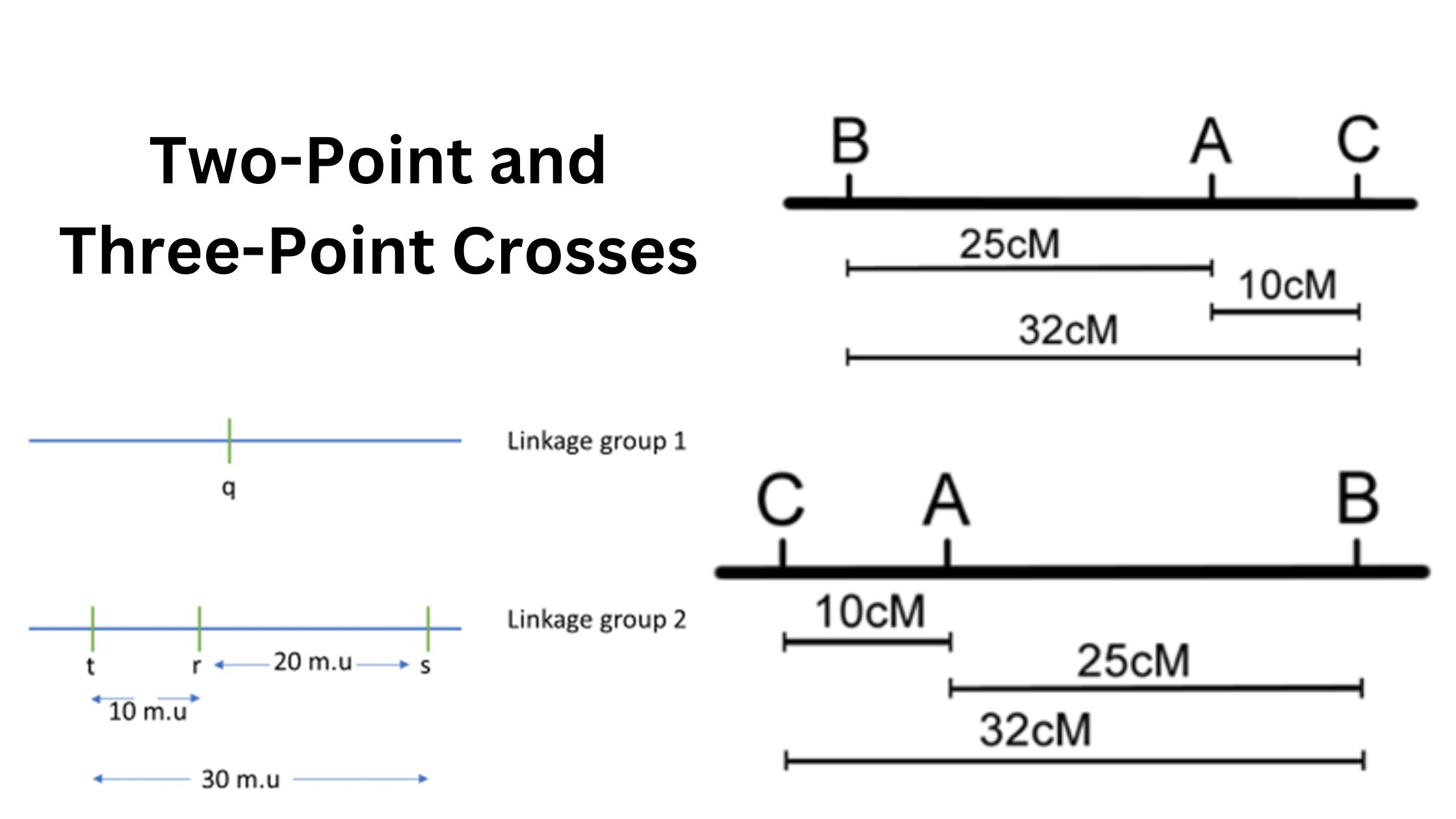
Nonsense Mutation – Definition, Causes, Mechanism, Examples
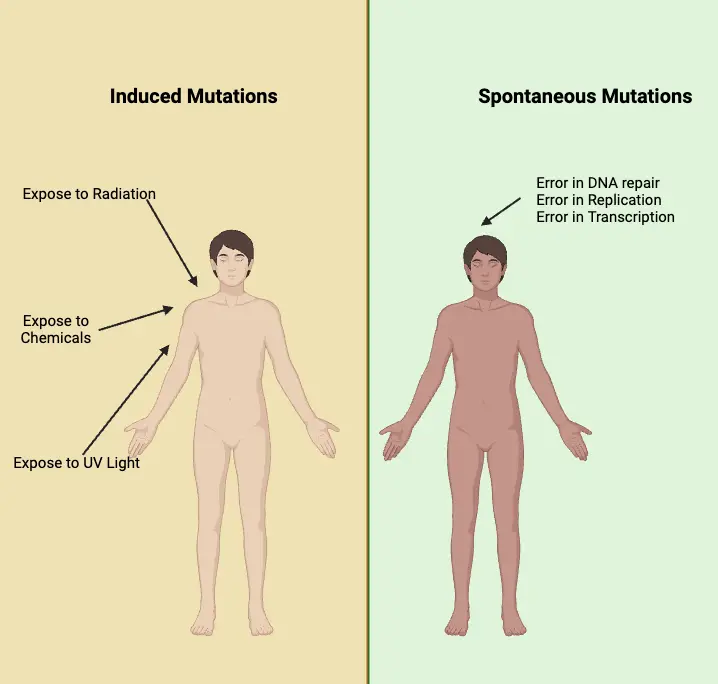
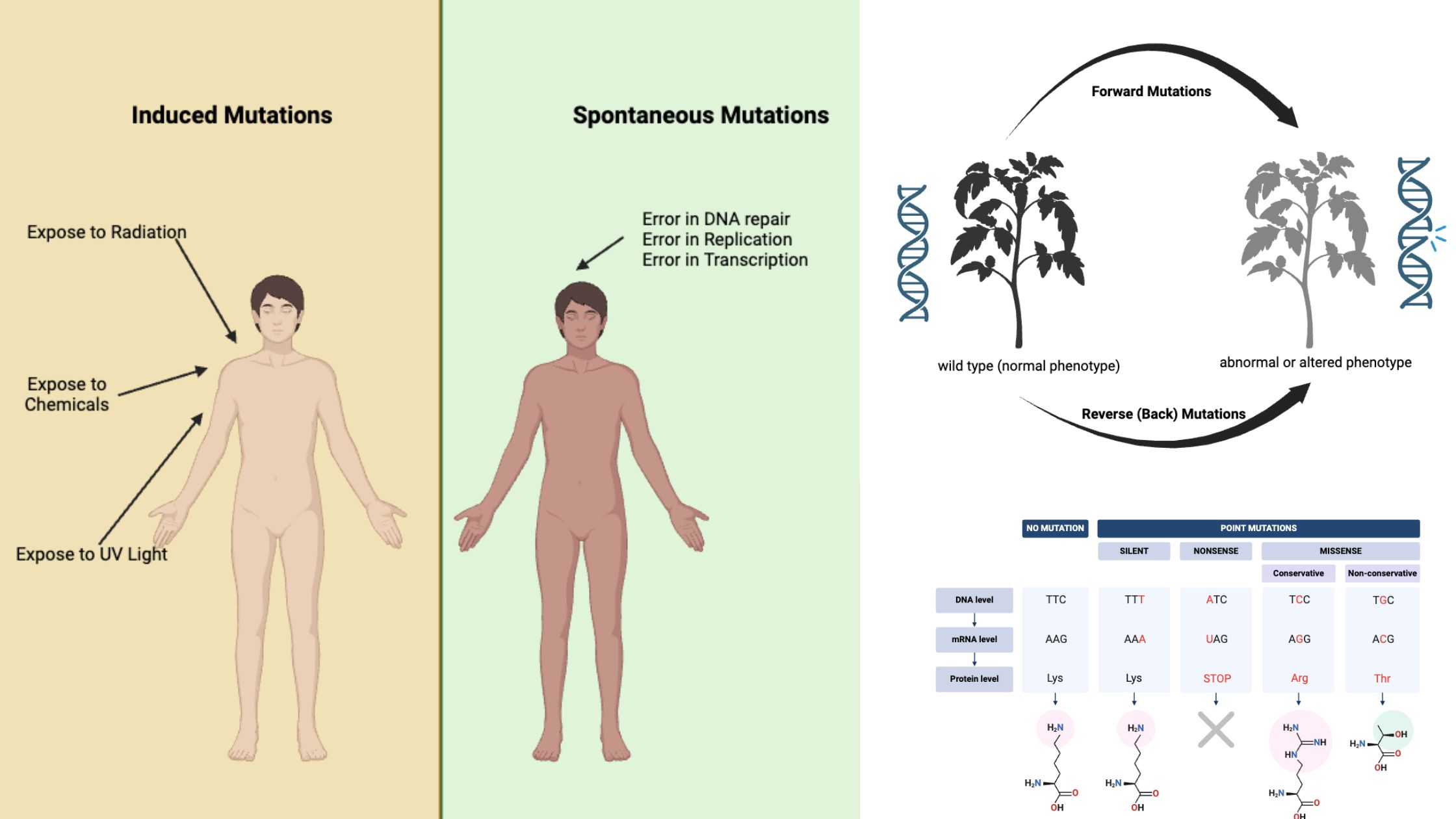
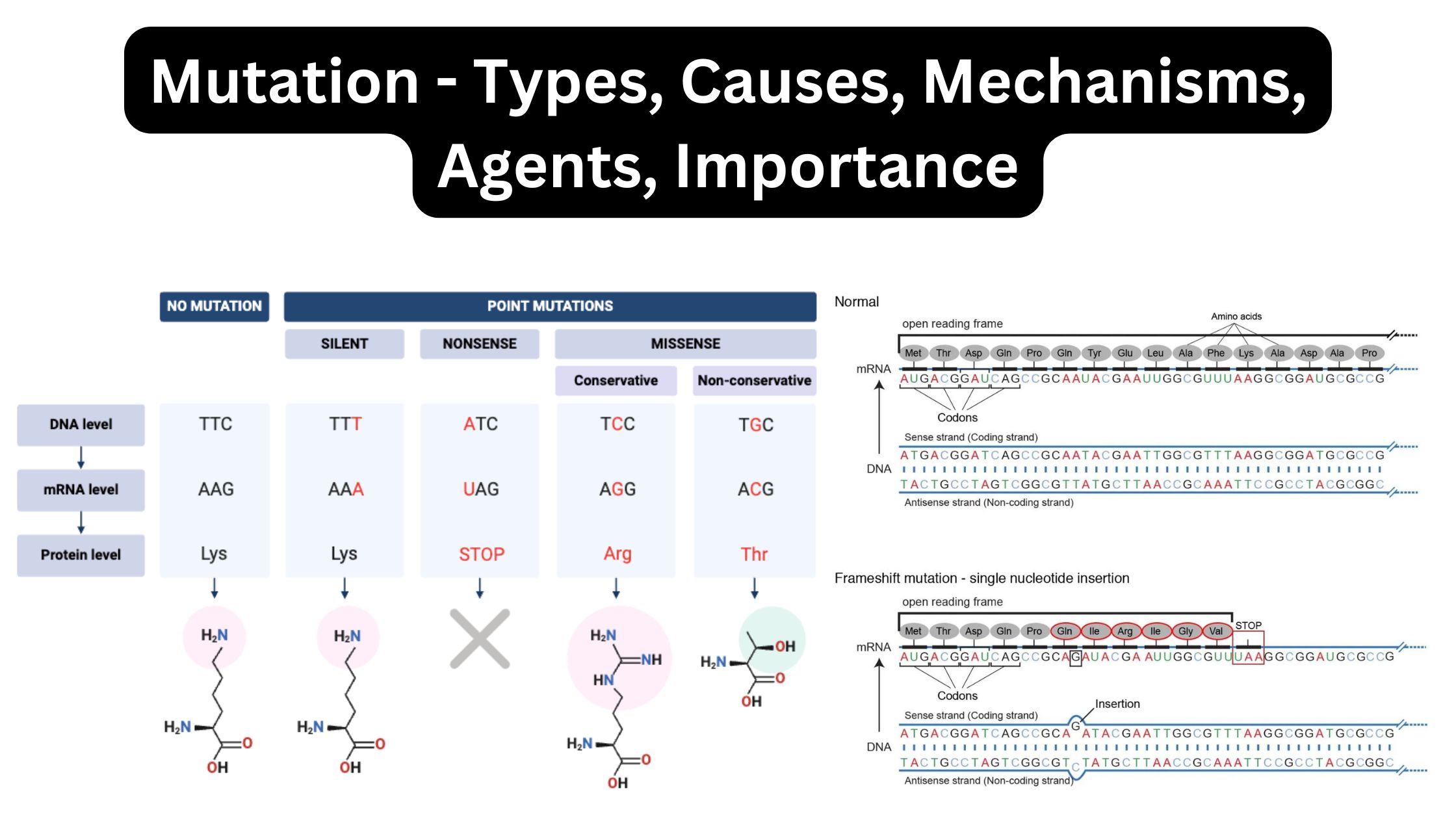
What is Nonsense Mutation? Definition of Nonsense Mutation A nonsense mutation is a genetic alteration that introduces a premature stop codon into the coding sequence of a gene, leading to the production of a truncated and often nonfunctional protein. Causes of nonsense mutation Nonsense mutations are a specific type of genetic mutation where a change … Read more