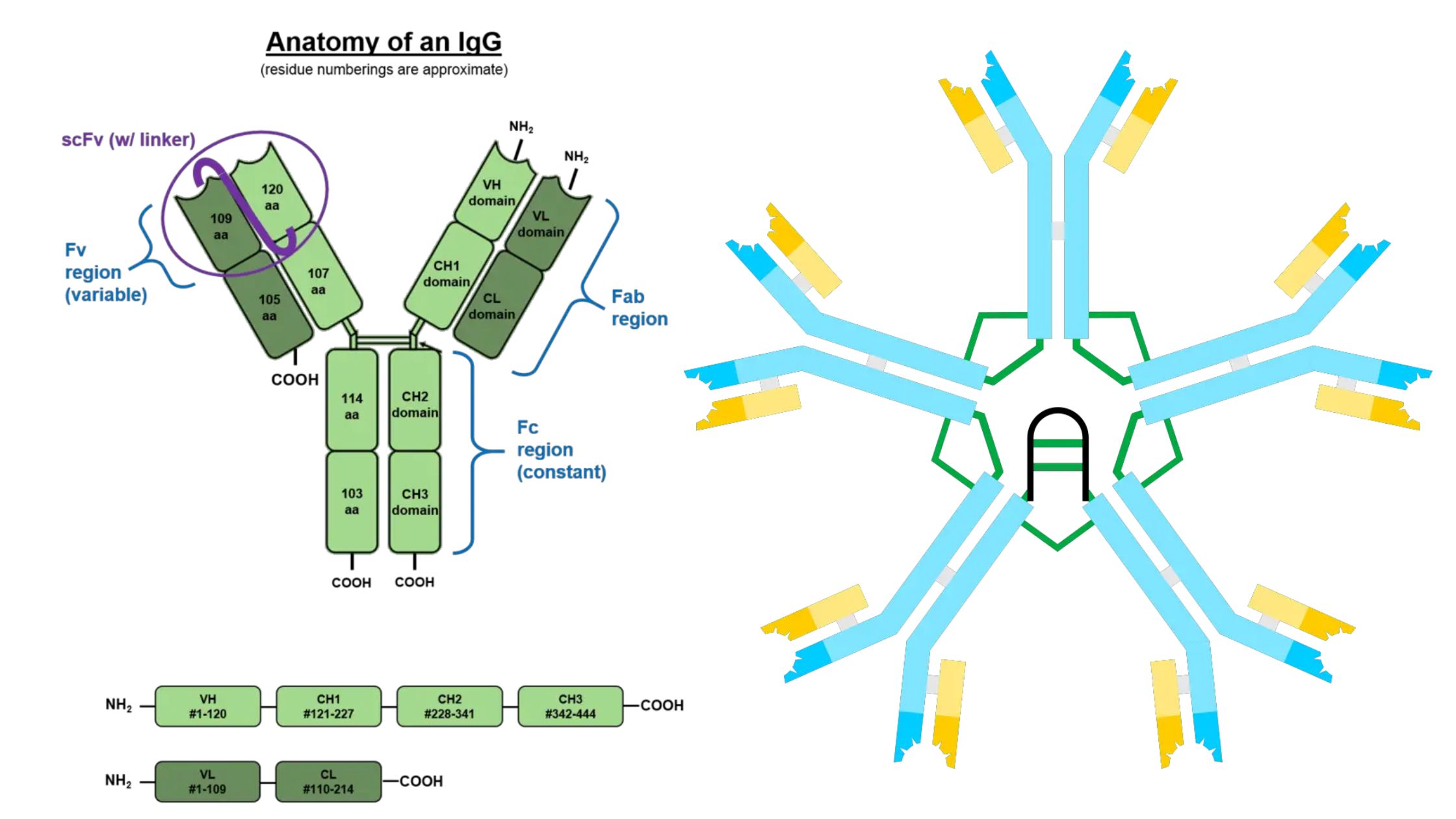
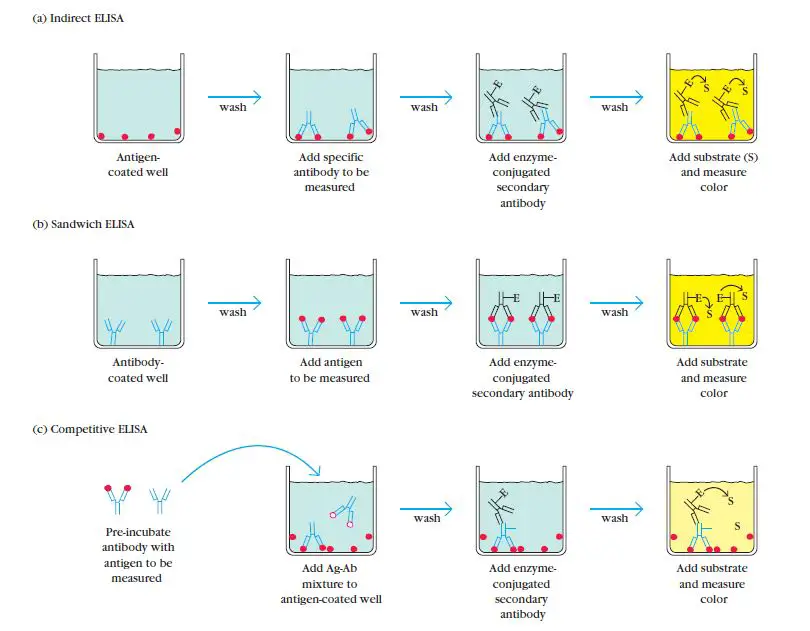
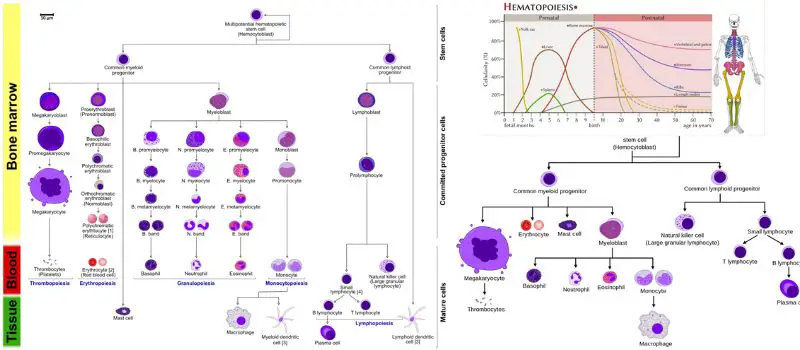
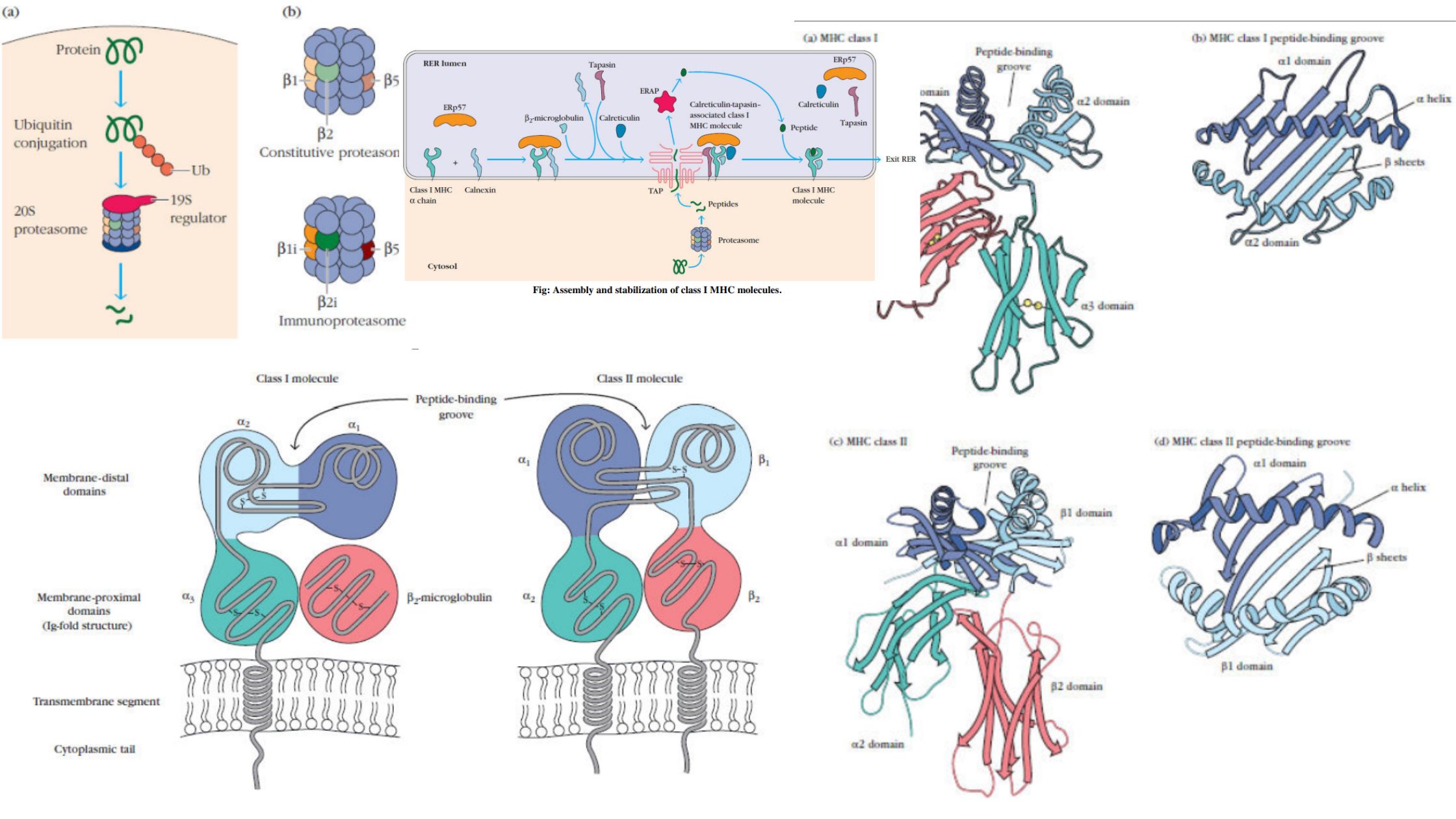
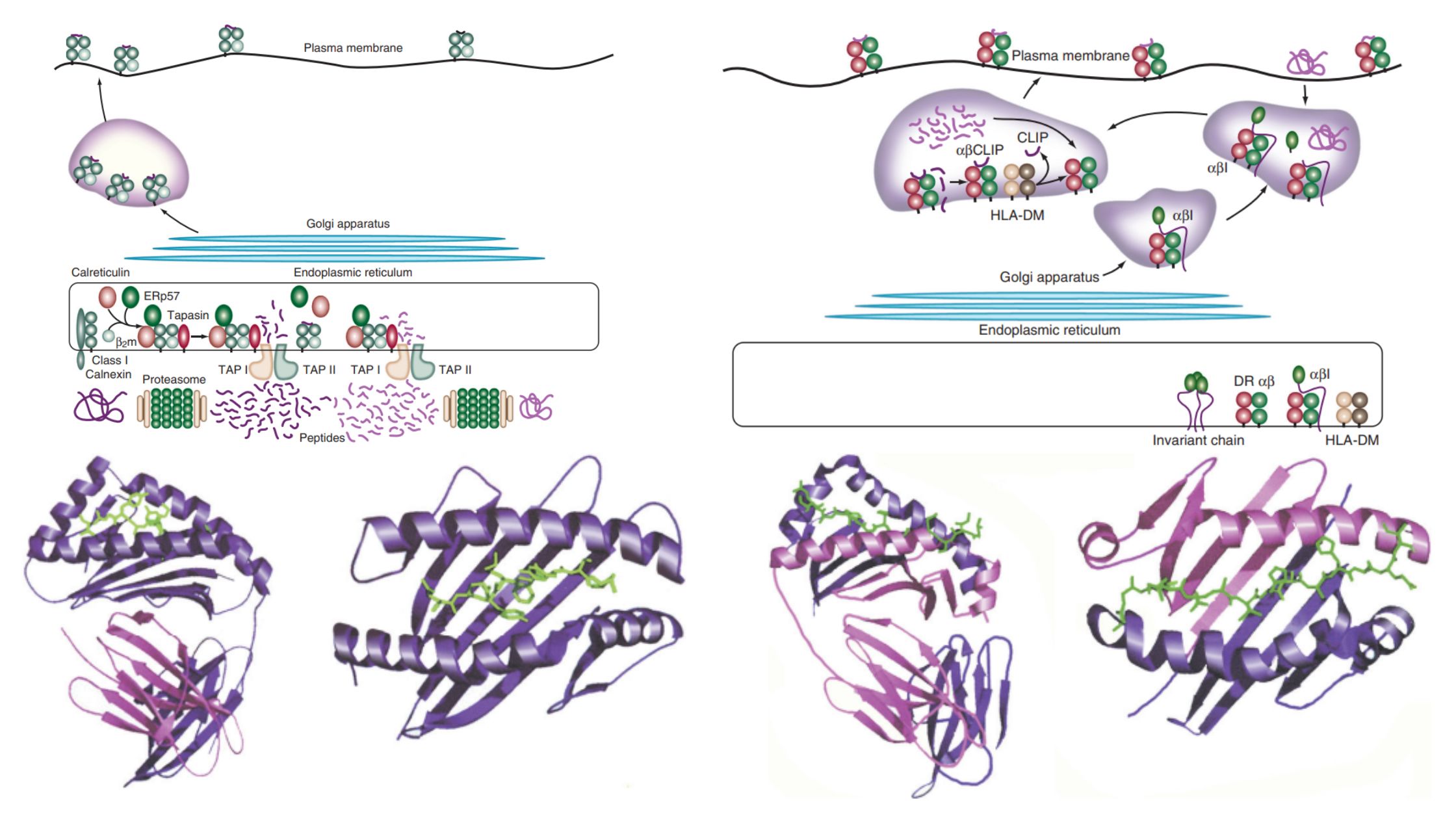
Lymphocytes – Definition, Development, Types and Functions
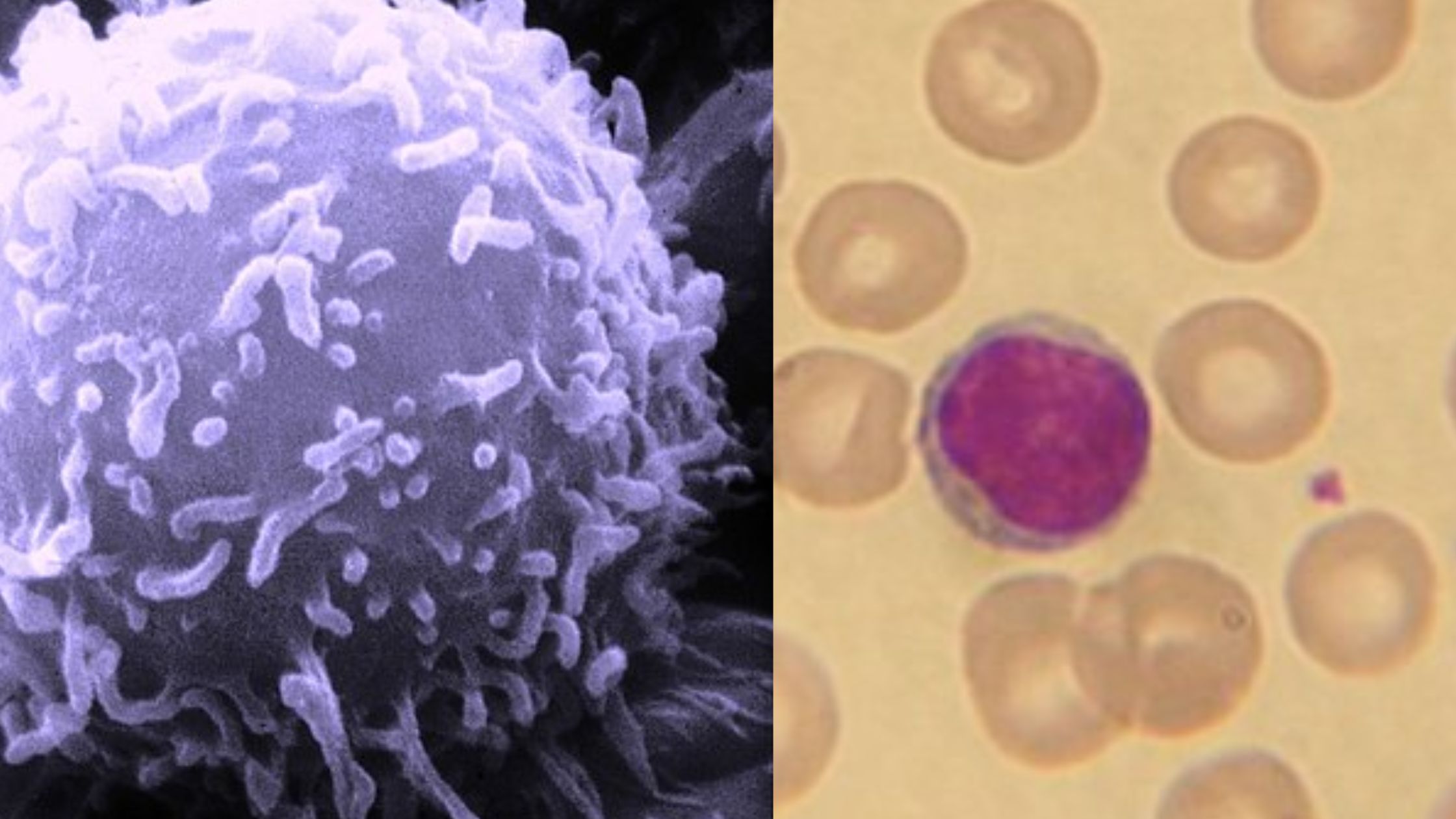
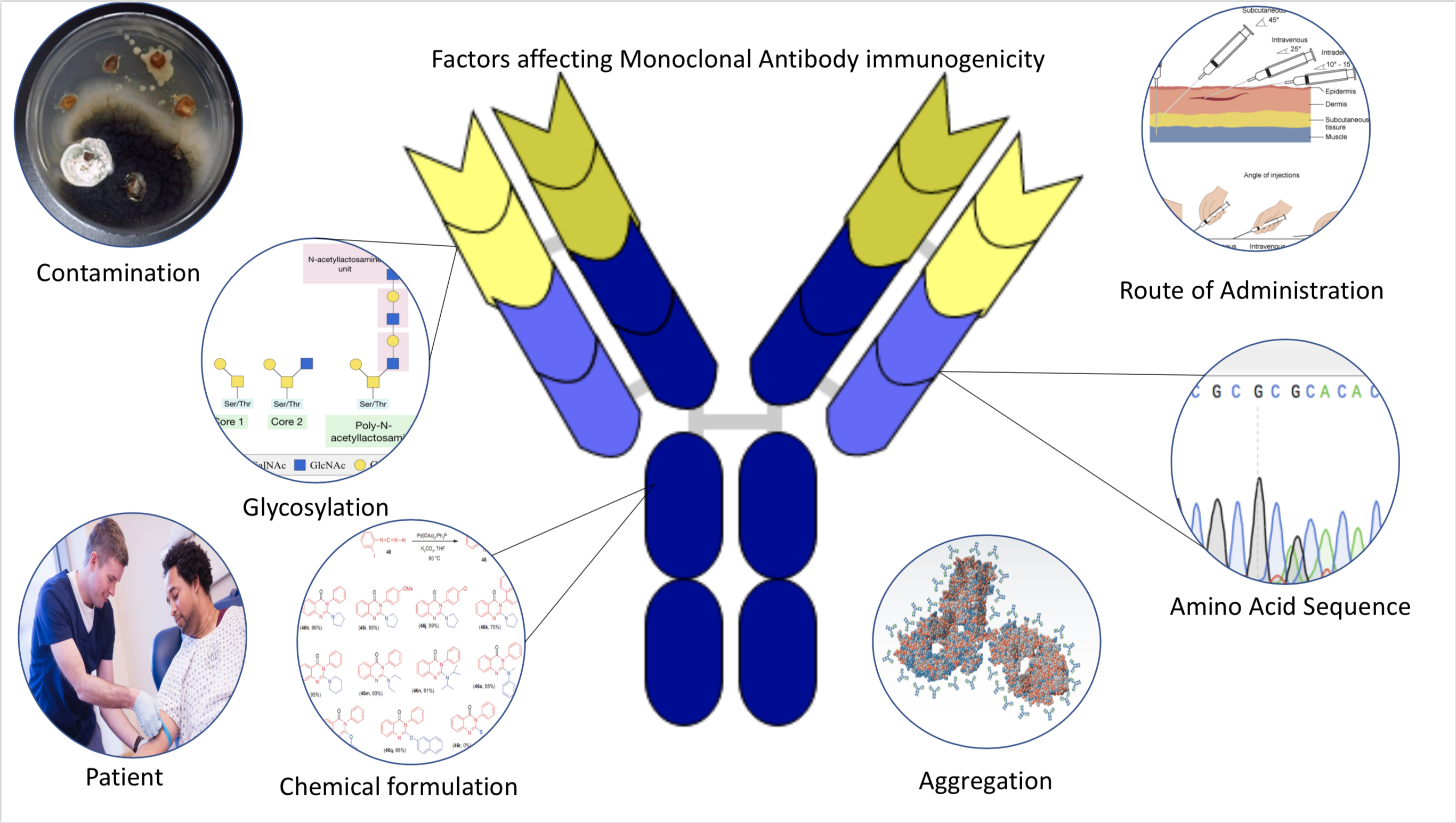
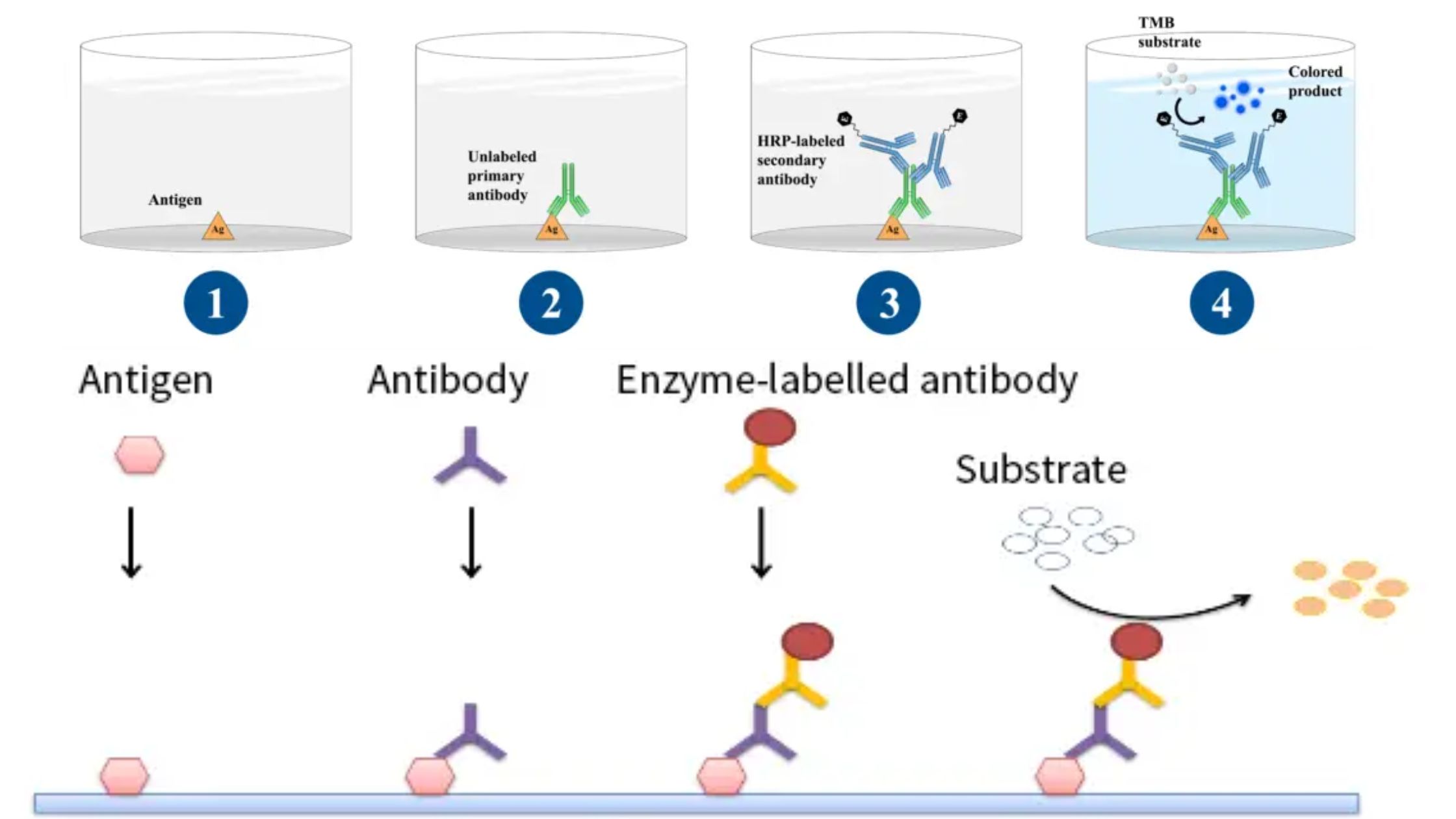
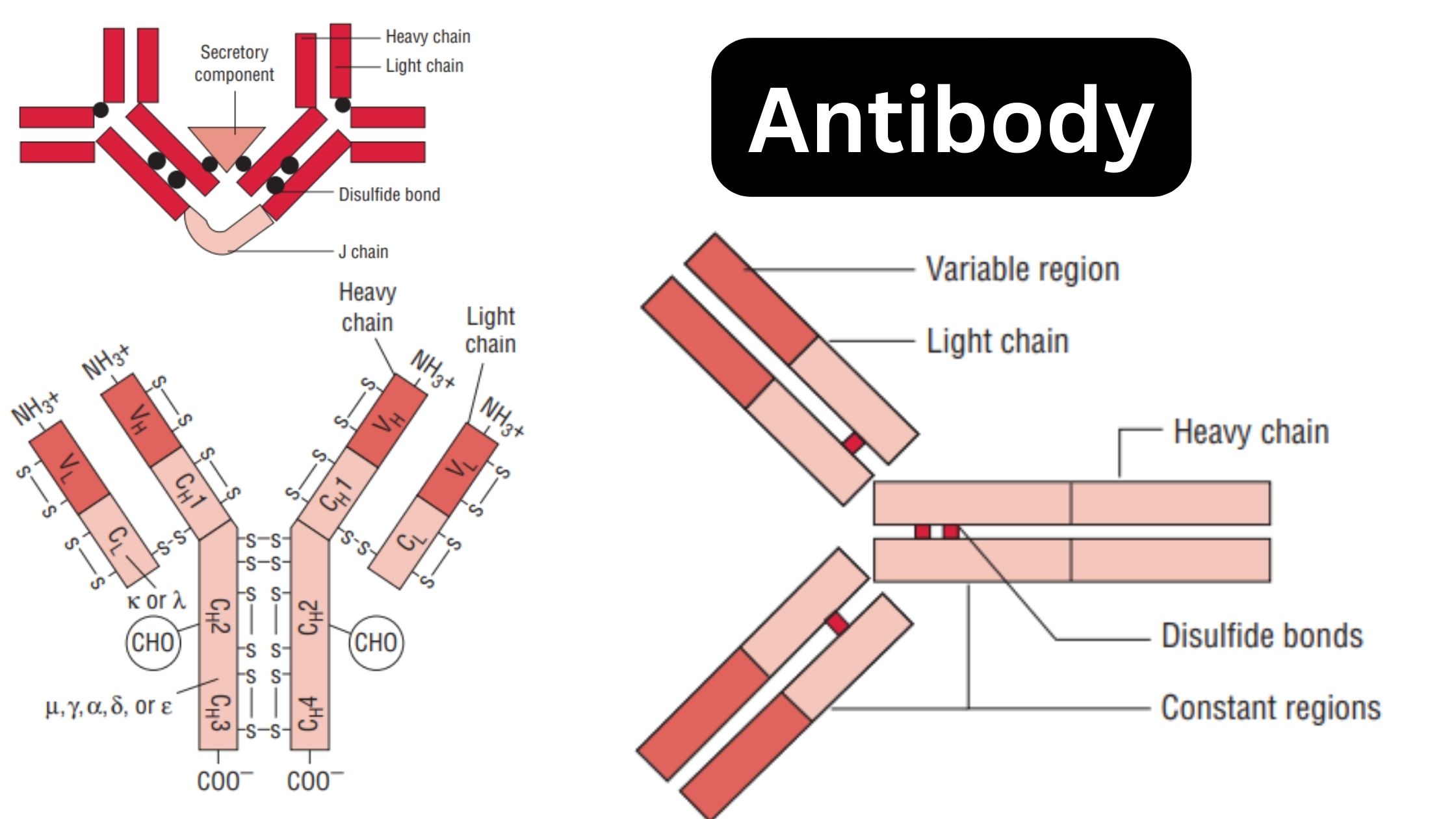
What are Lymphocytes? Lymphocytes are a specialized type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system’s adaptive response. They are the key mediators of both humoral and cellular immunity. Here are some important points about lymphocytes: Definition of Lymphocytes Lymphocytes are specialized white blood cells that are crucial for the … Read more