Oxidase Test – Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Application
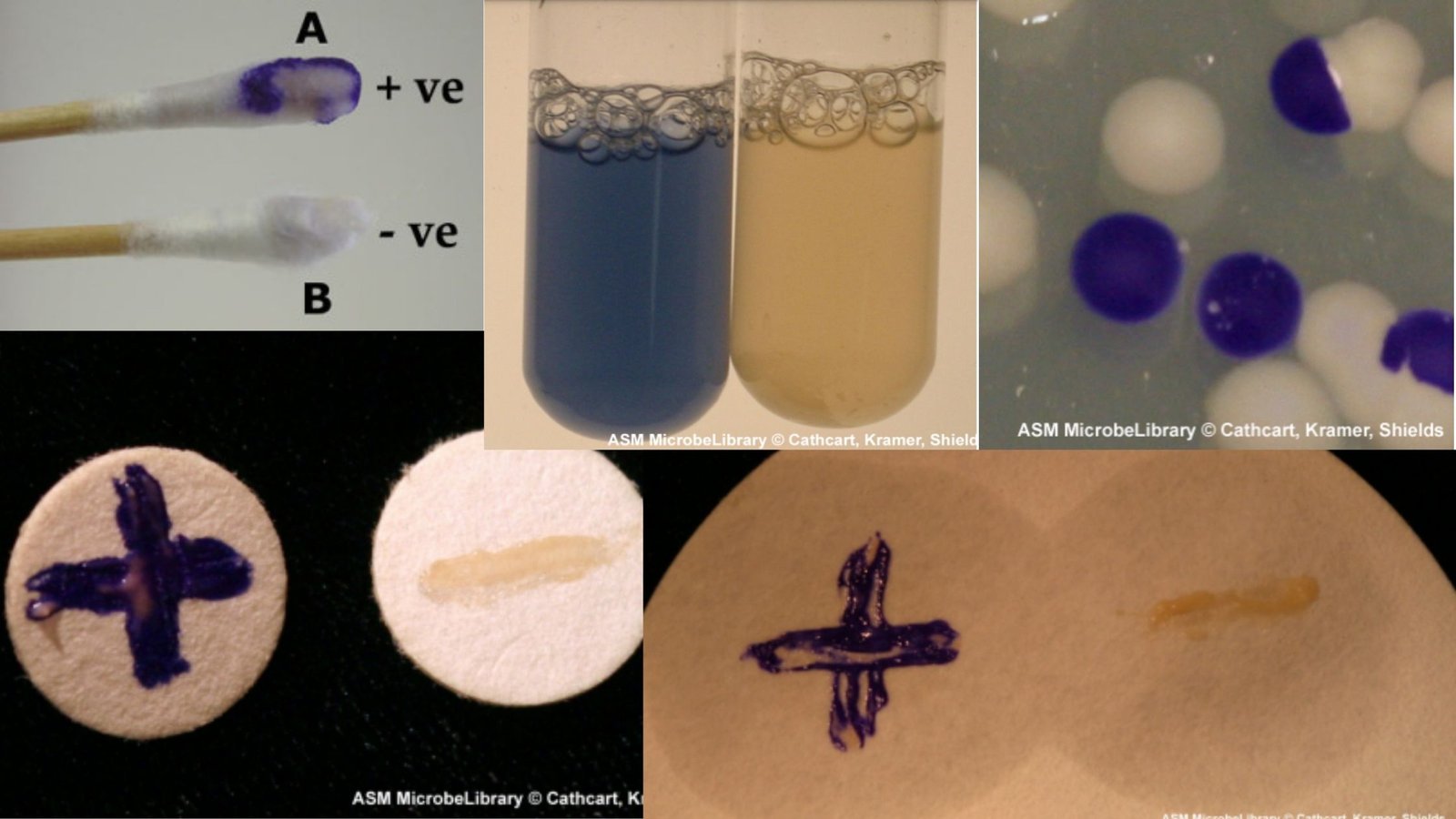
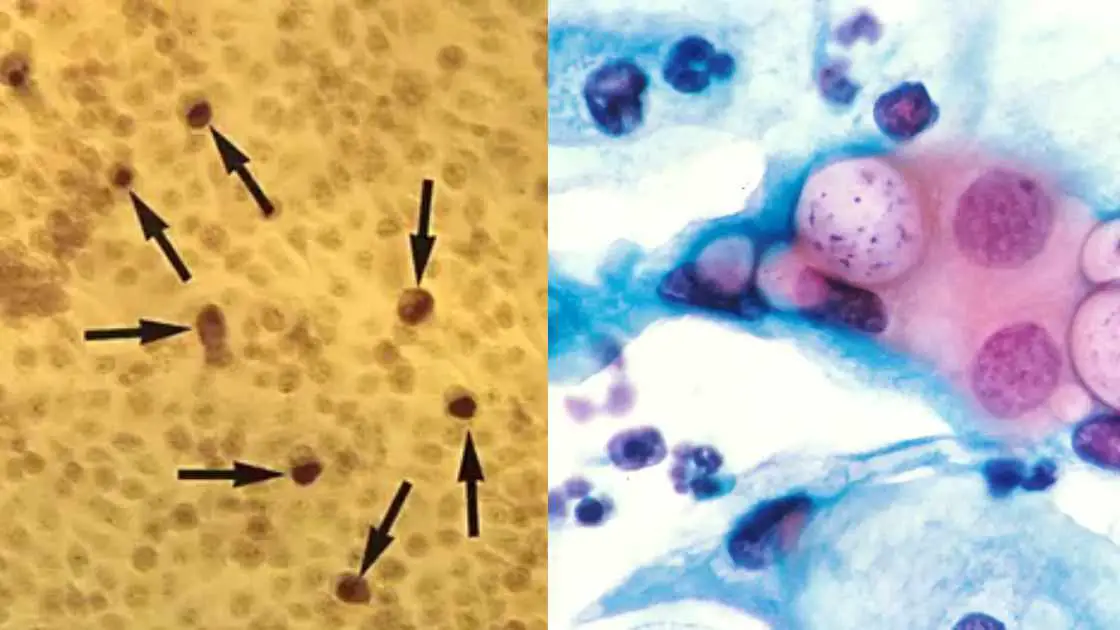
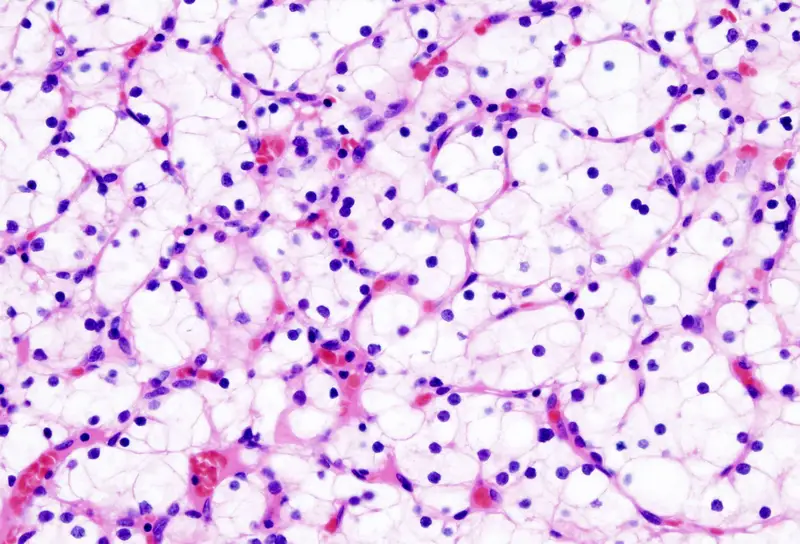
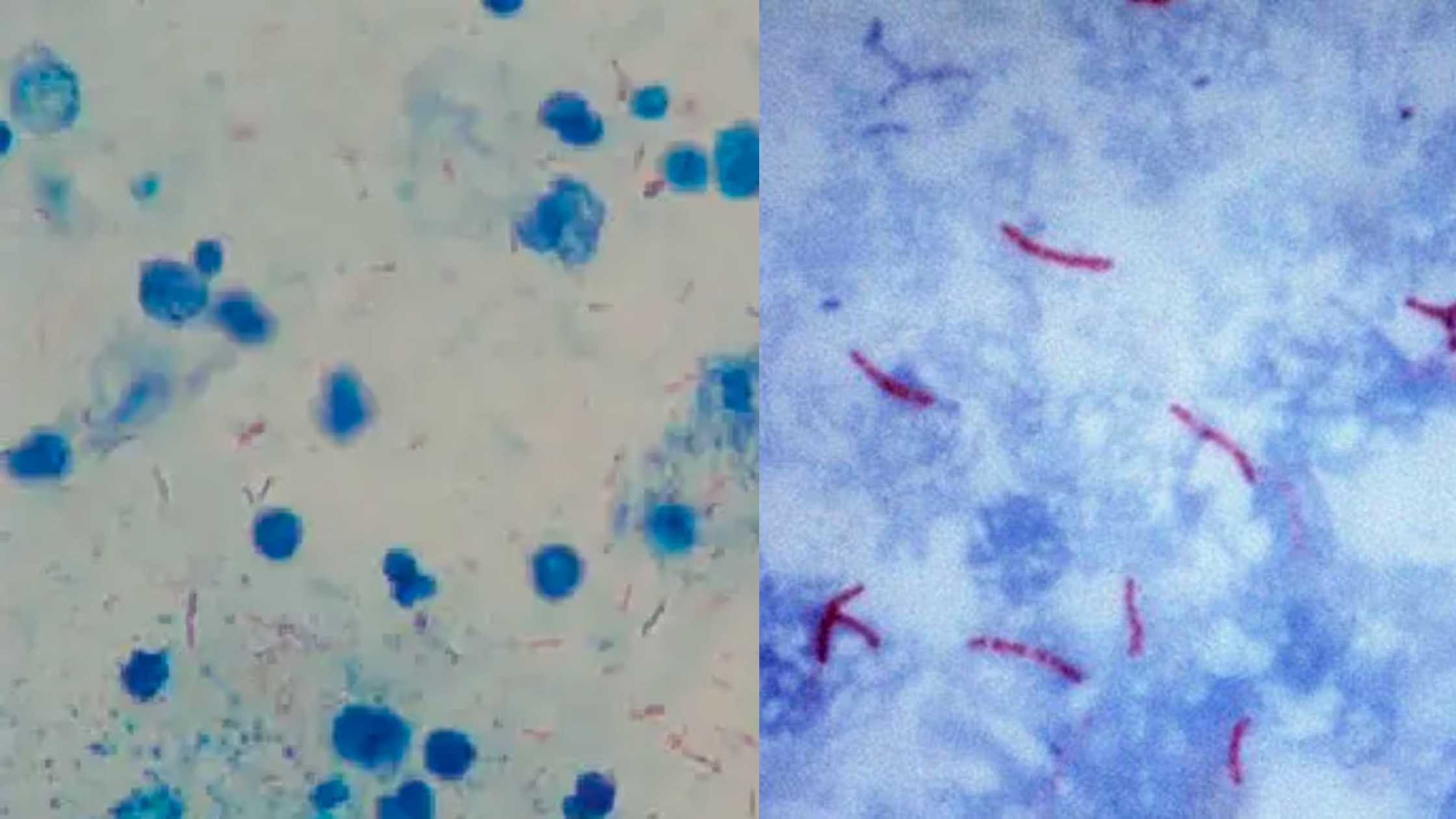
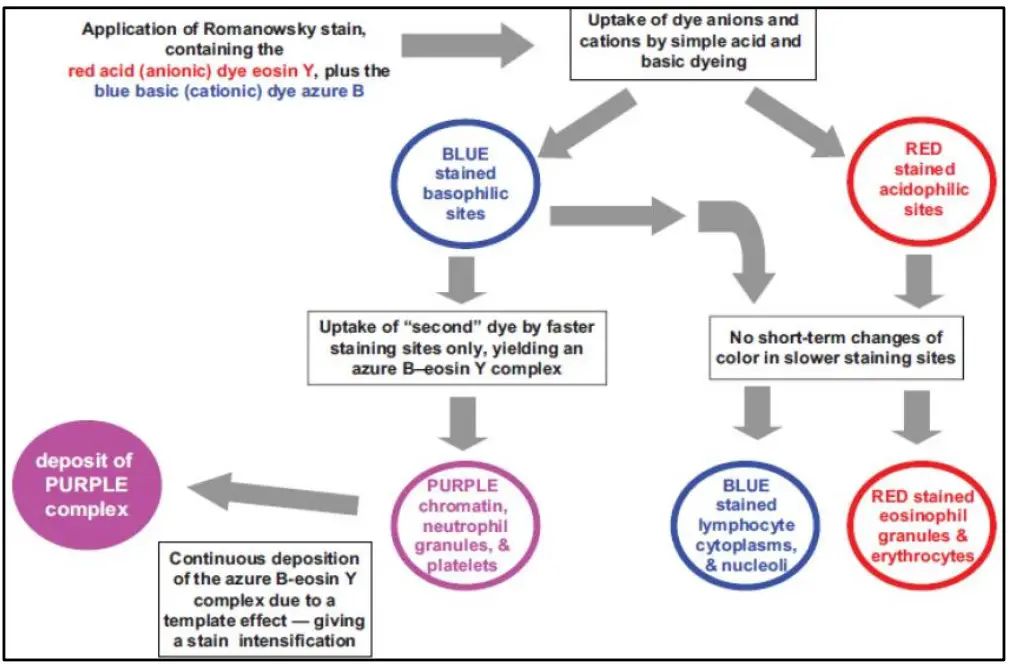
The oxidase test is a biochemical reaction that assays for the presence of cytochrome oxidase, an enzyme sometimes called indophenol oxidase. In the presence of an organism that contains the cytochrome oxidase enzyme, the reduced colorless reagent becomes an oxidized colored product .