Picric Acid Test for Glucose – Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
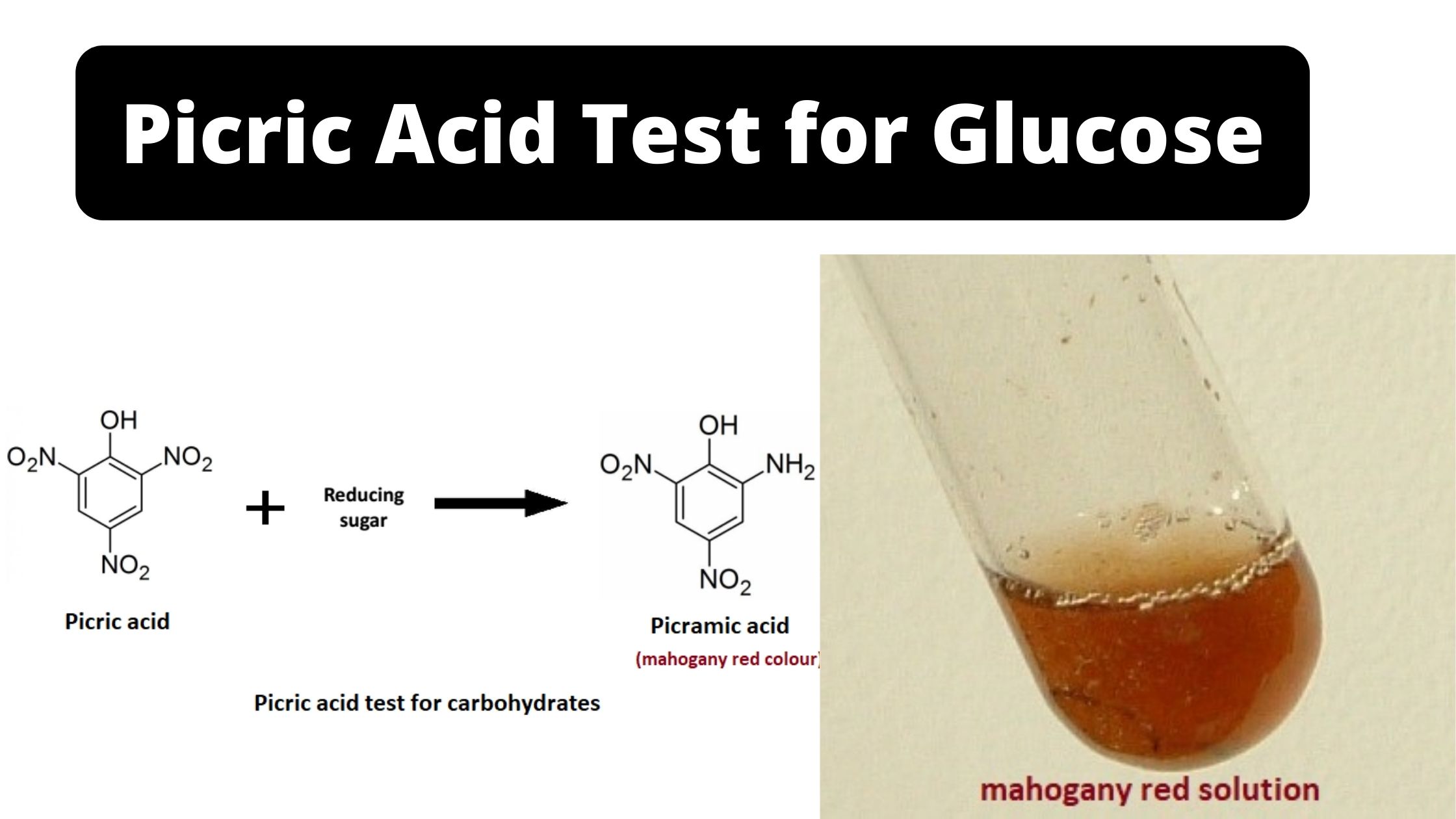
The Picric Acid Test is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars in a solution. It is a general chemical test and it is based on the reduction of picric acid under alkaline condition. Picric acid is a yellow crystalline compound (2,4,6-trinitrophenol) and it is converted into picramic acid when it reacts with a … Read more