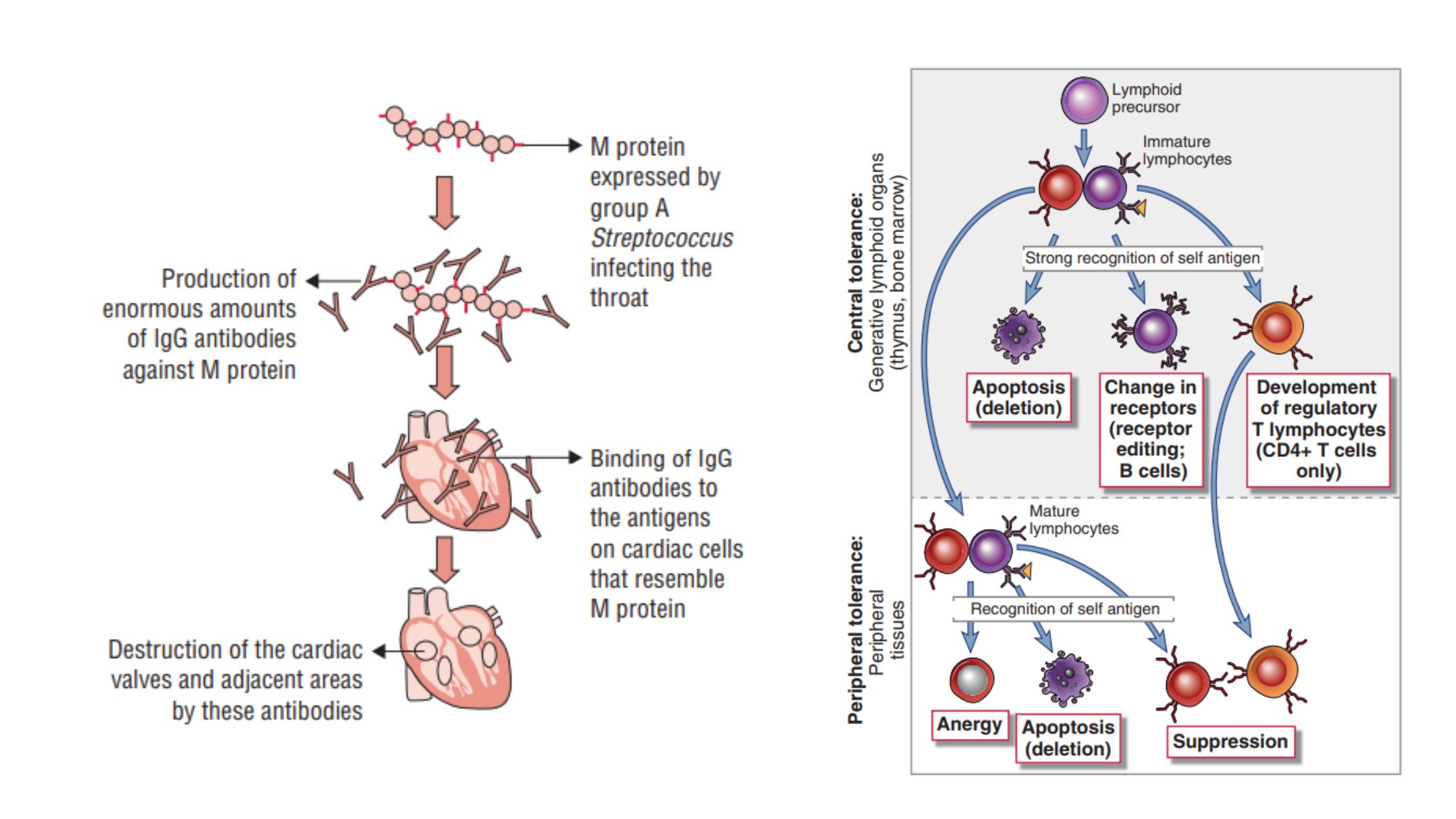
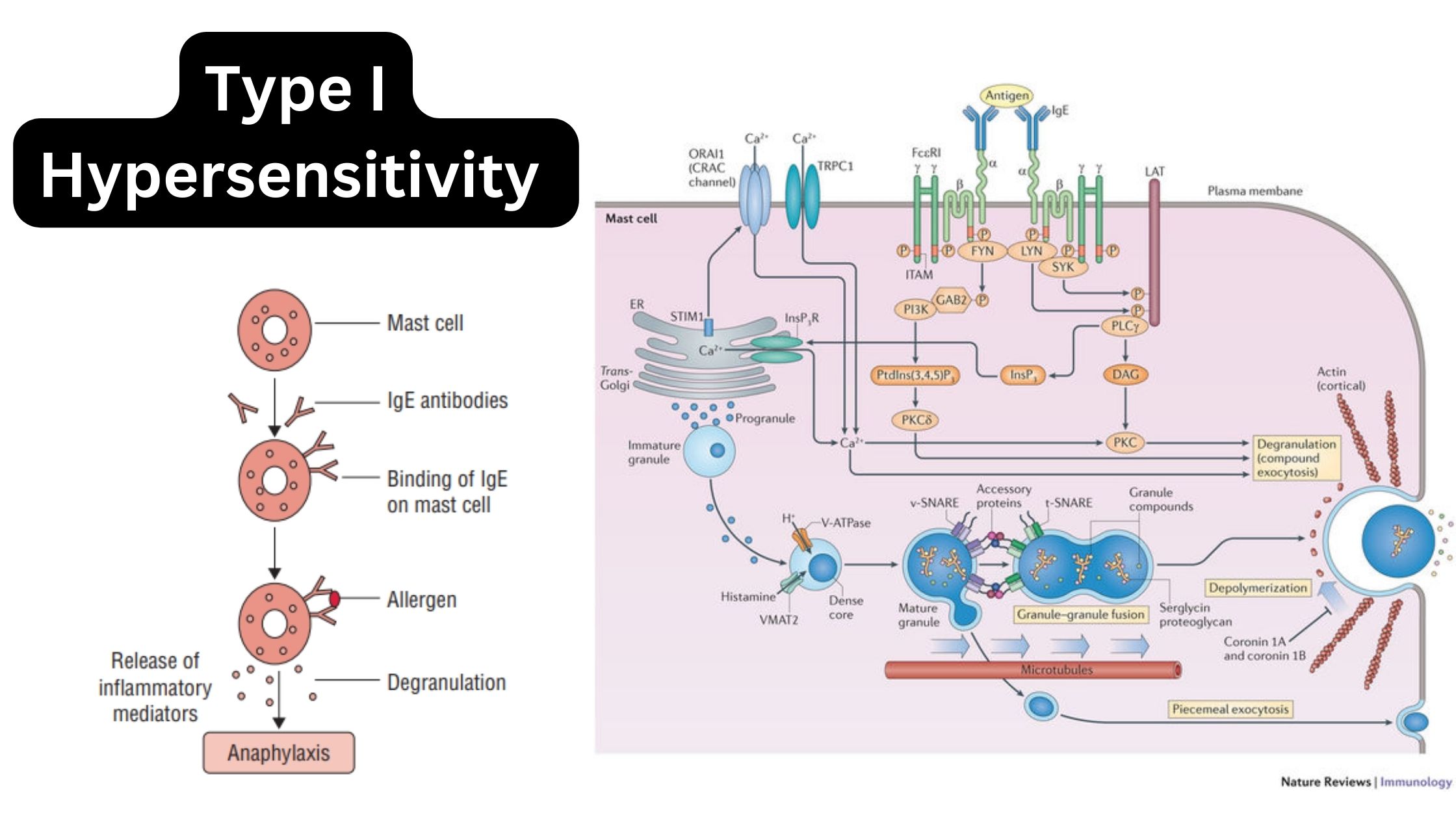
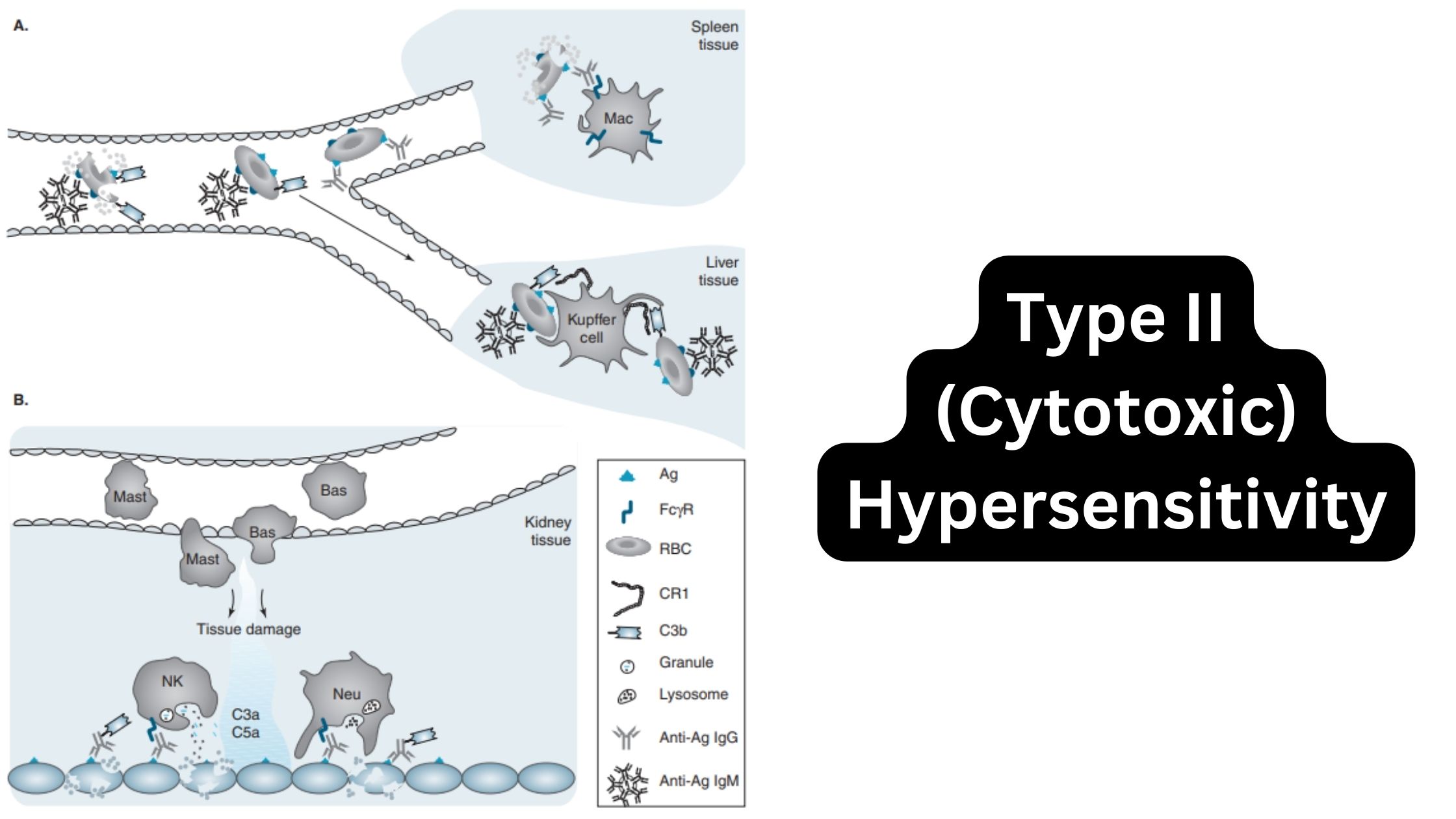
What is The Rh blood group? Nomenclature of Rh blood group Antigens of the Rh blood group The Rh blood group system consists of 49 antigens, with the most significant ones being D, C, E, c, and e. The specificity of most Rh antigens is determined by the sequence of amino acids in the proteins. … Read more