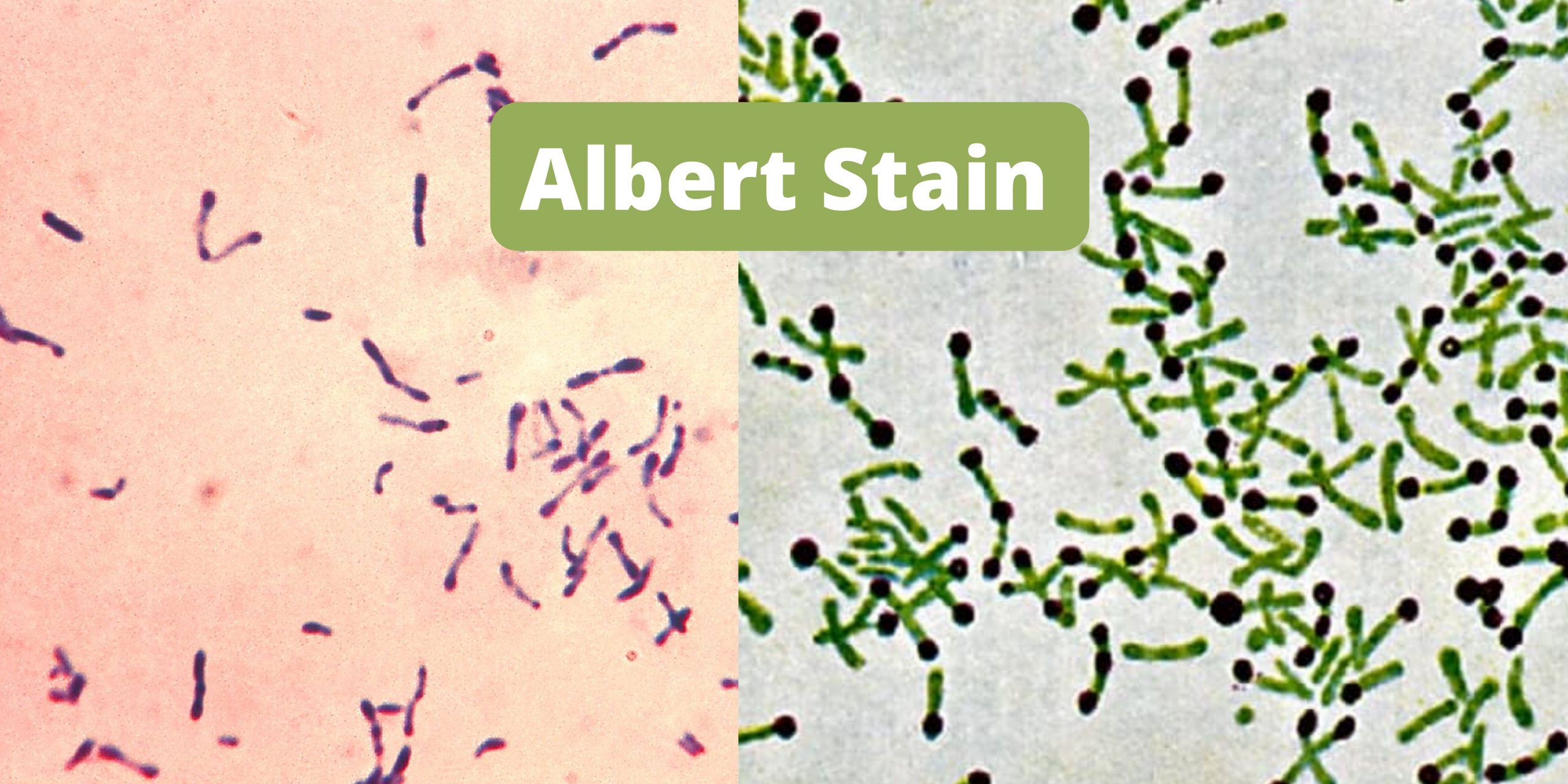
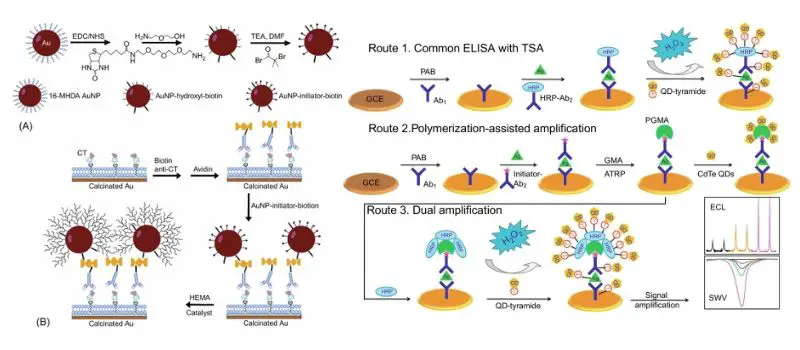
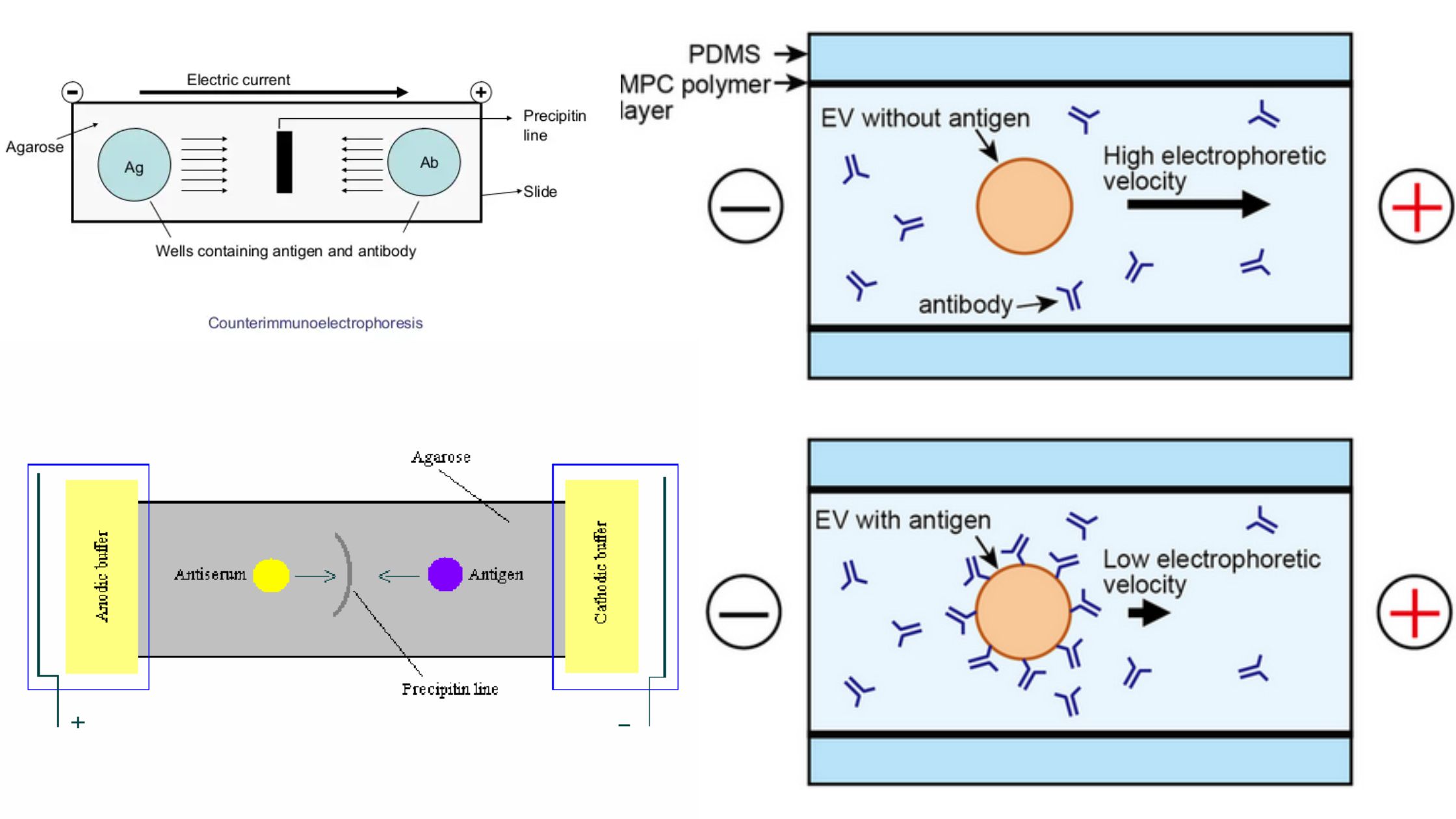
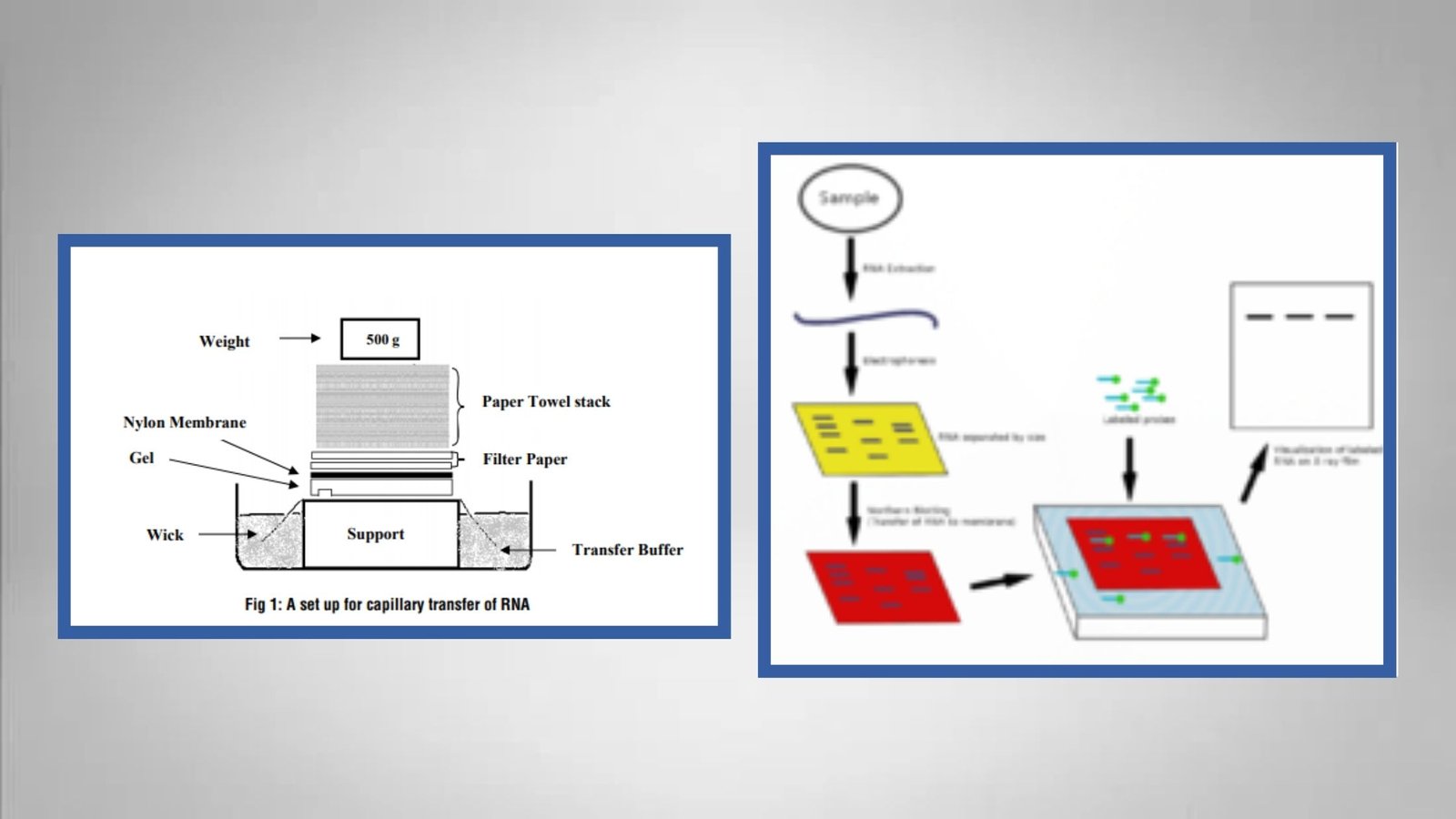
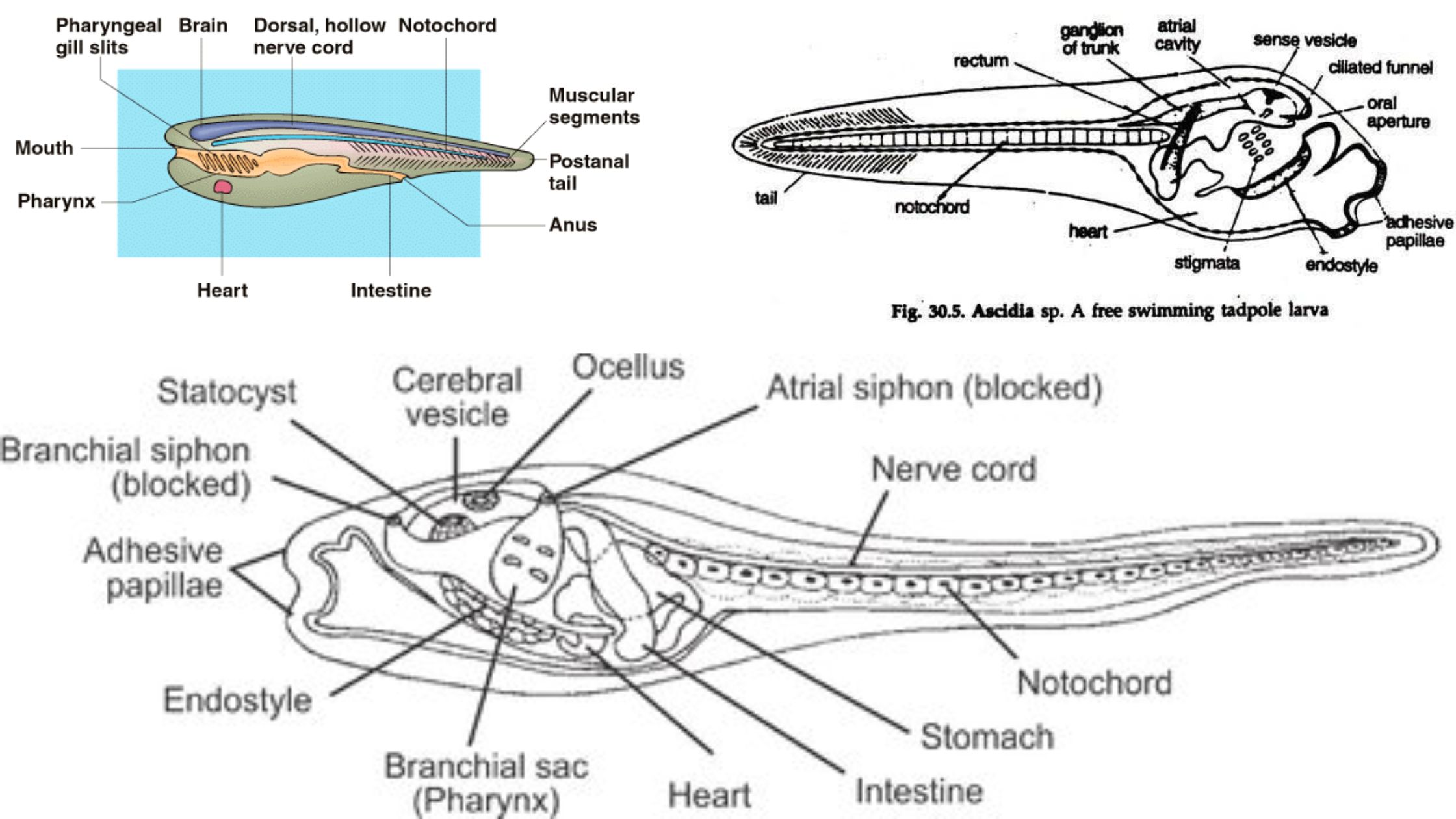
Albert Stain – Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
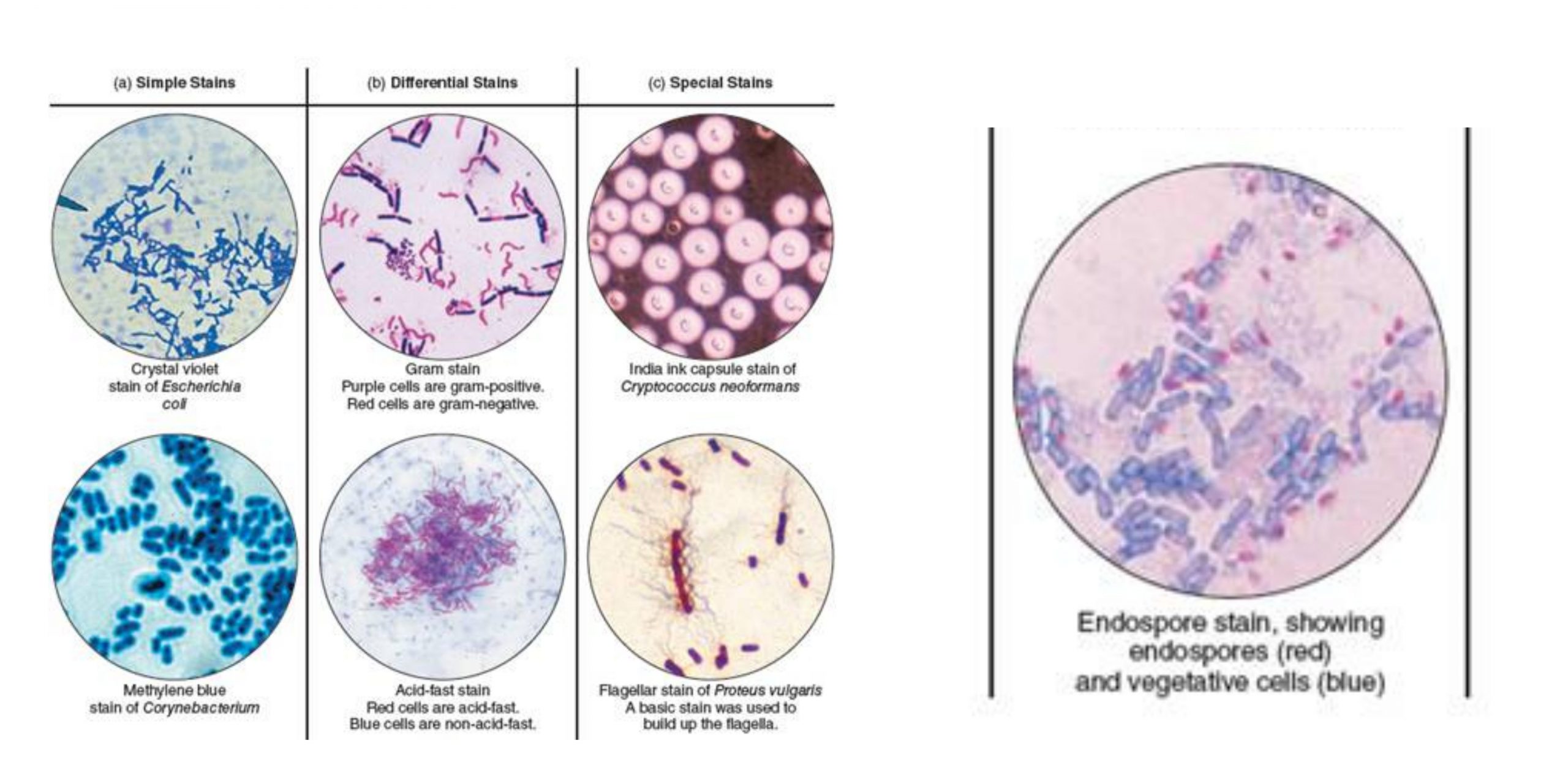
Different stains have been developed over time to distinguish bacteria species, separating them morphologically and the specific characteristics they possess. The most popular stain is Gram staining, acid-fast staining, and endospore staining. Each stain aims at identifying and defining bacteria according to their forms and morphologies.