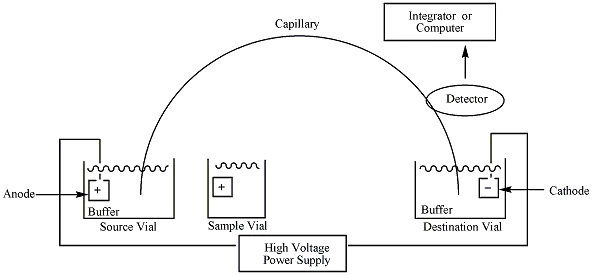
Capillary Electrophoresis – Definition, Principle, Types and Application
Capillary Electrophoresis (CE) is a type of electrophoresis technique that uses a narrow capillary to separate charged molecules (ions) based on their migration towards electrodes under the influence of an electric field. It is a high-resolution and fast method for the analysis of small molecules, DNA, and proteins. The importance of CE lies in its … Read more