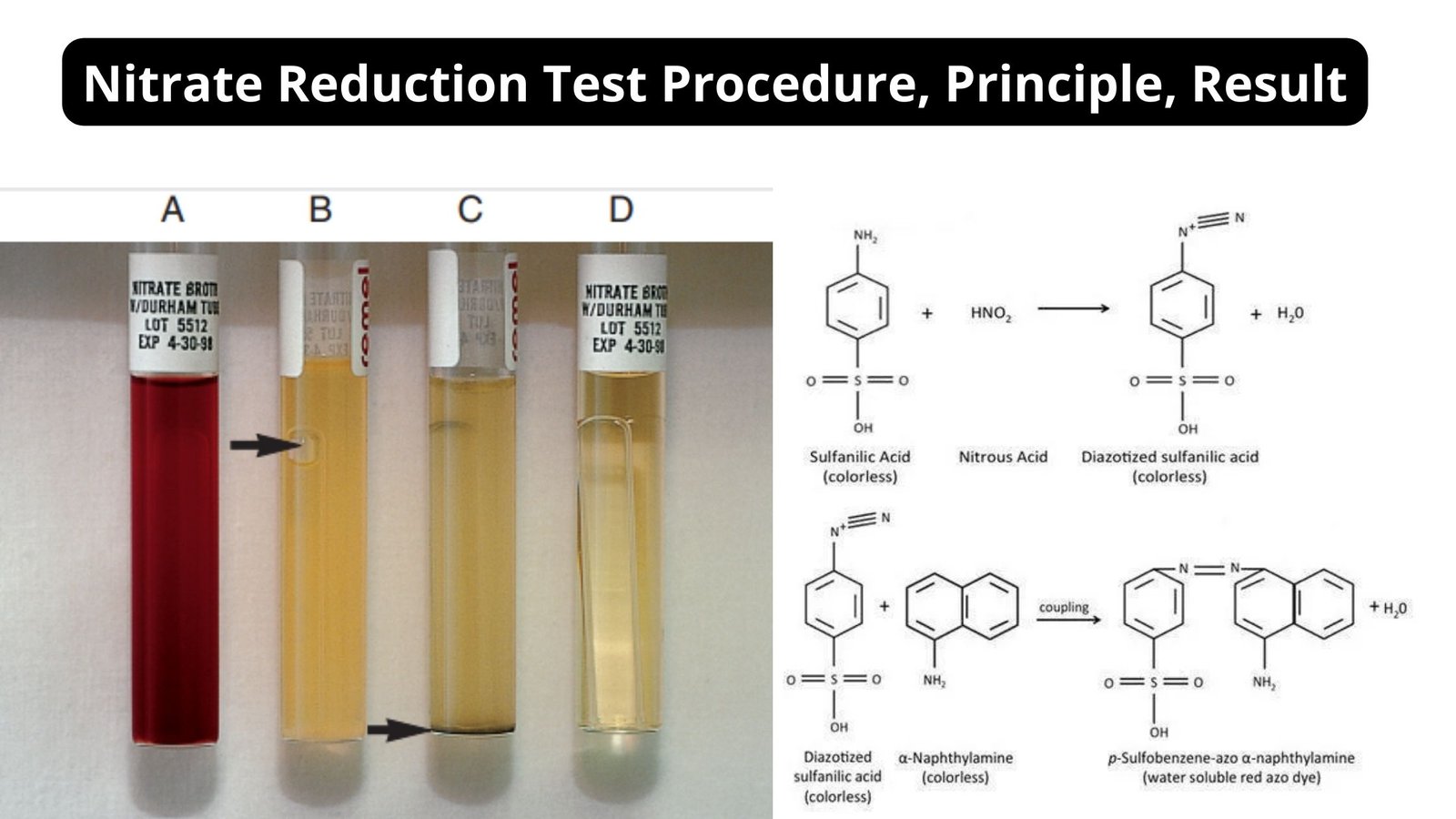
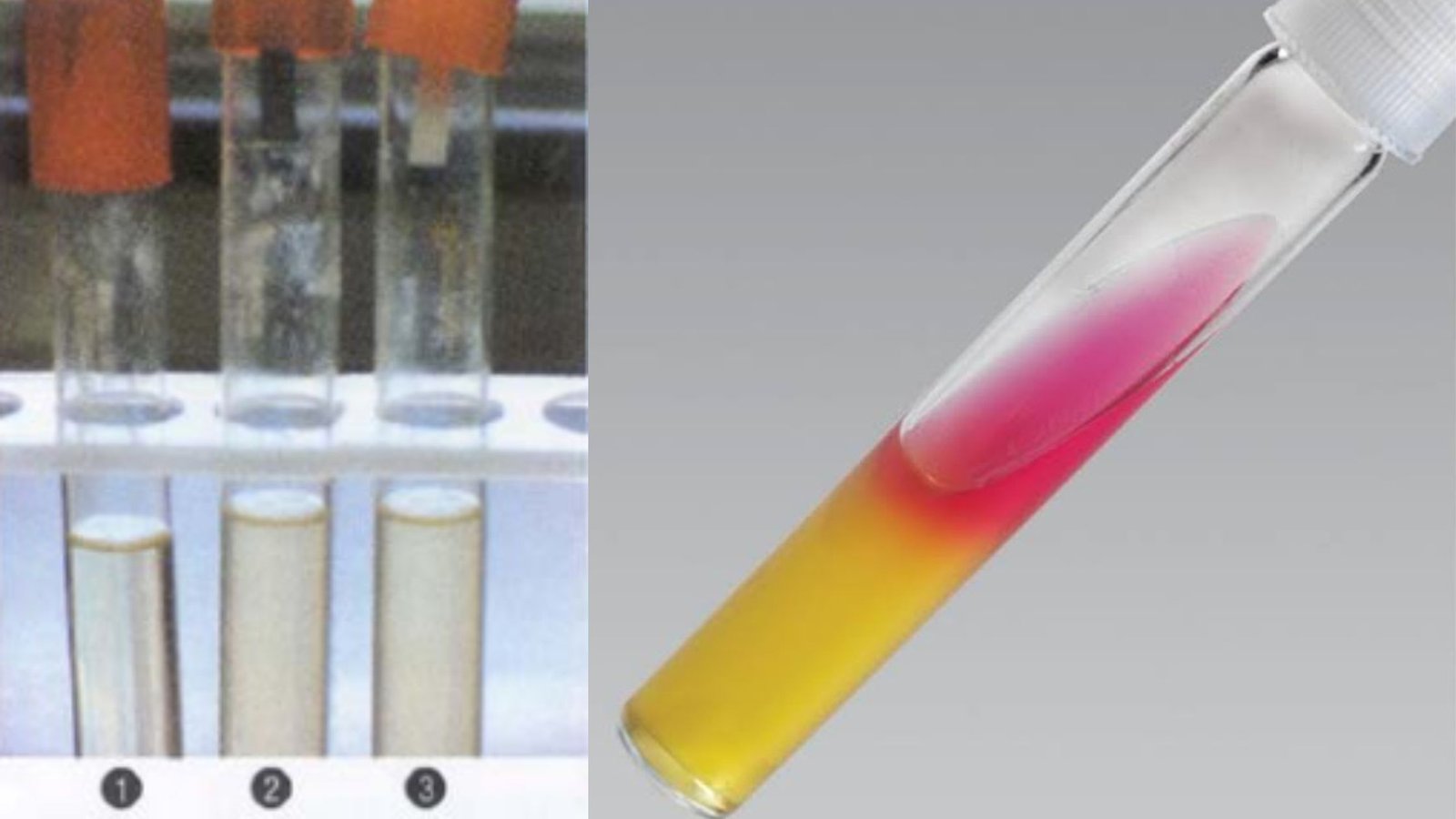
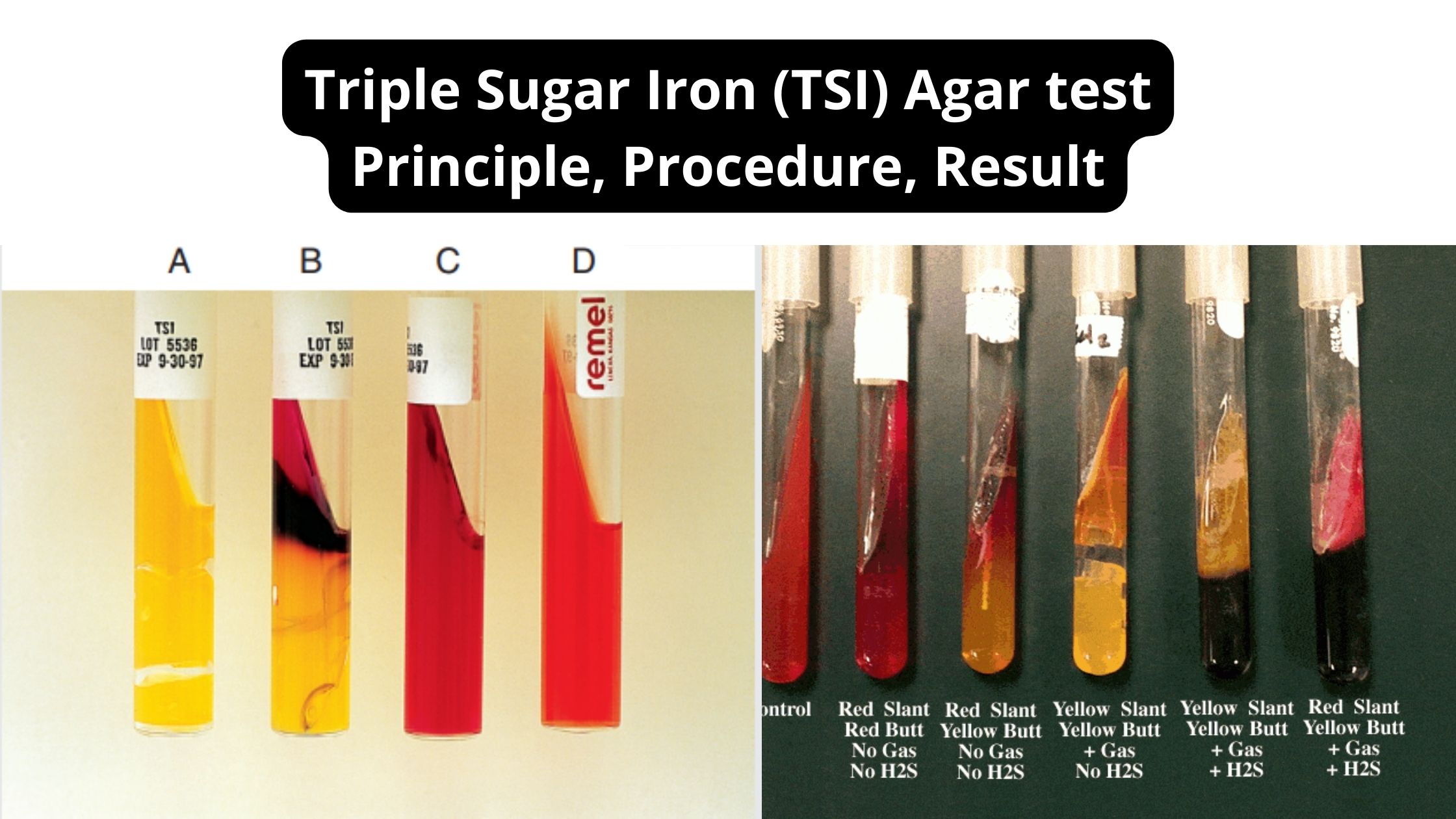
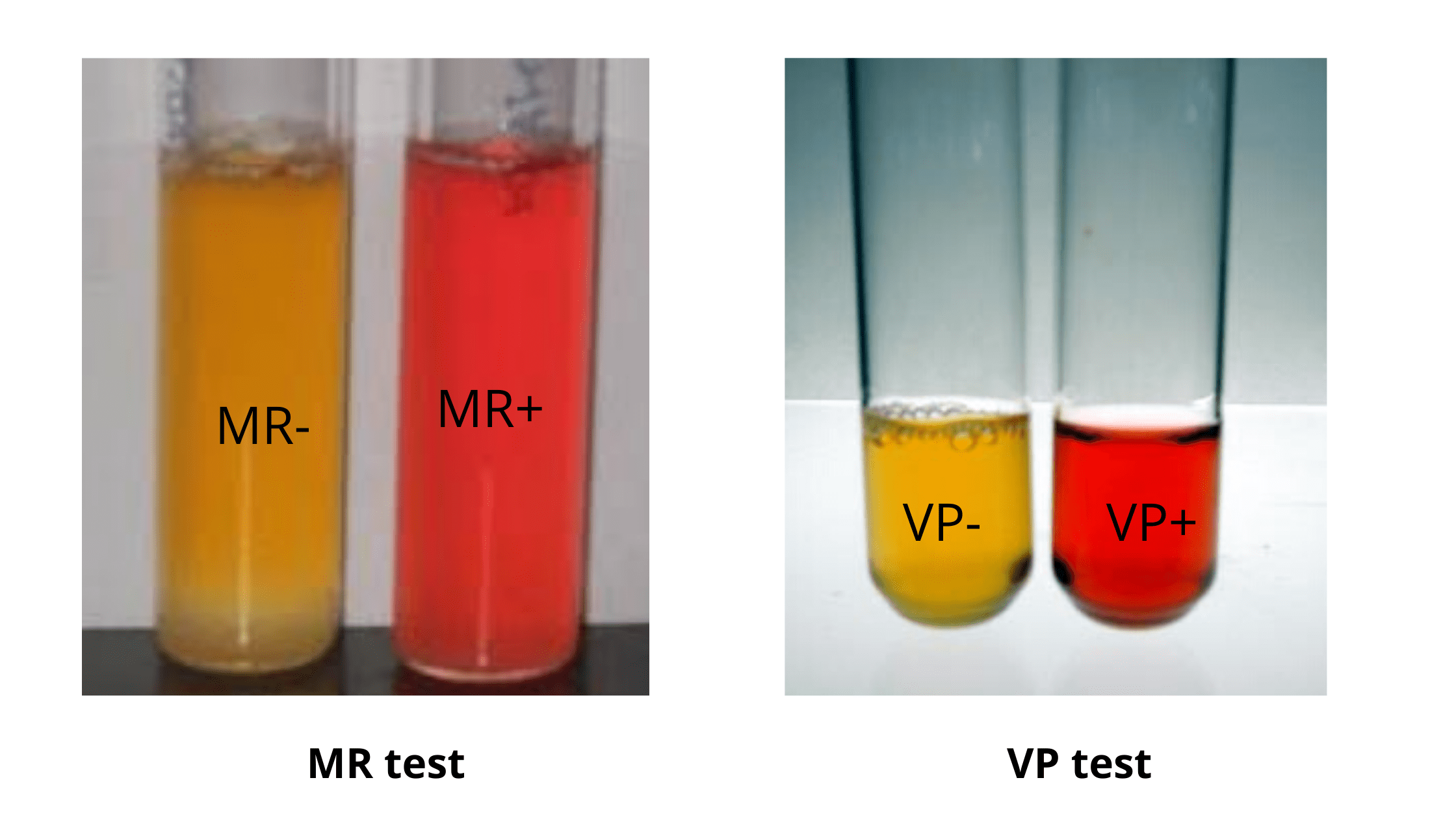
Determination of Magnesium In Milk
Magnesium is an essential mineral found in many foods, including milk. It plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, such as muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and bone health. The magnesium content in milk contributes to its nutritional value, making milk a beneficial part of a balanced diet. The amount of magnesium … Read more