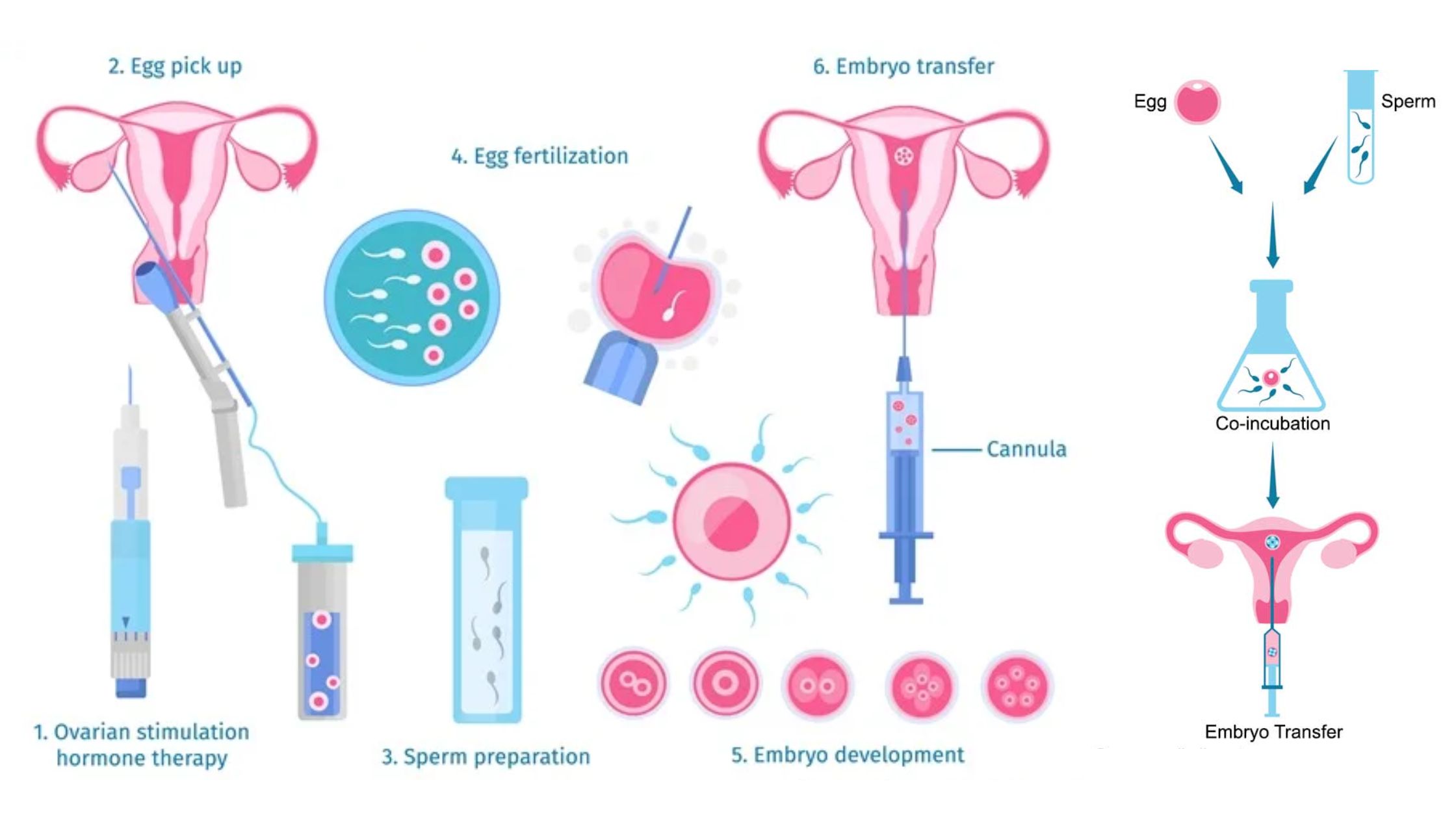
Agrobacterium-Mediated Gene Transfer – Protocol, Applications, Advantages
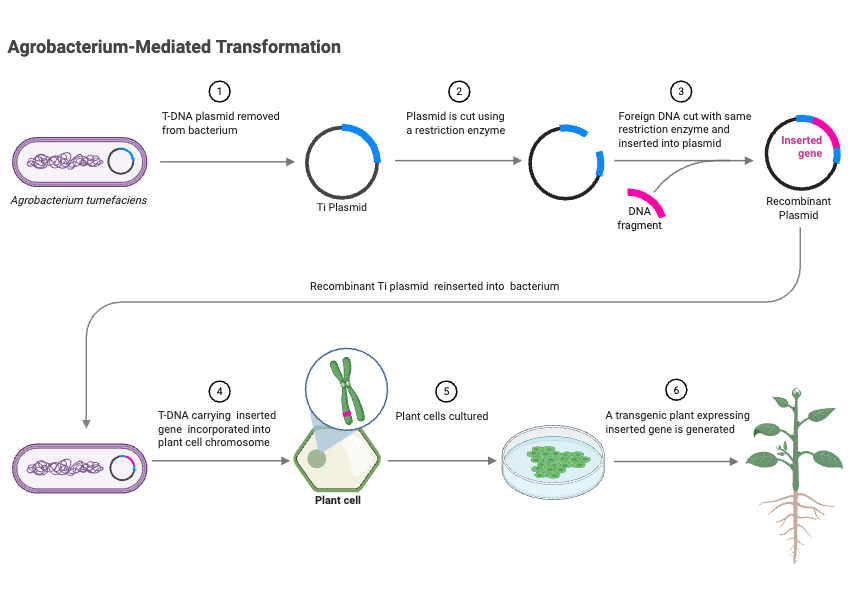
What is Agrobacterium? There are many types of Gram-negative bacteria in the genus Agrobacterium. They can be harmful to plants and are also useful for genetic engineering. It causes tumours in plants by moving a piece of DNA known as T-DNA from its Ti or Ri plasmid into the plant genome. This causes cells to … Read more