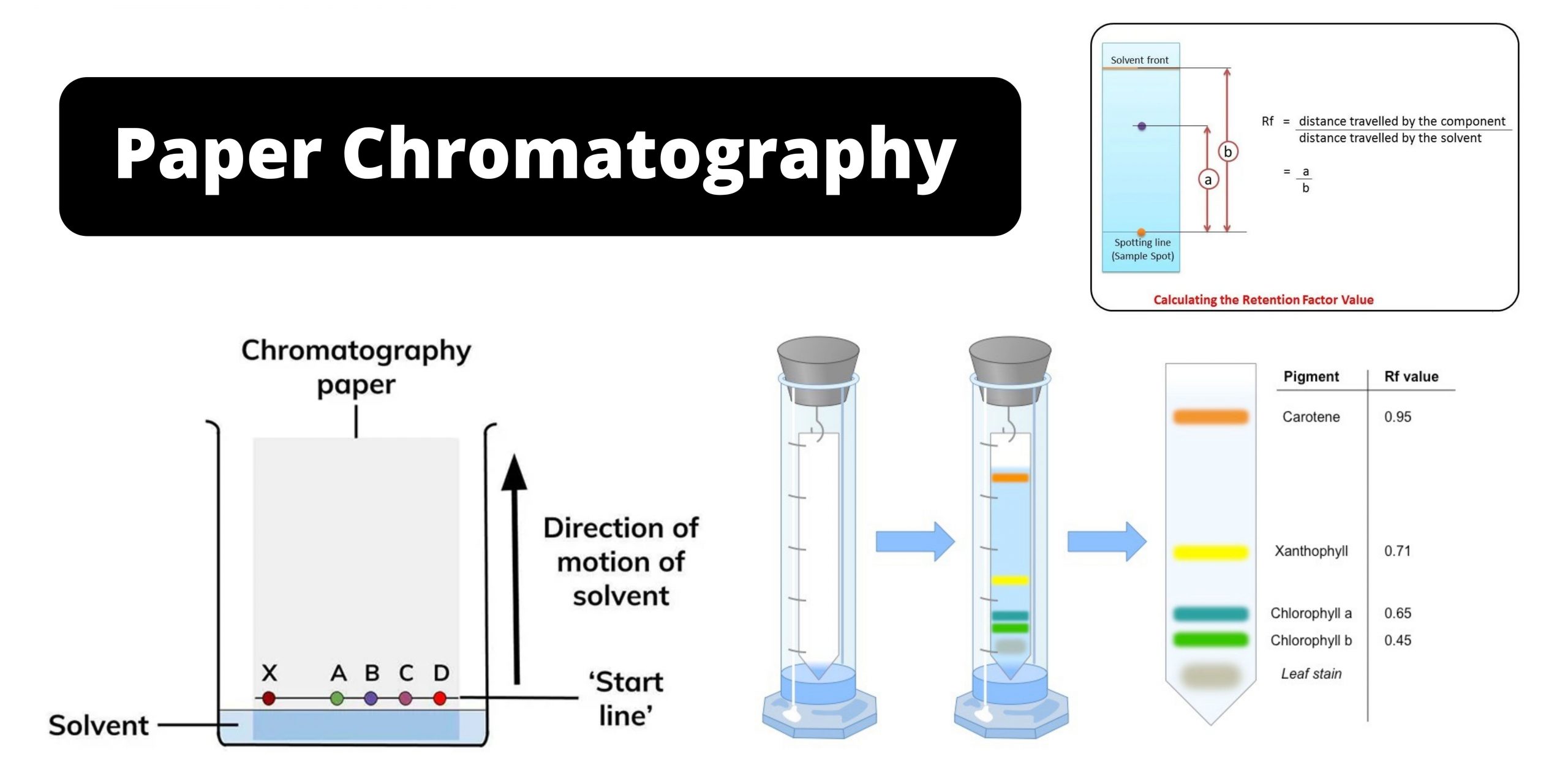
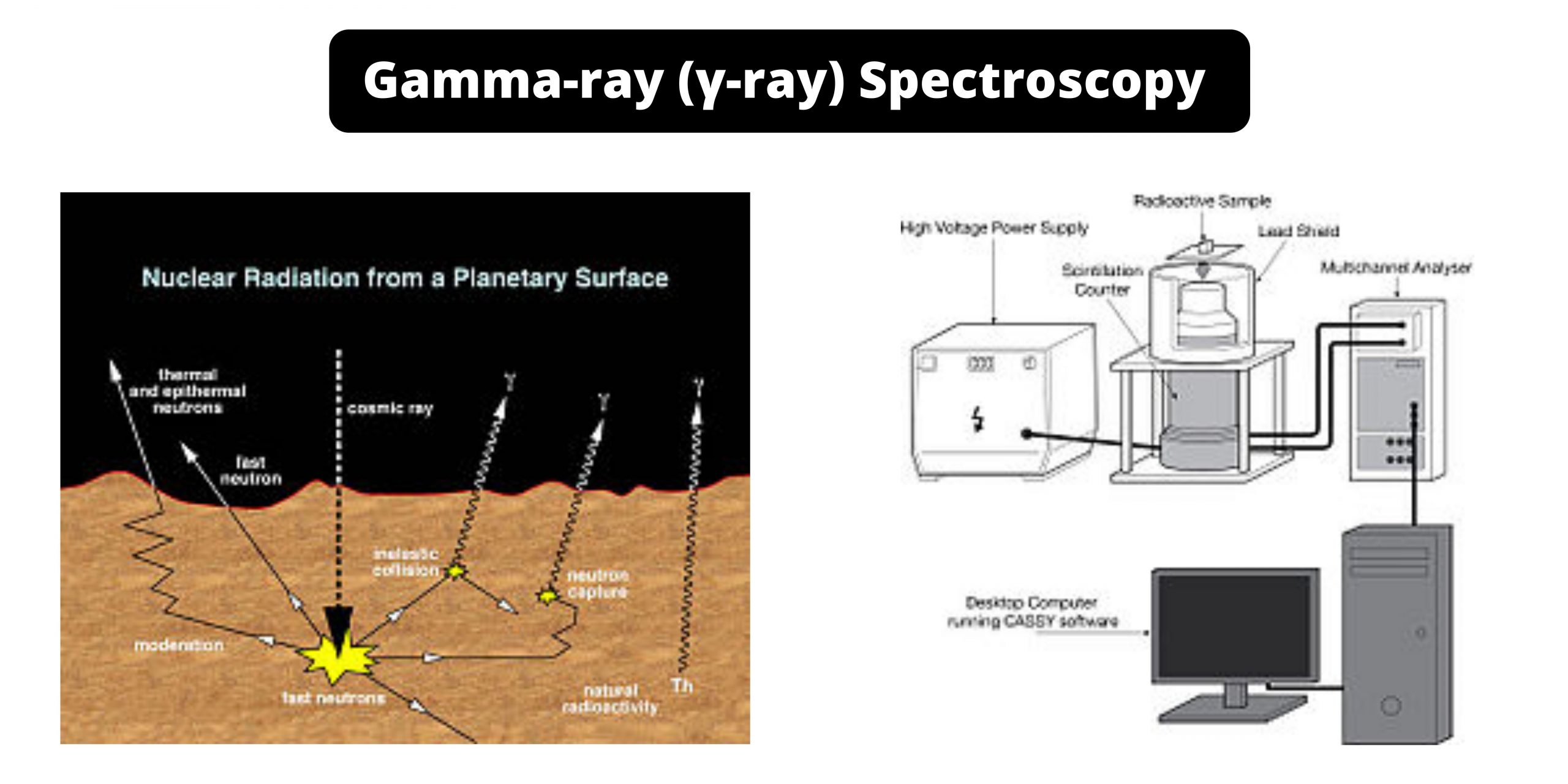
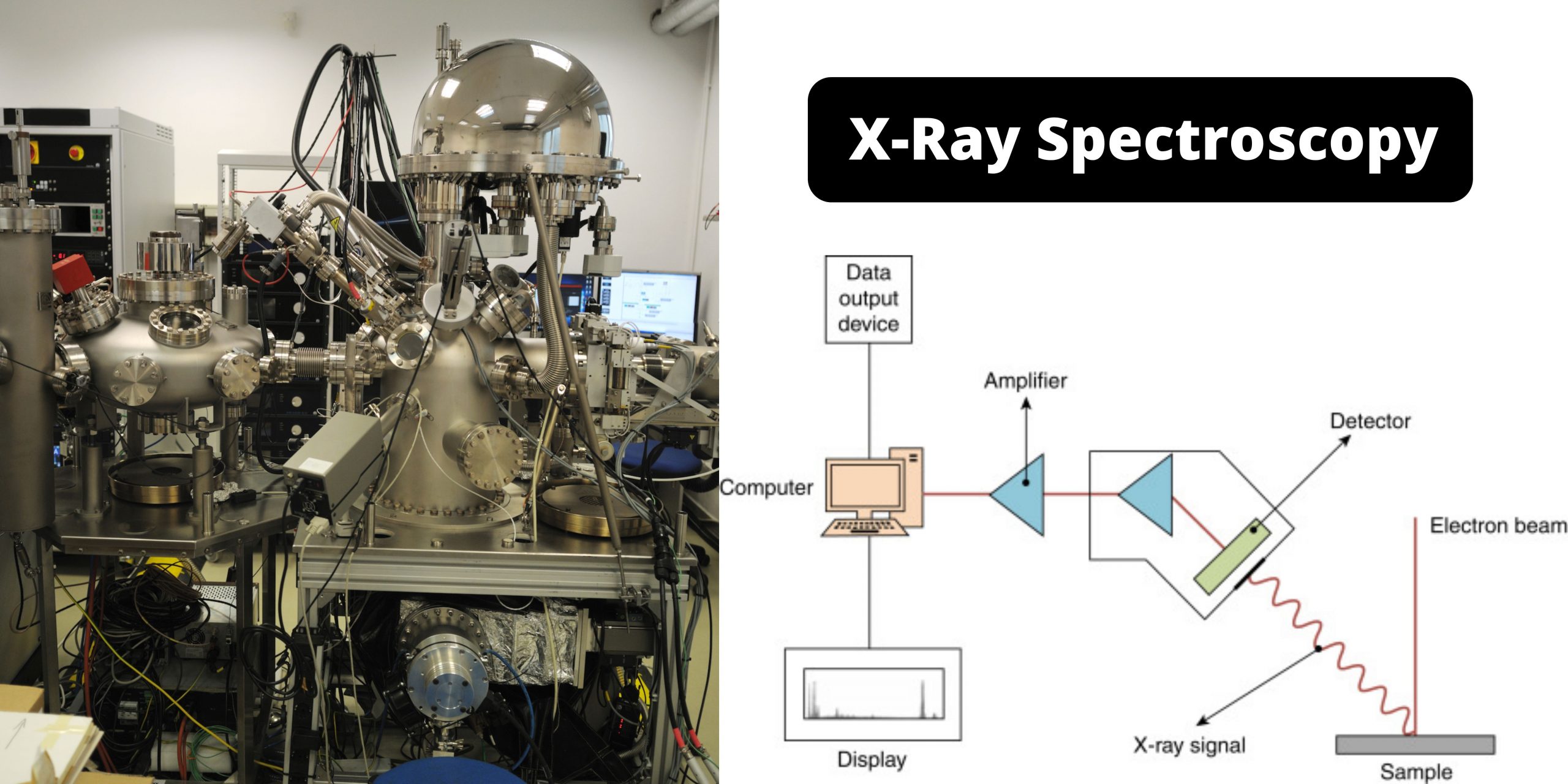
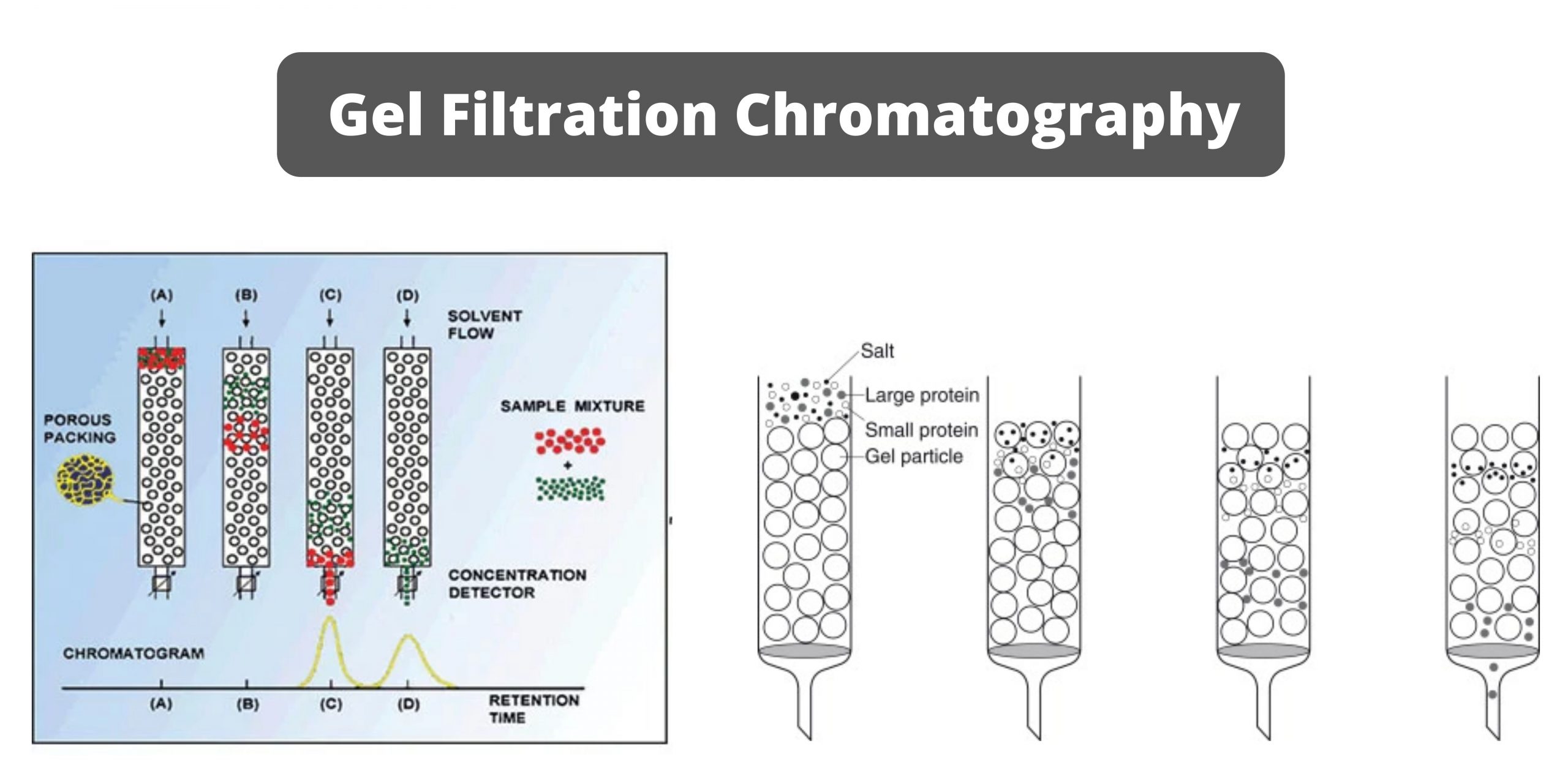
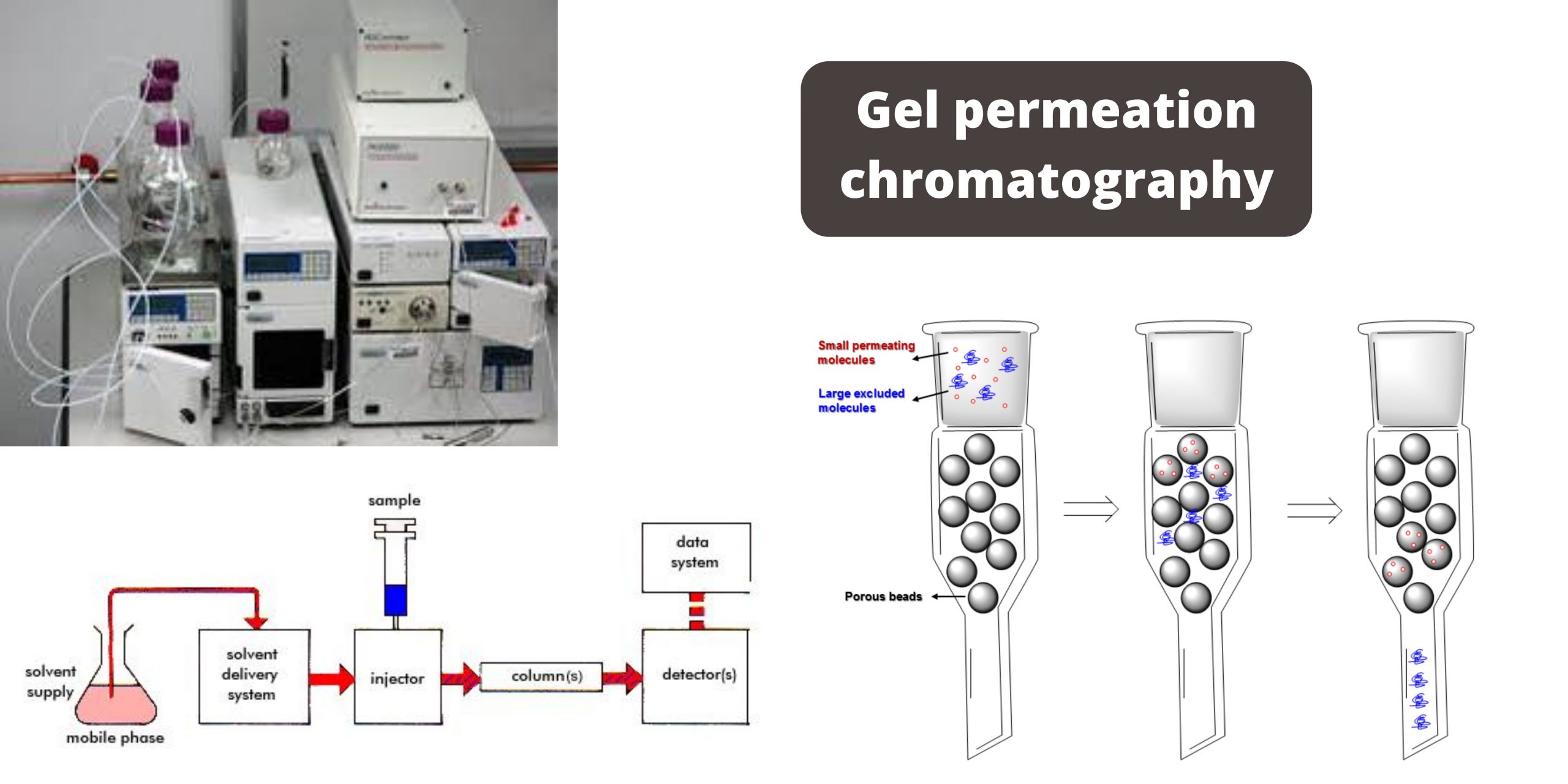
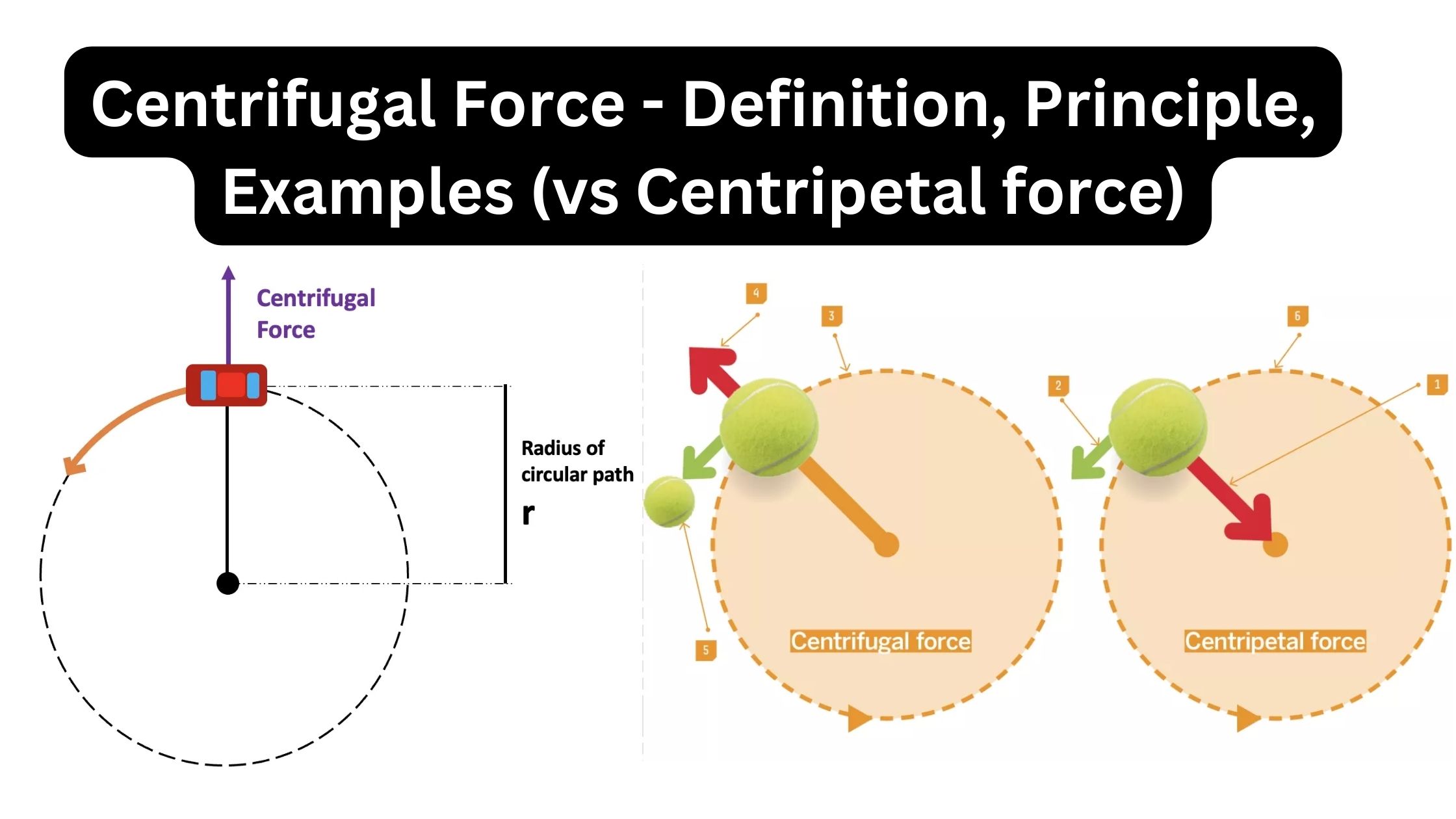
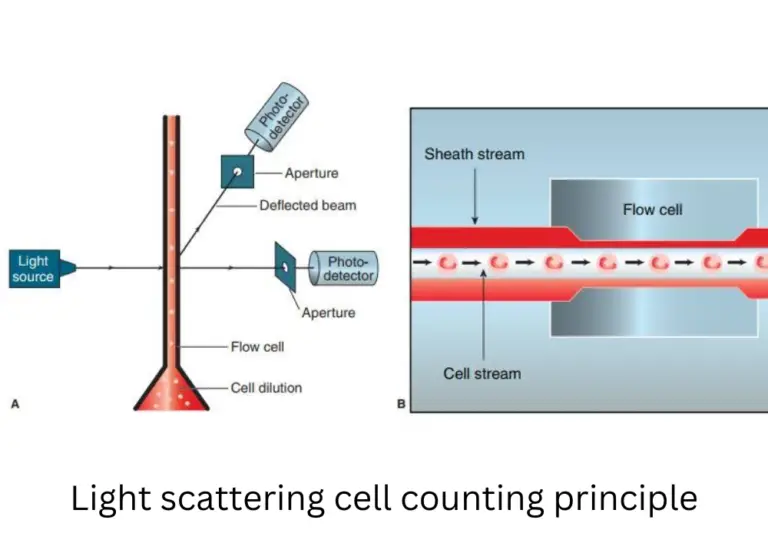
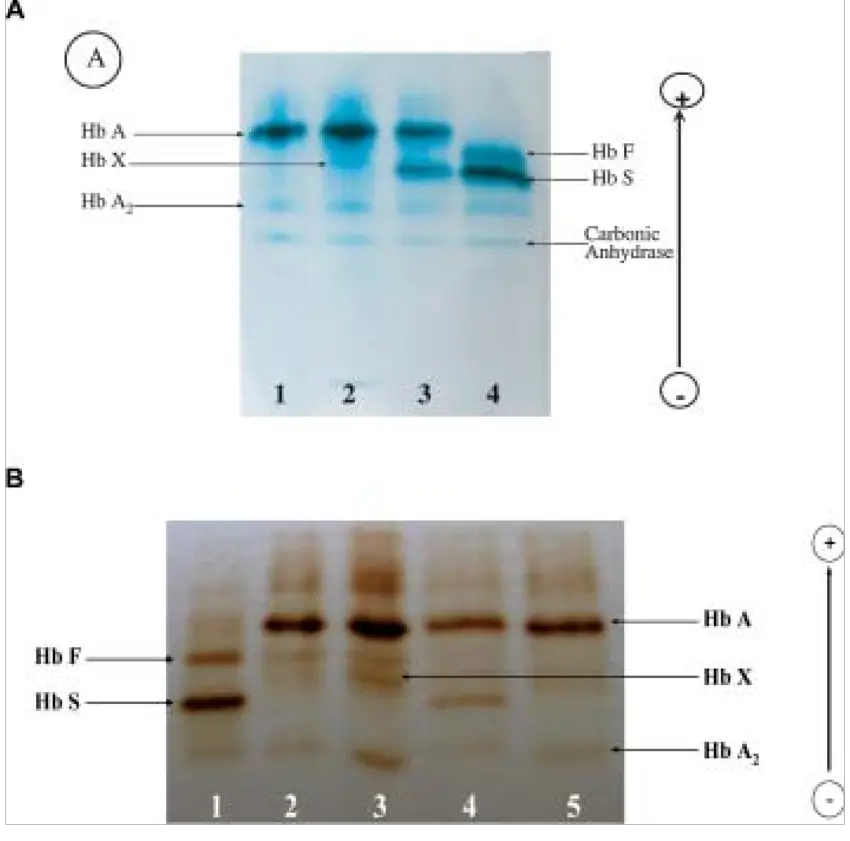
Paper Chromatography – Principle, Types, Instrumentation, Steps
What is Paper Chromatography? Types of Paper chromatography 1. Ascending paper chromatography – In this type the solvent is placed at bottom of paper and it is allowed to climb up by capillary action, the components are separated as they move upward. 2. Descending paper chromatography – In this variation the solvent moves downwards (by … Read more