Endocrinology – Definition, History, Endocrine system
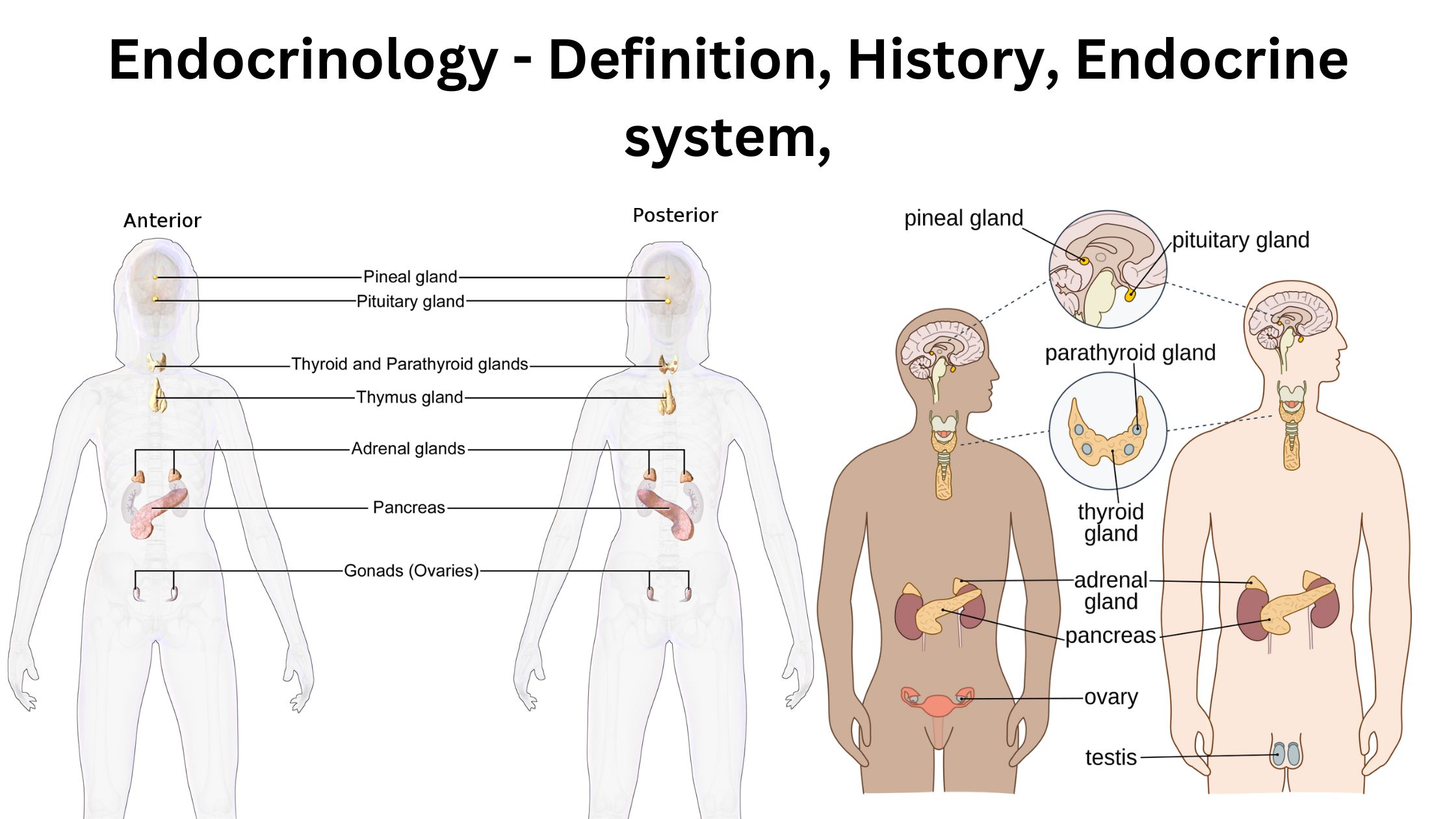
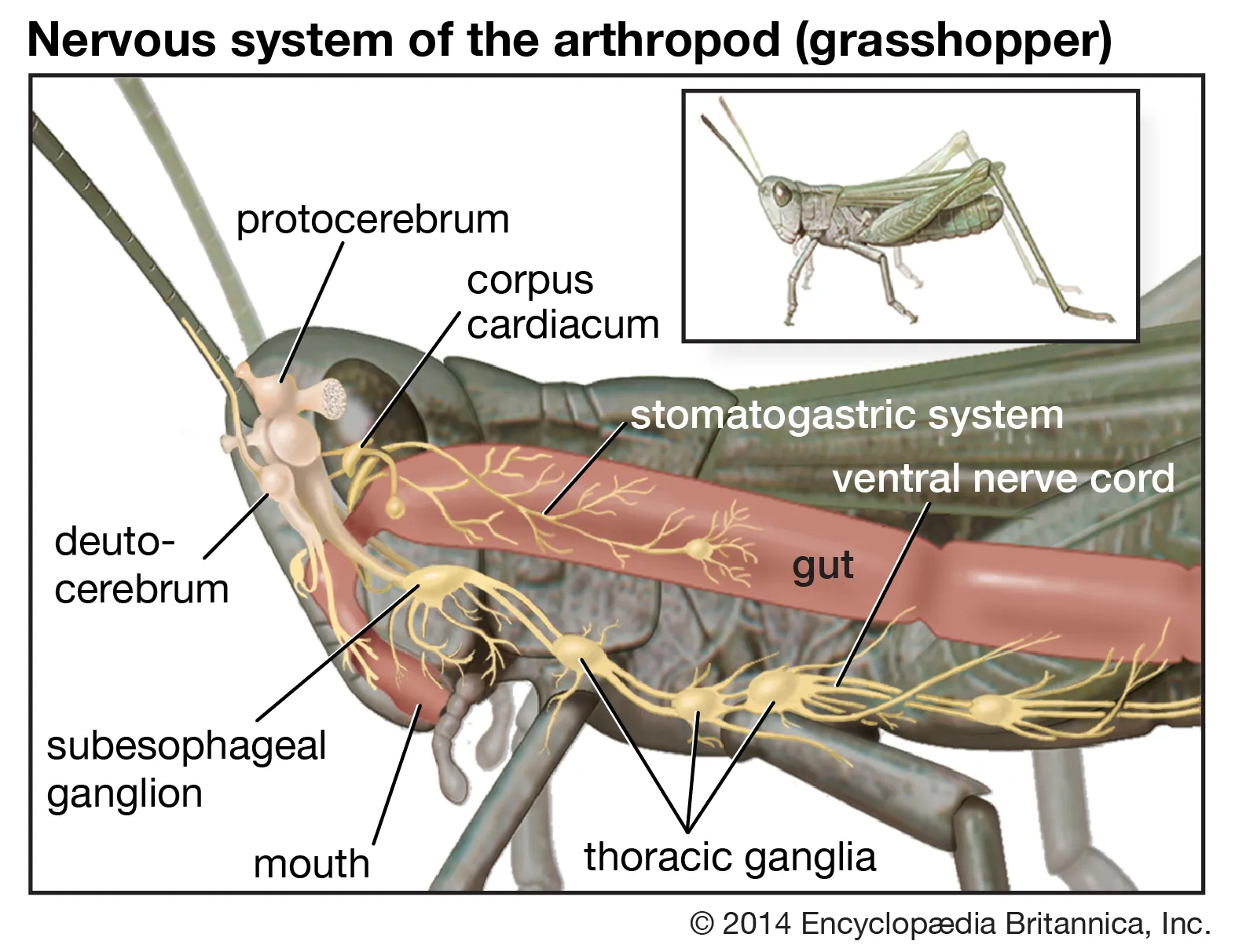
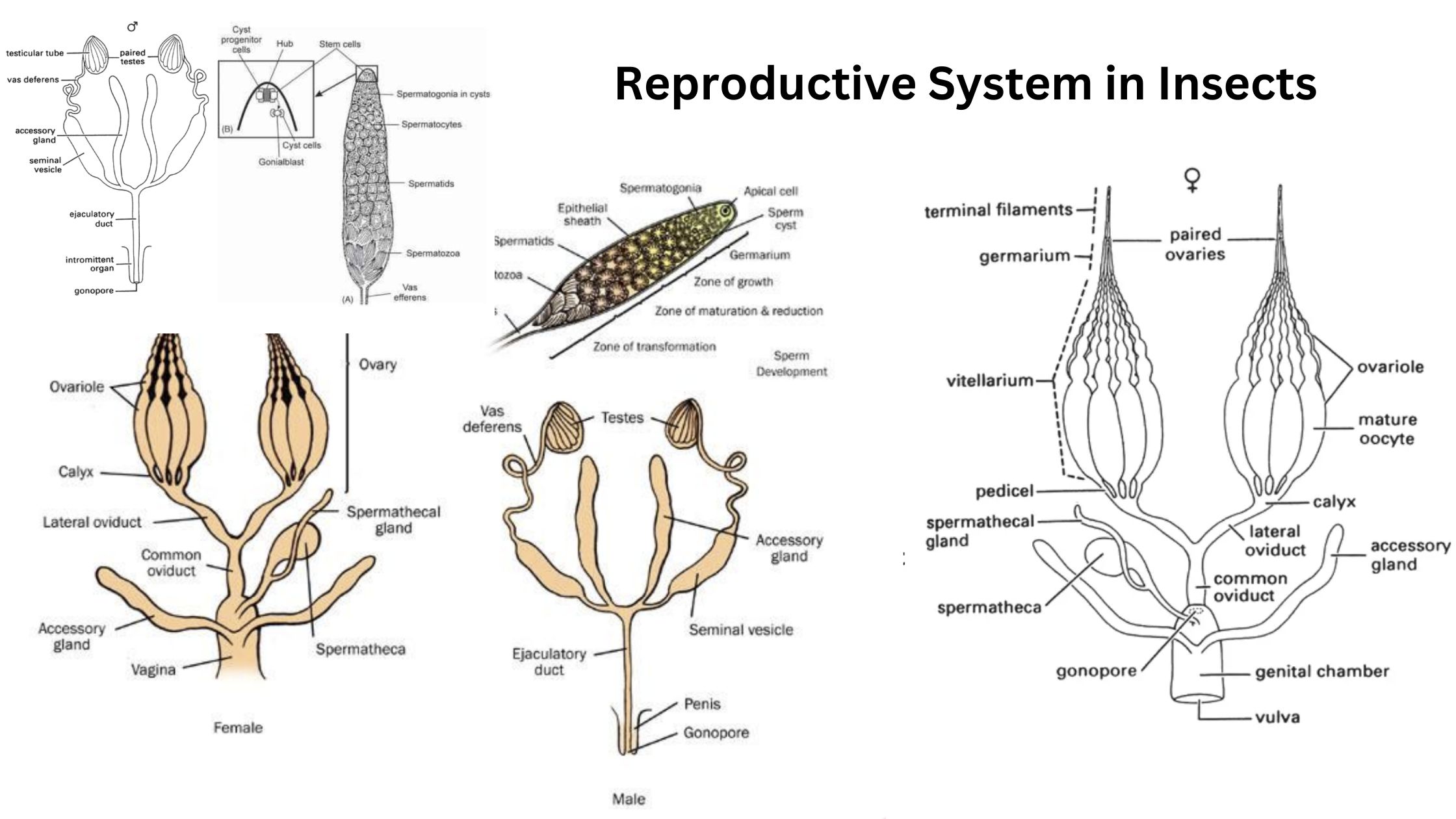
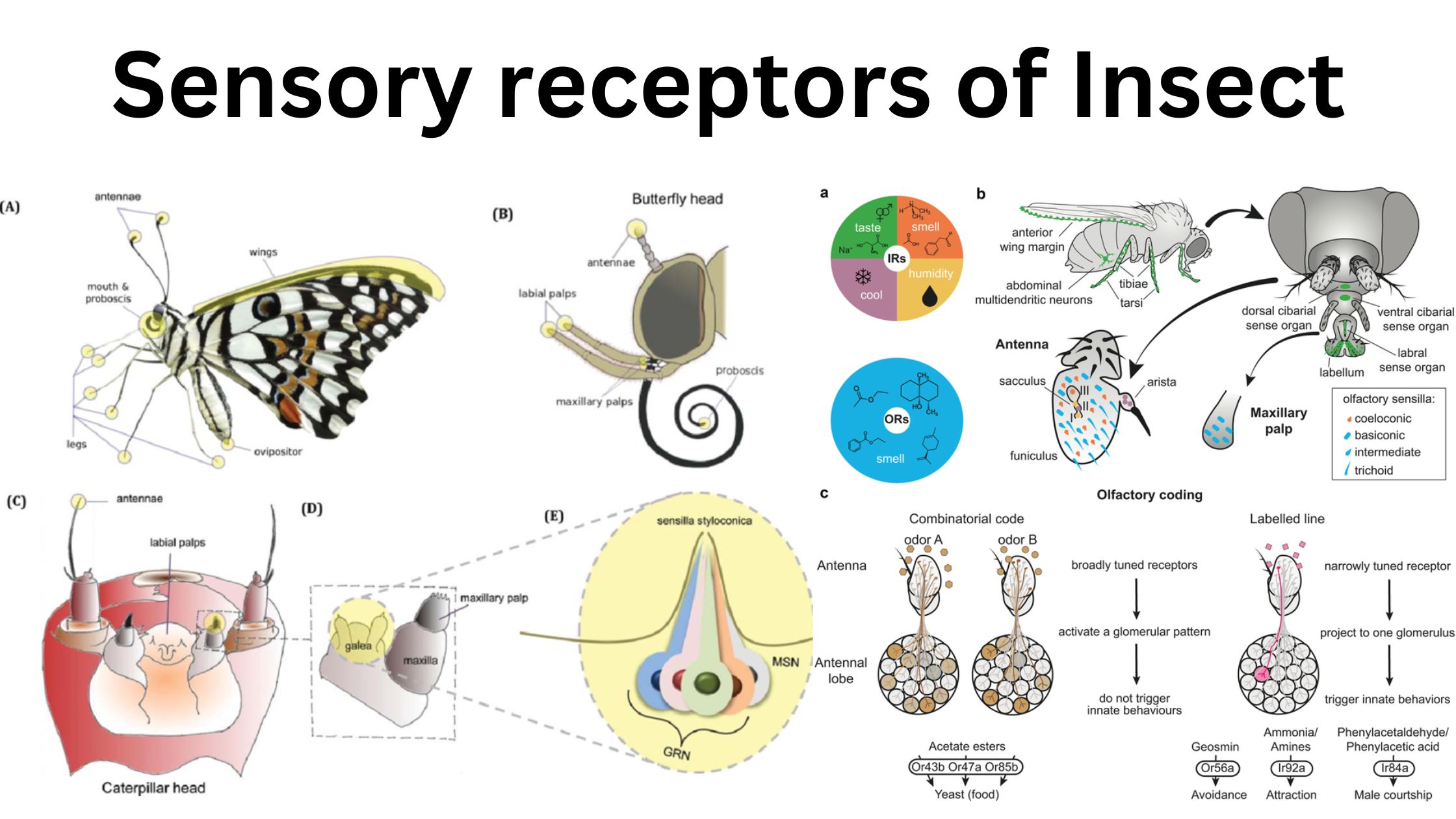
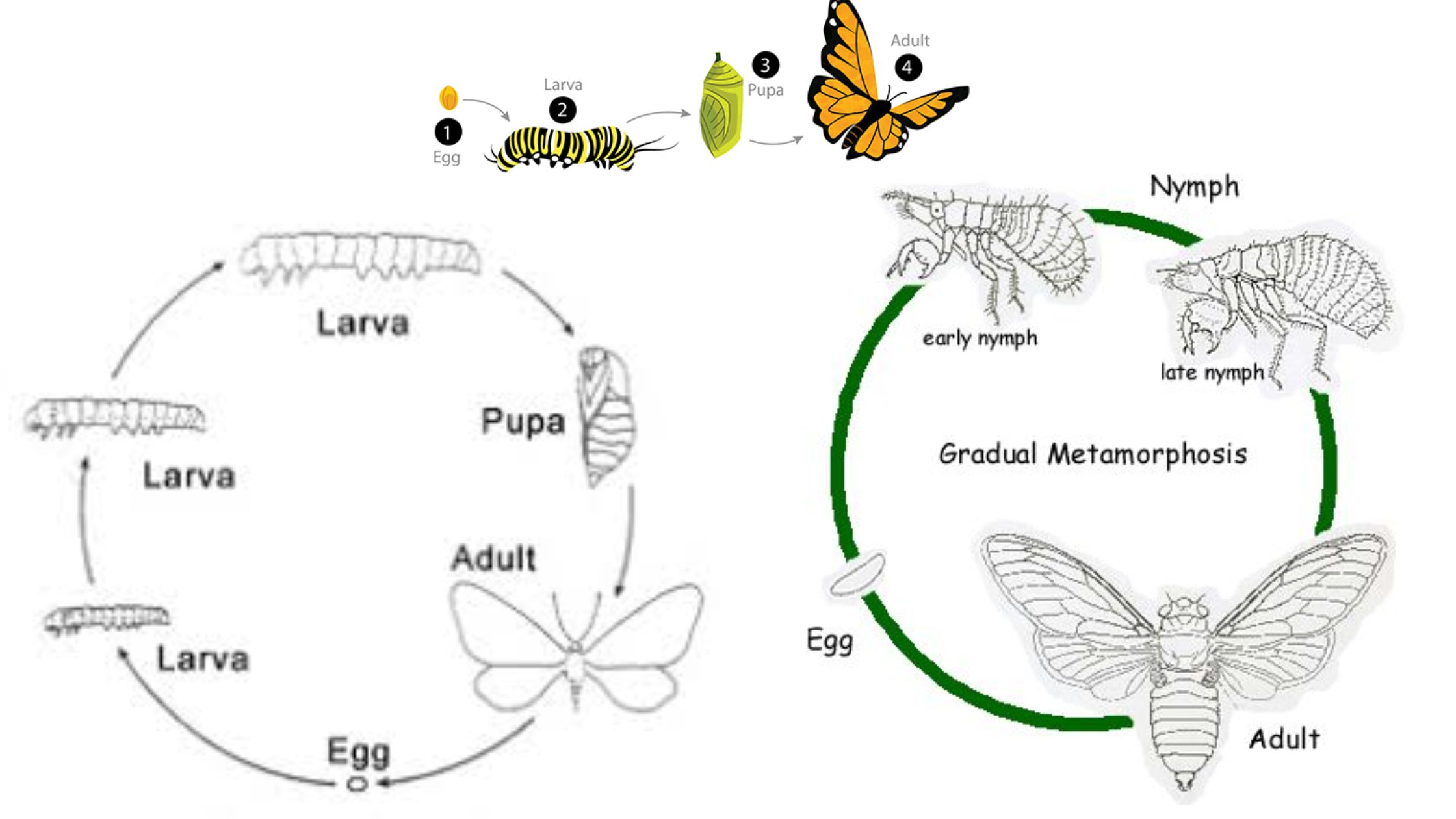
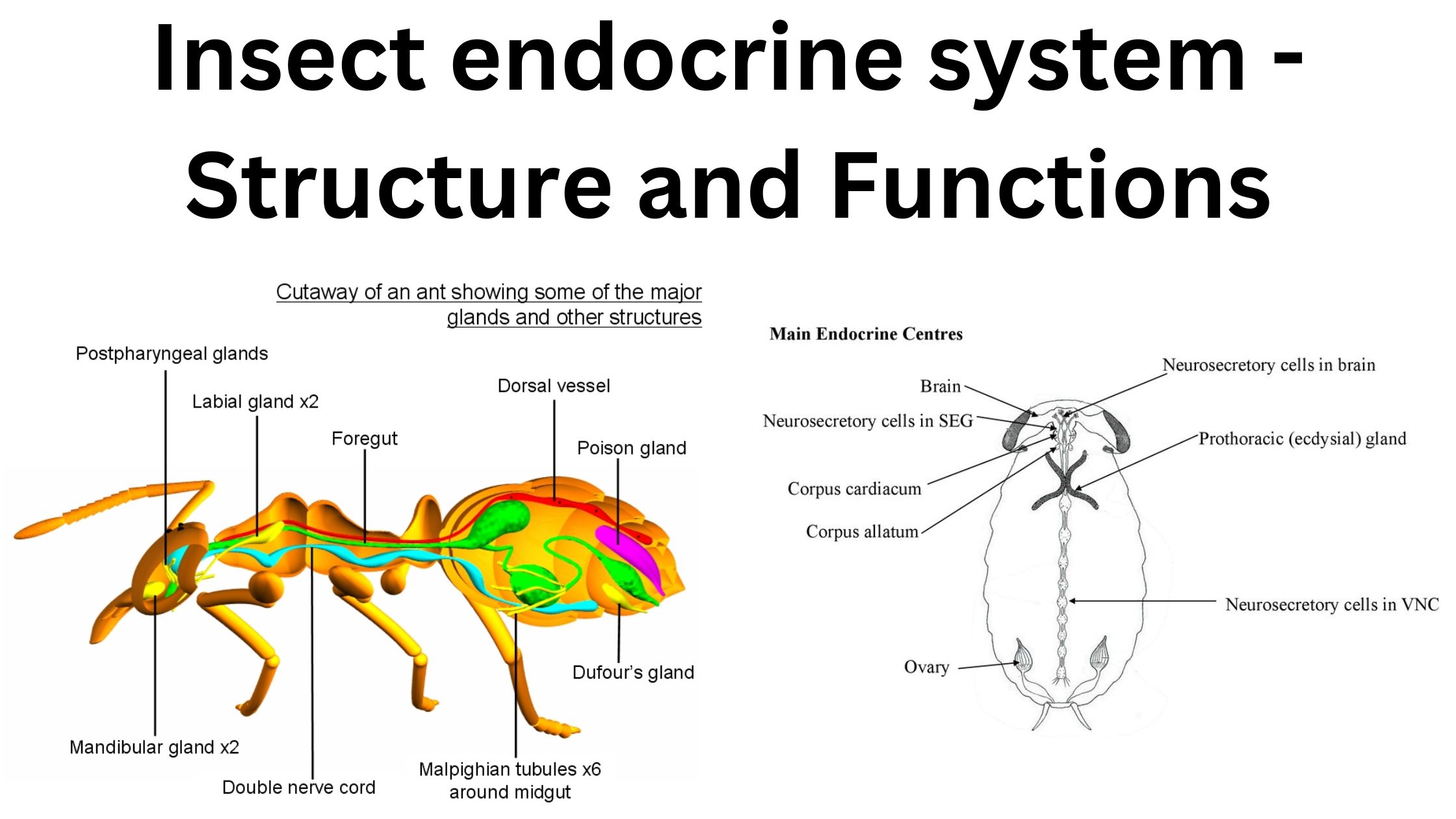
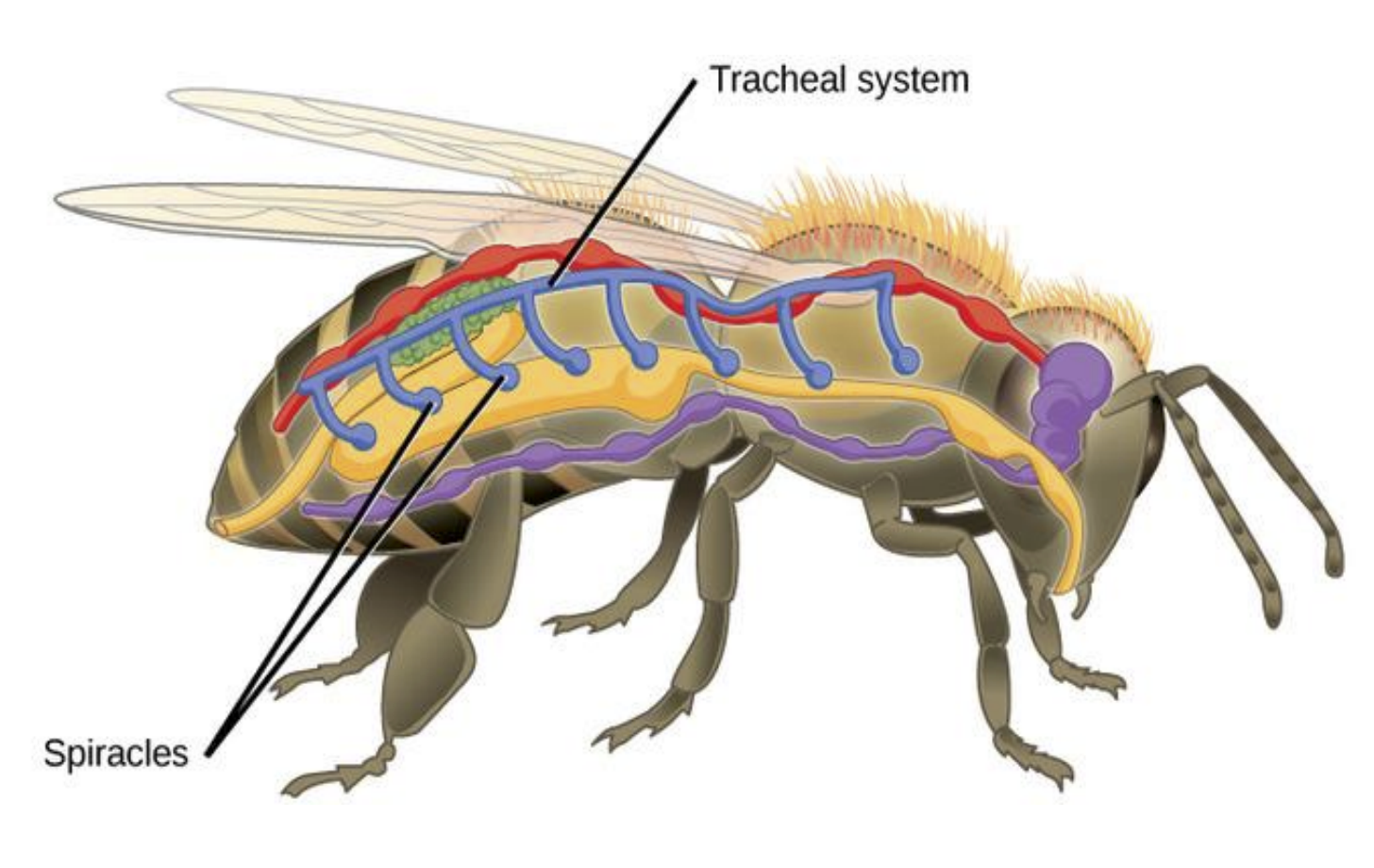
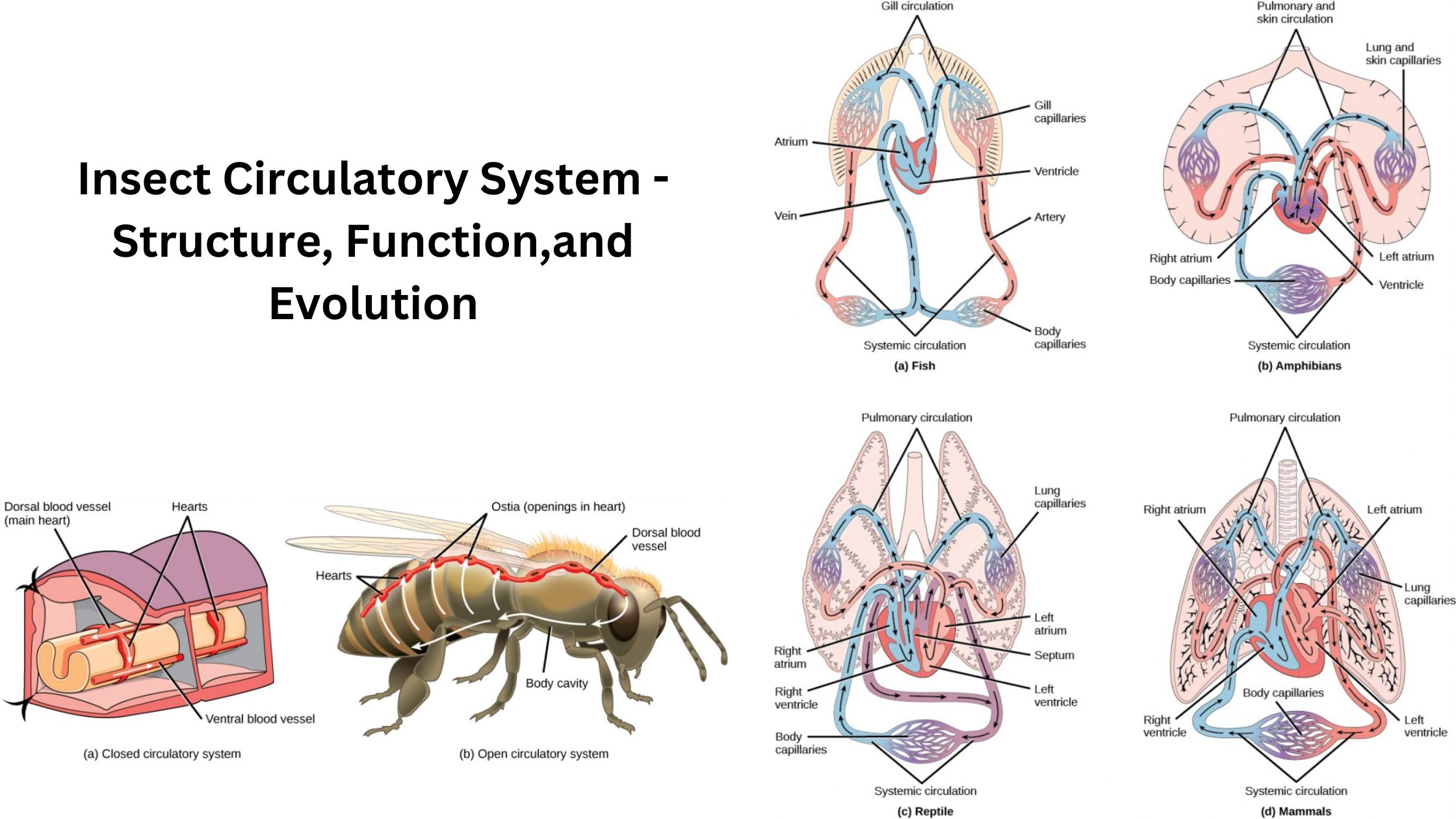
What is Endocrinology? Definition of Endocrinology Endocrinology is the branch of medicine and biology that studies the endocrine system, its glands, and the hormones they produce. It focuses on how hormones regulate various physiological processes, including growth, metabolism, reproduction, and behavior, as well as the diagnosis and treatment of hormonal disorders. History of endocrinology Endocrinology, … Read more