Microbial Degradation of Lignin – Microorganisms, Enzymes, Steps, Mechanisms, Challenges
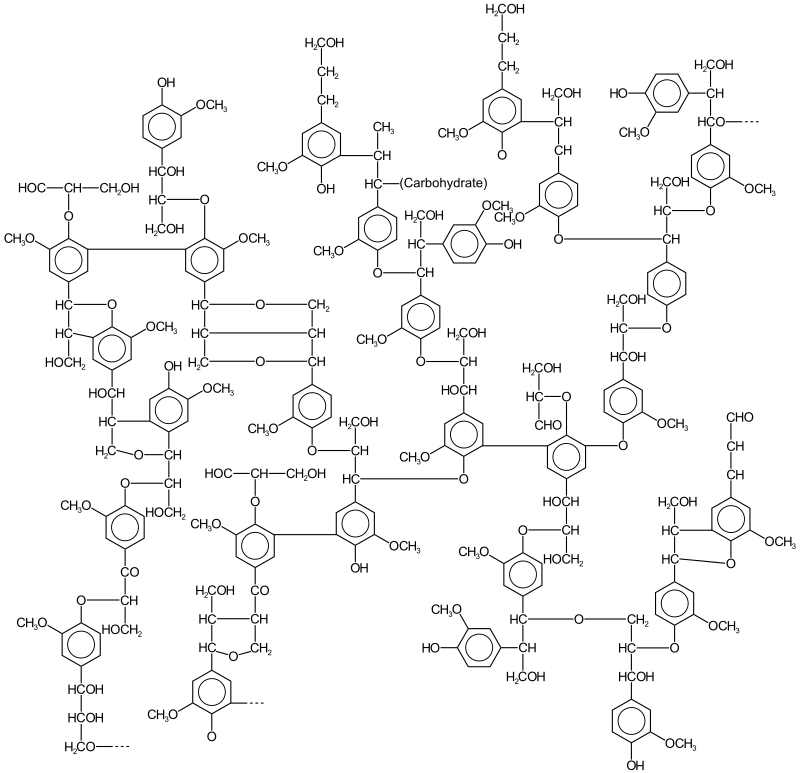
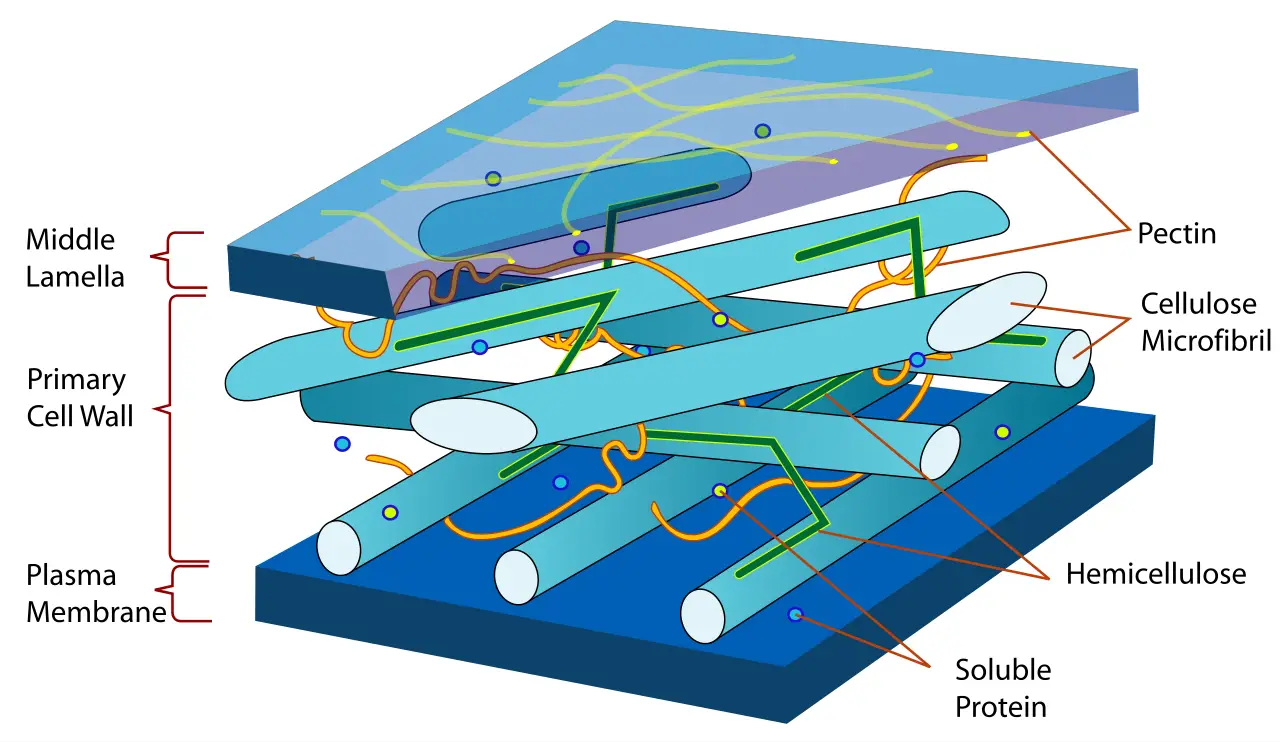
What is lignin? Lignin is a complex, high-molecular-weight polymer made mostly of phenolic compounds. It is found in the cell walls of vascular plants, especially in the secondary cell wall during the development of xylem, phloem fibres, and sclerenchyma cells, which give the plant strength, support, and waterproofing. It is made up of three main … Read more