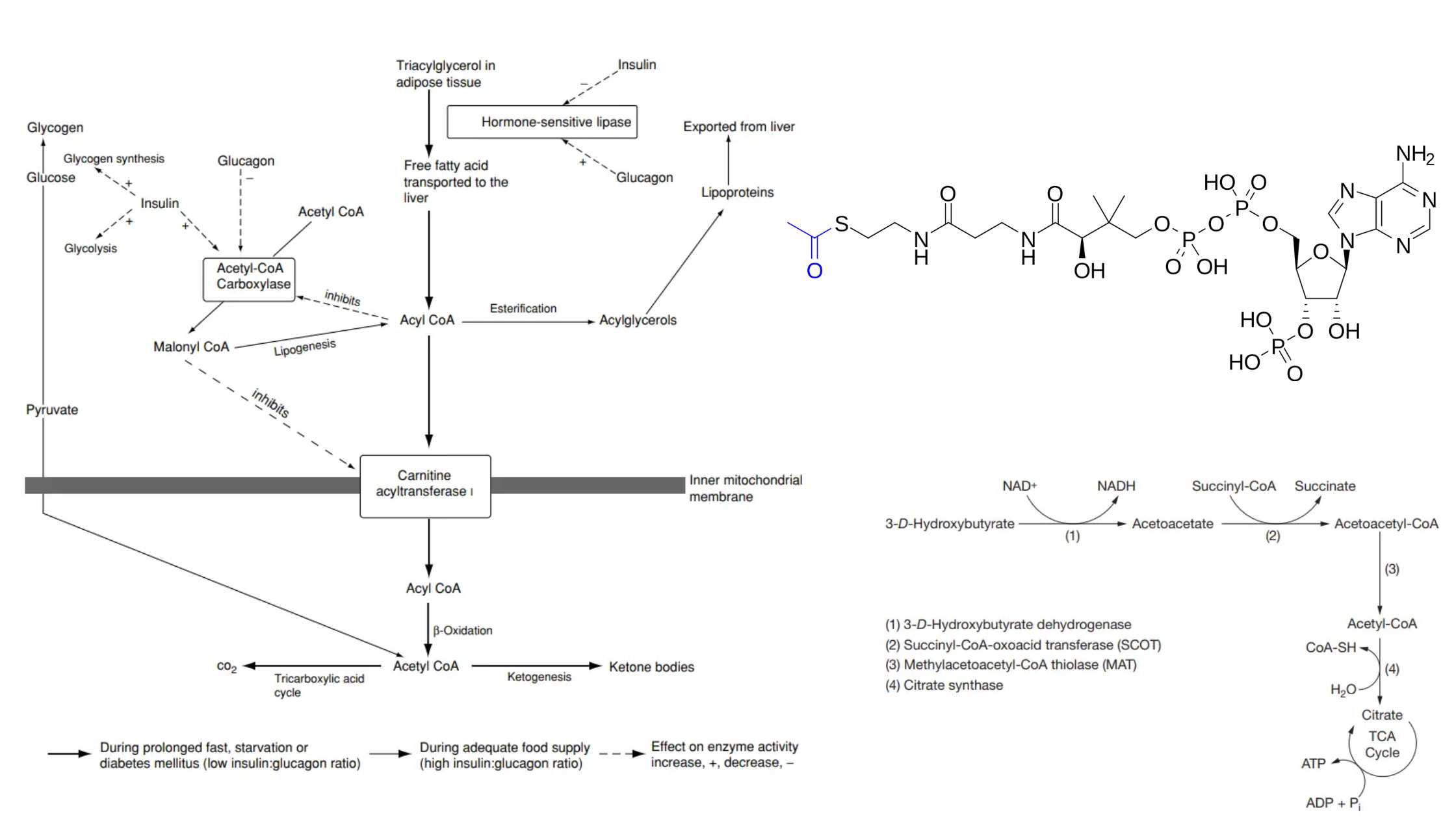
Cori Cycle – Definition, Steps, Regulation, Importance
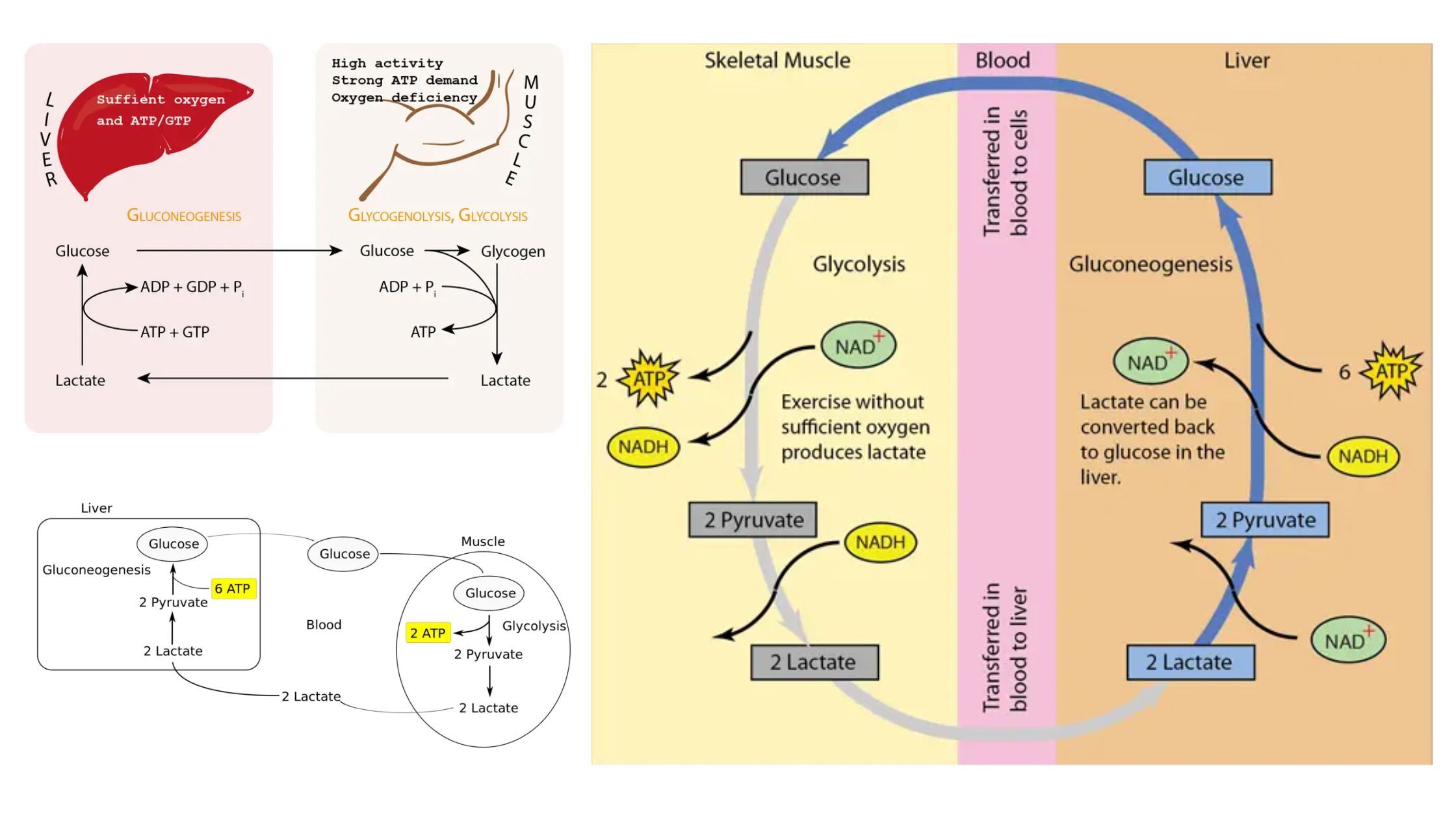
What is the Cori Cycle? Cori Cycle Definition The Cori Cycle is a metabolic pathway in which lactate produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles is transported to the liver, converted back into glucose, and then returned to the muscles for energy production. This cycle plays a crucial role in maintaining energy balance during periods of … Read more