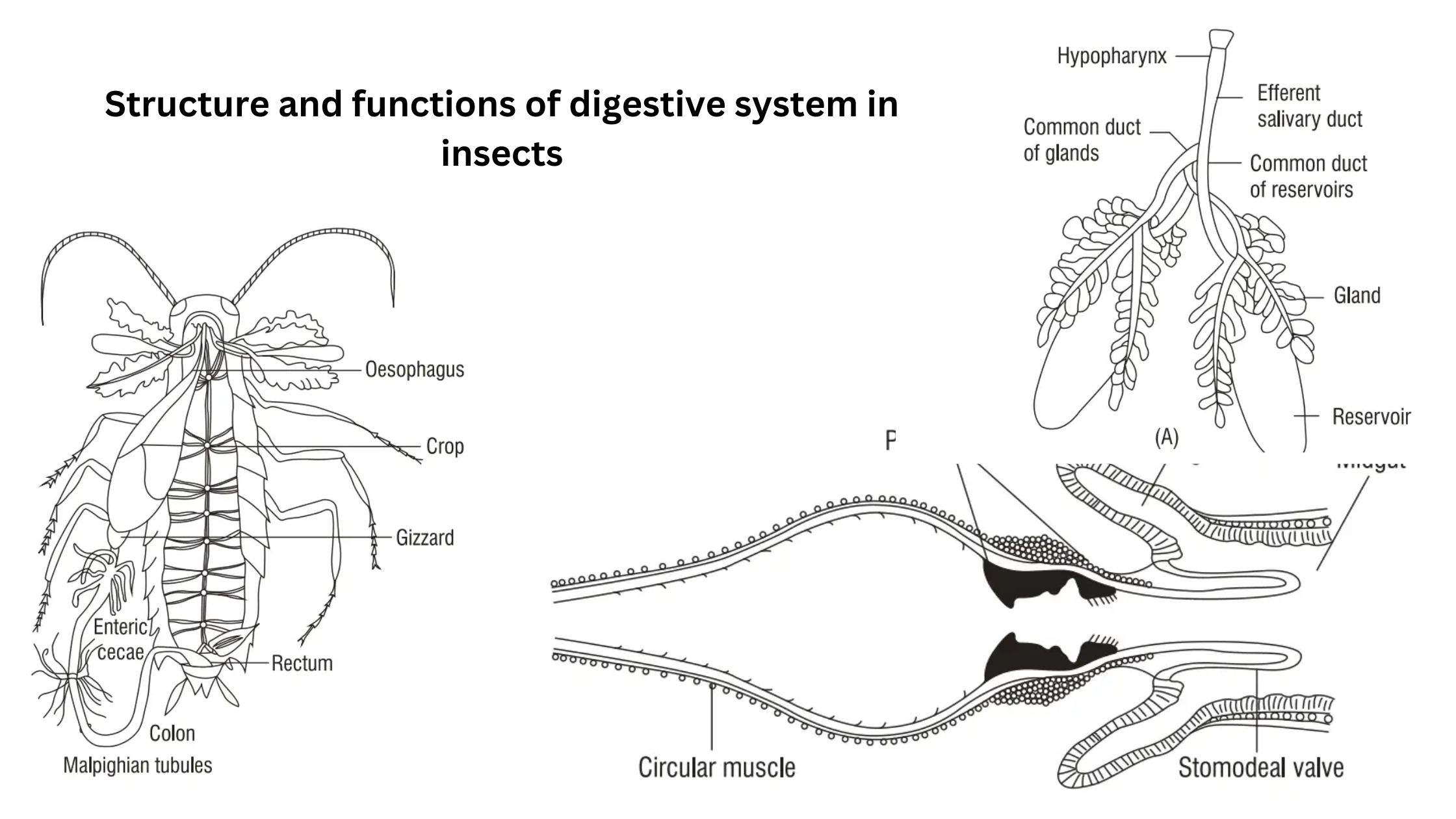
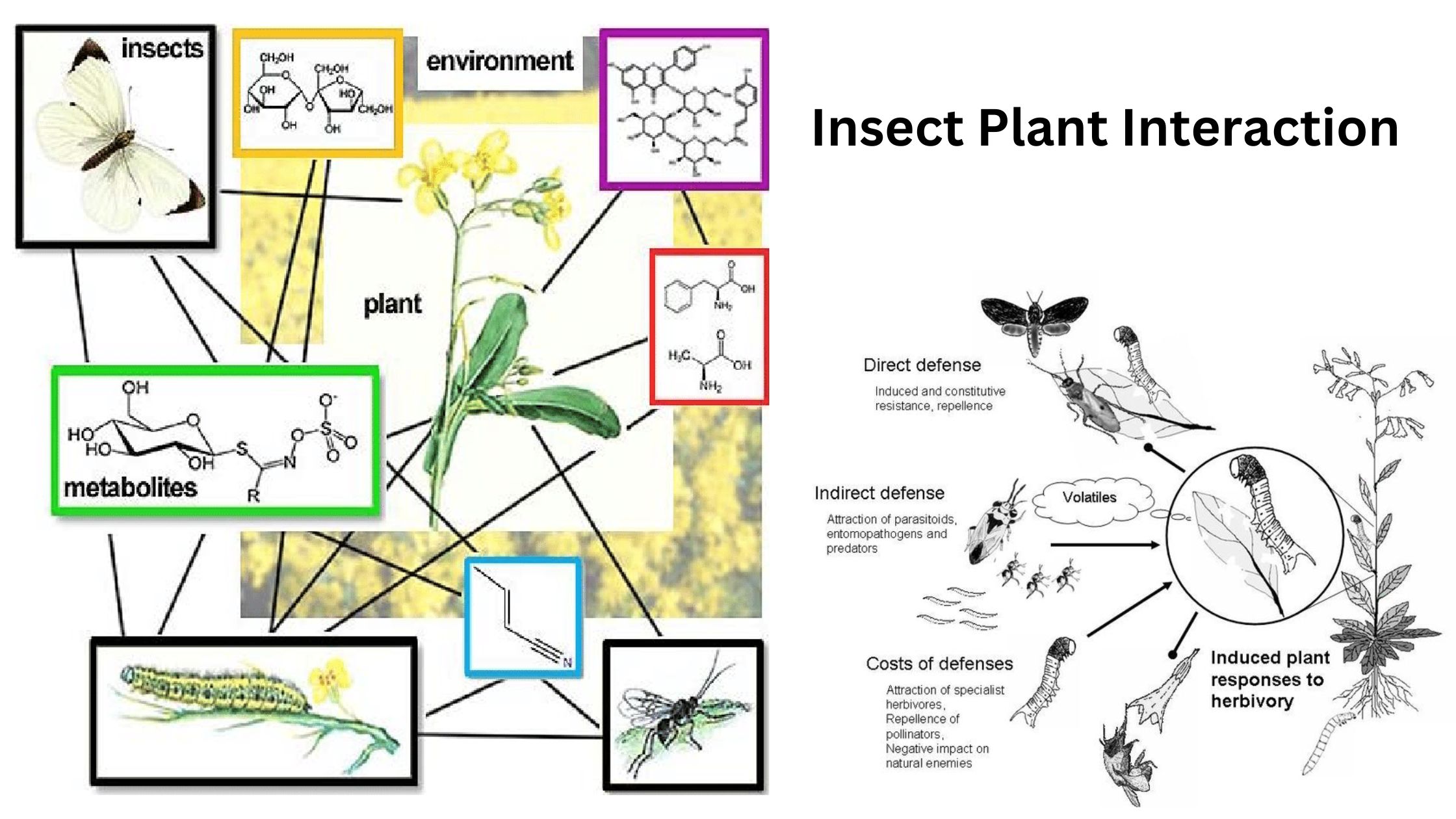
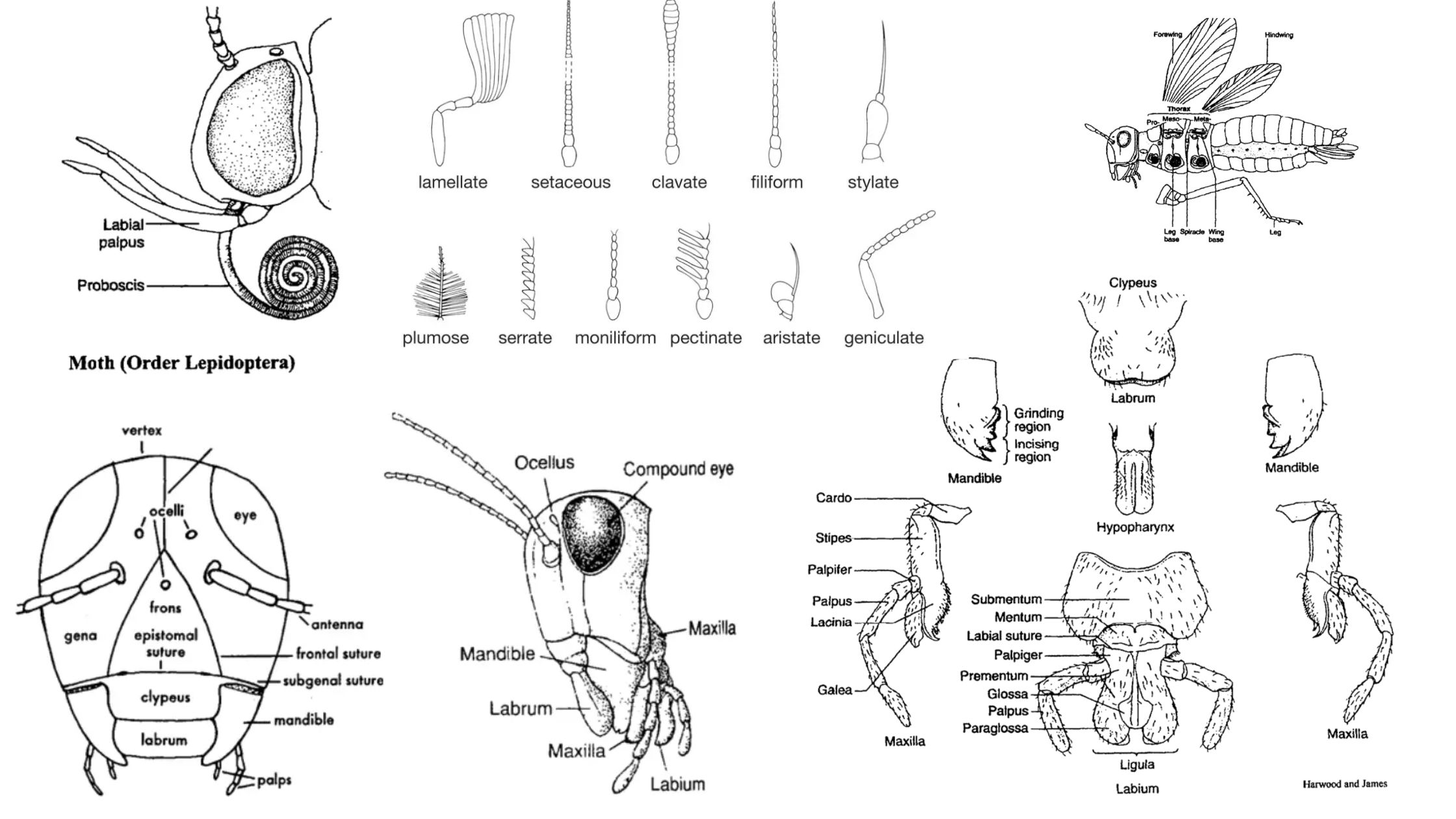
Digestive System of insects – Structure, functions
Insects exhibit a remarkable diversity in their feeding habits, leading to significant adaptations in their digestive systems. These adaptations can be classified based on their dietary preferences, which include phytophagous (plant-eating), entomophagous (insect-eating), wood-boring, wool-feeding, and saprophytic behaviors. Each of these feeding strategies necessitates specific structural modifications within the digestive system to efficiently process the … Read more